7 Essential Concepts of Ions and Isotopes
Understanding Ions and Isotopes: Unlocking the Secrets of Chemistry
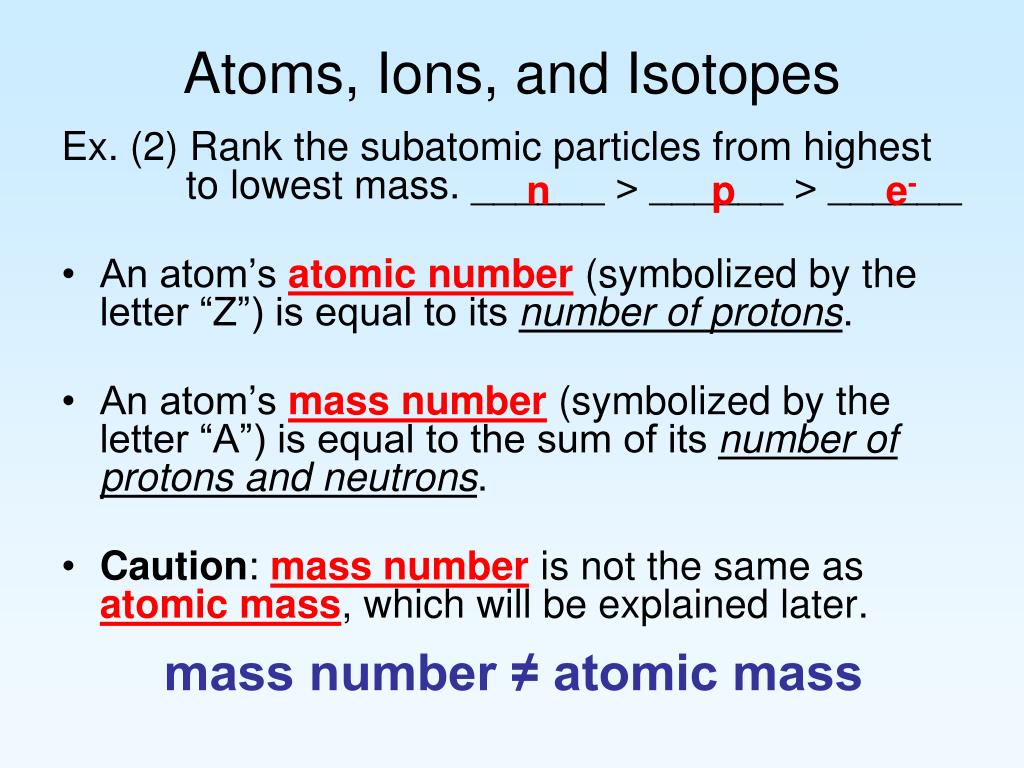
Chemistry, the study of matter and its interactions, relies heavily on understanding the building blocks of matter: atoms. Atoms, in turn, can exist in various forms, giving rise to ions and isotopes. These two concepts are fundamental to understanding chemical reactions, properties, and behavior. In this article, we will delve into the world of ions and isotopes, exploring their definitions, types, and significance in chemistry.
What are Ions?
Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. This process is known as ionization. Ions can be either cations (positively charged) or anions (negatively charged). Cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons, while anions are formed when an atom gains one or more electrons.
Types of Ions
There are two main types of ions:
- Monatomic ions: These are ions formed from a single atom. Examples include sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
- Polyatomic ions: These are ions formed from a group of atoms. Examples include ammonium ions (NH4+) and carbonate ions (CO32-).
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atomic mass of the isotopes. Isotopes can be stable or radioactive, with the latter undergoing radioactive decay to become more stable.
Types of Isotopes
There are two main types of isotopes:
- Stable isotopes: These are isotopes that do not undergo radioactive decay. Examples include carbon-12 and oxygen-16.
- Radioactive isotopes: These are isotopes that undergo radioactive decay. Examples include carbon-14 and uranium-238.
Significance of Ions and Isotopes
Ions and isotopes play a crucial role in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology.
- Chemical reactions: Ions and isotopes are involved in many chemical reactions, including acid-base reactions and nuclear reactions.
- Medical applications: Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, such as cancer treatment and imaging.
- Environmental science: Isotopes are used to study environmental processes, such as climate change and water cycles.
💡 Note: Ions and isotopes are not interchangeable terms. While ions refer to charged particles, isotopes refer to atoms with different numbers of neutrons.
Key Differences between Ions and Isotopes
While both ions and isotopes are related to atoms, there are key differences between them:
- Charge: Ions have a net positive or negative charge, while isotopes do not.
- Neutron number: Isotopes differ in neutron number, while ions do not.
- Atomic mass: Isotopes have different atomic masses due to differences in neutron number, while ions do not.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ions and isotopes are essential concepts in chemistry that help us understand the behavior of atoms and their interactions. By grasping the definitions, types, and significance of ions and isotopes, we can better appreciate the complexities of chemical reactions, medical applications, and environmental science. Remember, ions and isotopes are not interchangeable terms, and understanding their differences is crucial for a deeper understanding of chemistry.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
+A cation is a positively charged ion, while an anion is a negatively charged ion.
What is the purpose of using radioactive isotopes in medicine?
+Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, such as cancer treatment and imaging.
How do isotopes differ from ions?
+Isotopes differ from ions in that they have different numbers of neutrons, while ions have a net positive or negative charge.