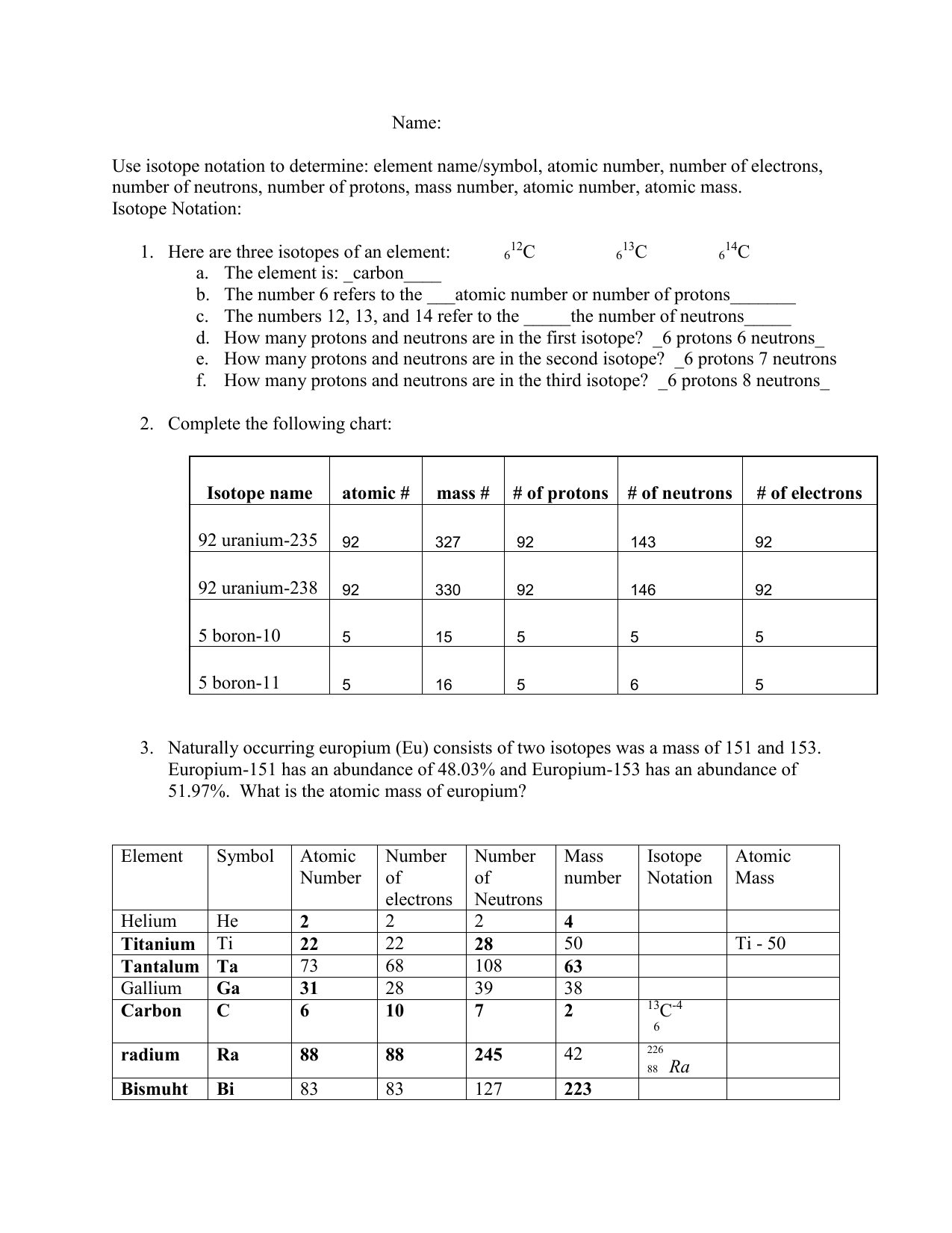
5 Ways to Master Natural Selection Patterns

Understanding the Fundamentals of Natural Selection
Natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology that explains how populations of living organisms adapt and evolve over time in response to environmental pressures. At its core, natural selection is a process that favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success, thereby passing those traits on to their offspring. Mastering natural selection patterns requires a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms and principles that drive this process.
