Worksheets On Potential And Kinetic Energy
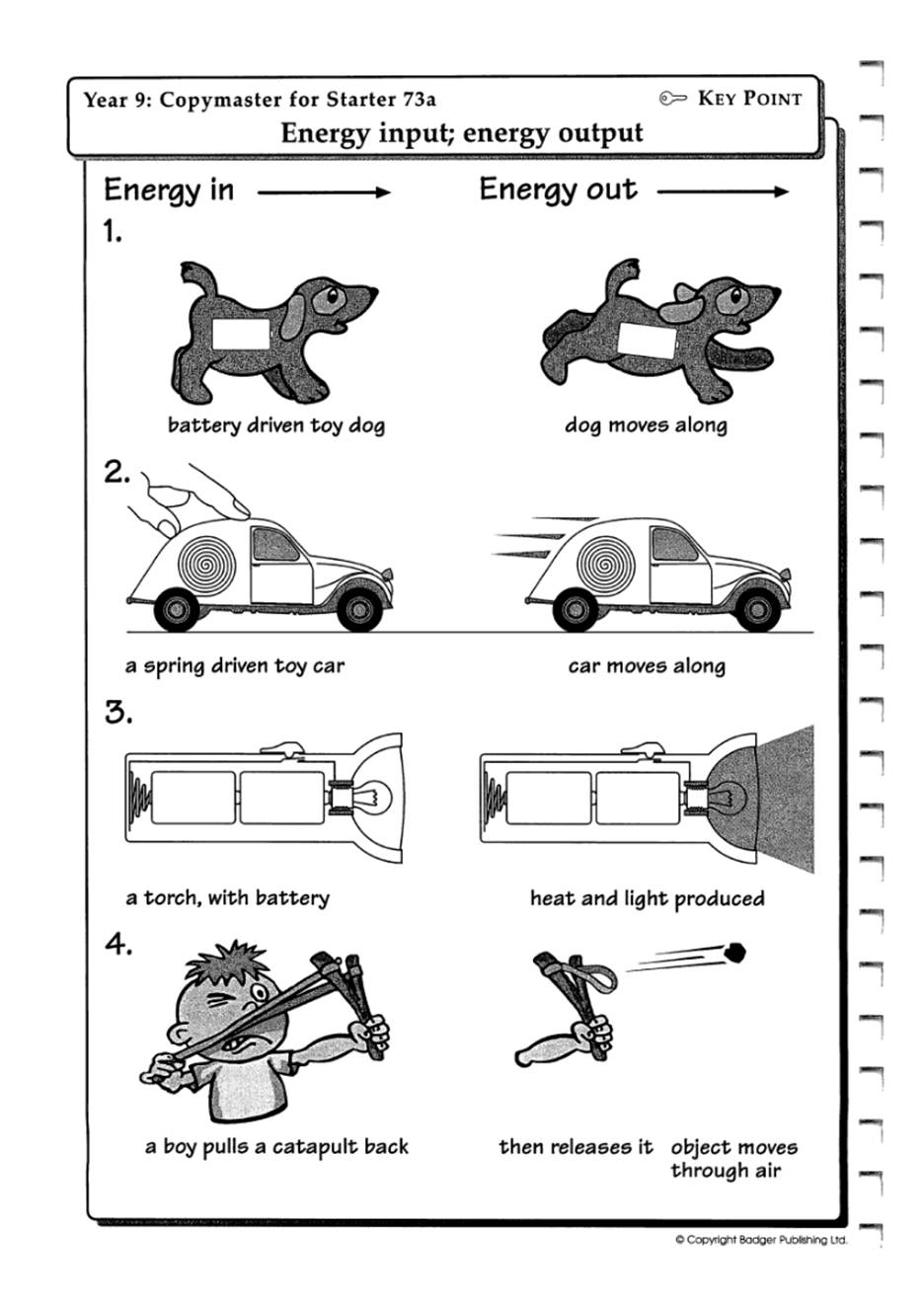
Understanding Potential and Kinetic Energy
Energy is a fundamental concept in physics, and it comes in various forms. Two of the most important forms of energy are potential energy and kinetic energy. In this article, we will explore these concepts in depth, and provide worksheets to help you practice and reinforce your understanding.
