5 Key Answers to Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet
Understanding Diffusion and Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental biological processes that play a crucial role in the functioning of living organisms. Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. In this blog post, we will explore five key answers to common questions about diffusion and osmosis.
1. What is the Difference Between Diffusion and Osmosis?
Diffusion vs. Osmosis
Diffusion and osmosis are often confused with each other, but they are distinct processes. Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, regardless of the type of particle. Osmosis, on the other hand, is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
📝 Note: Diffusion can occur in any substance, while osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules.
2. What is a Concentration Gradient?
A concentration gradient is a gradual change in the concentration of a substance across a given area. It is the driving force behind diffusion and osmosis. In diffusion, particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, down the concentration gradient. In osmosis, water molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
- Types of concentration gradients:
- Steep concentration gradient: A large difference in concentration between two areas.
- Shallow concentration gradient: A small difference in concentration between two areas.
3. What is a Semipermeable Membrane?
A semipermeable membrane is a thin layer of tissue that allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others. In osmosis, a semipermeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through while restricting other particles. This allows cells to regulate the amount of water they contain.
Characteristics of a Semipermeable Membrane:
- Allows water molecules to pass through
- Restricts other particles
- Thin layer of tissue
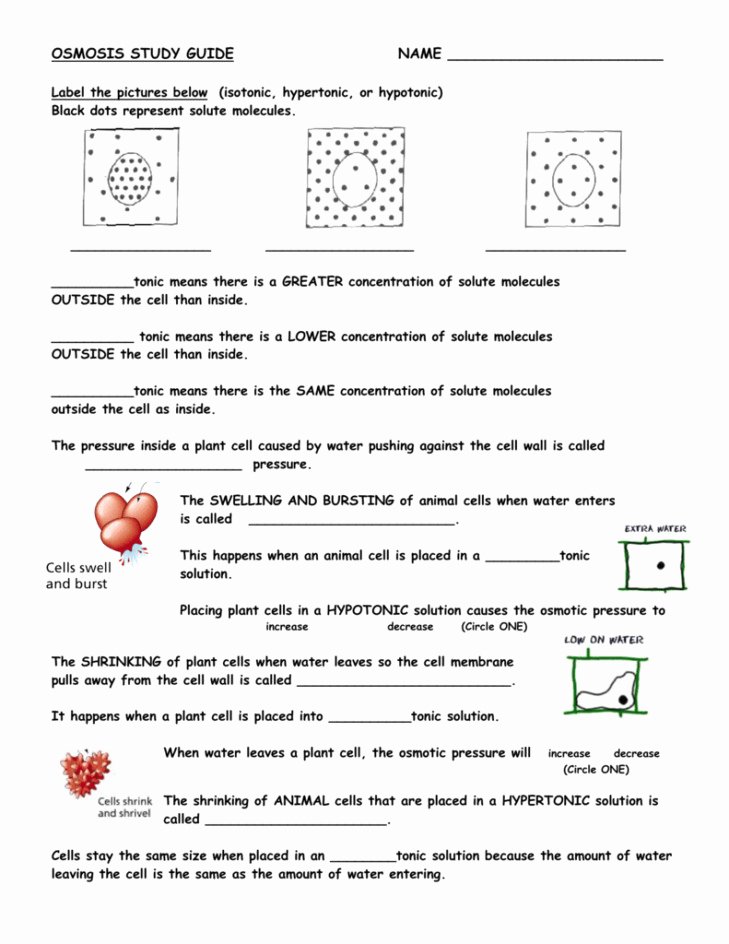
4. What is Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions?
Isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions are terms used to describe the concentration of a solution relative to a cell.
- Isotonic Solution: A solution with the same concentration as the cell.
- Hypotonic Solution: A solution with a lower concentration than the cell.
- Hypertonic Solution: A solution with a higher concentration than the cell.

| Solution Type | Concentration | Effect on Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Isotonic | Same as cell | No change |
| Hypotonic | Lower than cell | Cell swells |
| Hypertonic | Higher than cell | Cell shrinks |
5. What is the Importance of Osmosis in Living Organisms?
Osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance in living organisms. It helps regulate the amount of water in cells, tissues, and organs. In humans, osmosis helps maintain proper blood pressure, regulates the amount of water in cells, and helps remove waste products.
💧 Note: Osmosis is essential for maintaining proper fluid balance in living organisms.
In conclusion, understanding diffusion and osmosis is essential for grasping the fundamental biological processes that occur in living organisms. By recognizing the differences between diffusion and osmosis, understanding concentration gradients, semipermeable membranes, and the importance of osmosis, we can appreciate the intricate mechanisms that govern life.
What is the main difference between diffusion and osmosis?
+Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
What is a semipermeable membrane?
+A semipermeable membrane is a thin layer of tissue that allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others.
What is the importance of osmosis in living organisms?
+Osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance in living organisms, regulating the amount of water in cells, tissues, and organs.