Pattern 1: Adaptation to Environmental Pressures
One of the most significant natural selection patterns is the adaptation of populations to environmental pressures. This can occur in response to changes in climate, geography, or the presence of predators or competitors. For example, the peppered moth in England adapted from a light to a dark coloration in response to the industrial revolution, which led to a increase in dark-colored tree trunks due to pollution. This adaptation allowed the dark-colored moths to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predation.
Key Points:
- Environmental pressures can drive the adaptation of populations
- Adaptations can occur in response to changes in climate, geography, or the presence of predators or competitors
- The peppered moth is a classic example of adaptation to environmental pressures
Pattern 2: Genetic Variation and Mutation
Genetic variation and mutation are essential components of natural selection. Without genetic variation, populations would not have the raw material necessary for adaptation and evolution. Mutations can occur spontaneously or as a result of environmental factors, such as exposure to radiation or chemicals. These mutations can result in new traits or alter existing ones, providing the variation necessary for natural selection to act upon.
Key Points:
- Genetic variation and mutation are essential components of natural selection
- Mutations can occur spontaneously or as a result of environmental factors
- Genetic variation provides the raw material necessary for adaptation and evolution
Pattern 3: Gene Flow and Genetic Drift
Gene flow and genetic drift are two important mechanisms that can influence the pattern of natural selection. Gene flow occurs when individuals with different genotypes interbreed, resulting in the exchange of genetic material between populations. Genetic drift, on the other hand, occurs when random events, such as genetic mutations or changes in population size, affect the frequency of a particular gene or trait. These mechanisms can either enhance or reduce the effectiveness of natural selection.
Key Points:
- Gene flow and genetic drift can influence the pattern of natural selection
- Gene flow occurs when individuals with different genotypes interbreed
- Genetic drift occurs when random events affect the frequency of a particular gene or trait
Pattern 4: Selection and Speciation
Natural selection can also drive the process of speciation, which is the formation of new species. When populations become reproductively isolated, either due to geographical barriers or genetic differences, they can evolve into distinct species. This process is often driven by natural selection, as individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce.
Key Points:
- Natural selection can drive the process of speciation
- Reproductive isolation can lead to the formation of new species
- Selection can act on traits that are better suited to the environment
Pattern 5: Coevolution and Symbiotic Relationships
Coevolution and symbiotic relationships are important patterns in natural selection that involve the interaction between different species. Coevolution occurs when two or more species evolve together, with each species influencing the evolution of the other. Symbiotic relationships, such as mutualism or parasitism, can also drive the evolution of species. For example, the relationship between clownfish and sea anemones is a classic example of mutualism, where both species benefit from each other’s presence.
Key Points:
- Coevolution and symbiotic relationships are important patterns in natural selection
- Coevolution occurs when two or more species evolve together
- Symbiotic relationships can drive the evolution of species
🌟 Note: Mastering natural selection patterns requires a deep understanding of the underlying mechanisms and principles that drive this process. By recognizing these patterns, you can gain a better understanding of the natural world and the evolution of species.
In conclusion, natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology that explains how populations of living organisms adapt and evolve over time. By recognizing the patterns of natural selection, including adaptation to environmental pressures, genetic variation and mutation, gene flow and genetic drift, selection and speciation, and coevolution and symbiotic relationships, you can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the evolution of species.
What is natural selection?
+Natural selection is a process that favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success, thereby passing those traits on to their offspring.
What is adaptation?
+Adaptation is the process by which populations of living organisms become better suited to their environment over time.
What is coevolution?
+Coevolution is the process by which two or more species evolve together, with each species influencing the evolution of the other.