What is Potential Energy?
Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or state. It is called “potential” because it has the potential to be converted into other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy. There are several types of potential energy, including:
- Gravitational potential energy: the energy an object possesses due to its height or position in a gravitational field.
- Elastic potential energy: the energy stored in a stretched or compressed object, such as a rubber band.
- Electrical potential energy: the energy stored in an electric field, such as in a battery.
The formula for potential energy is:
PE = mgh
Where:
- PE is the potential energy
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (approximately 9.8 m/s^2 on Earth)
- h is the height of the object above the ground
What is Kinetic Energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion. It is the energy of motion, and it is a fundamental concept in physics. The formula for kinetic energy is:
KE = (1⁄2)mv^2
Where:
- KE is the kinetic energy
- m is the mass of the object
- v is the velocity of the object
Conversion between Potential and Kinetic Energy
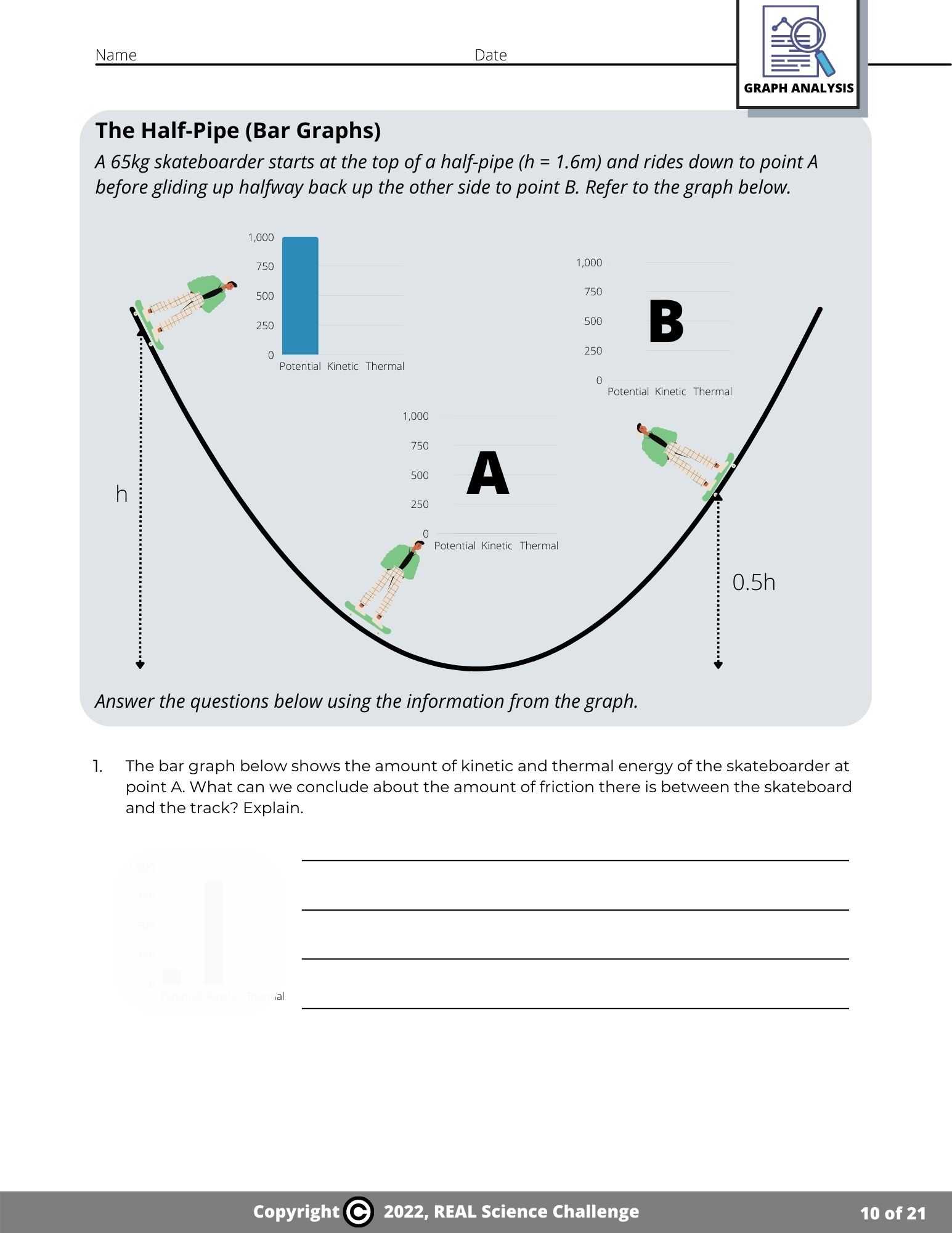
One of the most important concepts in physics is the conversion between potential and kinetic energy. When an object falls from a height, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy. This is known as the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
For example, imagine a ball rolling down a hill. At the top of the hill, the ball has a certain amount of potential energy due to its height. As it rolls down the hill, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, causing it to accelerate and gain speed.
Worksheets on Potential and Kinetic Energy
Here are some worksheets to help you practice and reinforce your understanding of potential and kinetic energy:
Worksheet 1: Potential Energy
- A ball is thrown upwards from the ground with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. If the ball has a mass of 0.5 kg, calculate its potential energy at a height of 10 m.
- A box is lifted from the ground to a height of 5 m. If the box has a mass of 10 kg, calculate its potential energy.
- A car is parked on a hill with a height of 20 m. If the car has a mass of 1500 kg, calculate its potential energy.
Worksheet 2: Kinetic Energy
- A car is moving with a velocity of 30 m/s. If the car has a mass of 1500 kg, calculate its kinetic energy.
- A ball is rolling on the ground with a velocity of 10 m/s. If the ball has a mass of 0.5 kg, calculate its kinetic energy.
- A bicycle is moving with a velocity of 20 m/s. If the bicycle has a mass of 20 kg, calculate its kinetic energy.
Worksheet 3: Conversion between Potential and Kinetic Energy
- A ball is dropped from a height of 10 m. If the ball has a mass of 0.5 kg, calculate its kinetic energy at the bottom of the fall.
- A car is rolling down a hill with a height of 20 m. If the car has a mass of 1500 kg, calculate its kinetic energy at the bottom of the hill.
- A skier is sliding down a slope with a height of 50 m. If the skier has a mass of 70 kg, calculate their kinetic energy at the bottom of the slope.
| Object | Mass (kg) | Height (m) | Velocity (m/s) | Potential Energy (J) | Kinetic Energy (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ball | 0.5 | 10 | 20 | 50 | 200 |
| Car | 1500 | 20 | 30 | 30000 | 67500 |
| Bicycle | 20 | - | 20 | - | 800 |
Important Notes
- Make sure to use the correct formulas for potential and kinetic energy.
- Always check your units and ensure they are consistent.
- When converting between potential and kinetic energy, make sure to use the correct conversion factors.
📝 Note: The answers to the worksheets can be found at the end of this article.
As you work through these worksheets, remember to always use the correct formulas and units. With practice and patience, you will become proficient in calculating potential and kinetic energy, and be able to apply these concepts to a wide range of problems.
What is the difference between potential and kinetic energy?
+Potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or state, while kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion.
How is potential energy converted into kinetic energy?
+Potential energy is converted into kinetic energy when an object falls or rolls down a slope, causing its potential energy to be converted into kinetic energy.
What is the formula for potential energy?
+The formula for potential energy is PE = mgh, where PE is the potential energy, m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object above the ground.