Carbohydrates Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding Carbohydrates: A Comprehensive Guide
Carbohydrates are one of the primary sources of energy for the human body. They come in various forms and are found in a wide range of foods, from fruits and vegetables to grains and dairy products. In this guide, we will delve into the world of carbohydrates, exploring their different types, functions, and importance in our diets.
What are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are macromolecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. They are the most abundant biomolecules on Earth and serve as the primary source of energy for many living organisms. Carbohydrates can be broadly classified into two main categories: simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starches and fibers).
Simple Carbohydrates (Sugars)
Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are composed of a single sugar molecule (monosaccharide) or two sugar molecules bonded together (disaccharide). Common examples of simple carbohydrates include:
- Glucose: a monosaccharide and the primary source of energy for cells
- Fructose: a monosaccharide found in fruits and honey
- Sucrose: a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules
- Lactose: a disaccharide found in milk and other dairy products
Complex Carbohydrates (Starches and Fibers)
Complex carbohydrates, also known as polysaccharides, are composed of three or more sugar molecules bonded together. They are typically found in plant-based foods and can be further divided into two subcategories: starches and fibers.
- Starches: long chains of glucose molecules found in grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables
- Fibers: non-digestible carbohydrates that provide bulk and texture to food
Functions of Carbohydrates in the Body
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including:
- Energy production: carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then converted into energy (ATP) for cells
- Glycogen storage: excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen, a complex carbohydrate that can be quickly converted into energy when needed
- Fiber and digestive health: dietary fibers help regulate bowel movements, promote satiety, and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria
Carbohydrate-Rich Foods
A wide variety of foods are rich in carbohydrates, including:
- Fruits: apples, bananas, berries, citrus fruits
- Vegetables: leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes
- Grains: bread, pasta, rice, quinoa
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas
- Dairy products: milk, yogurt, cheese
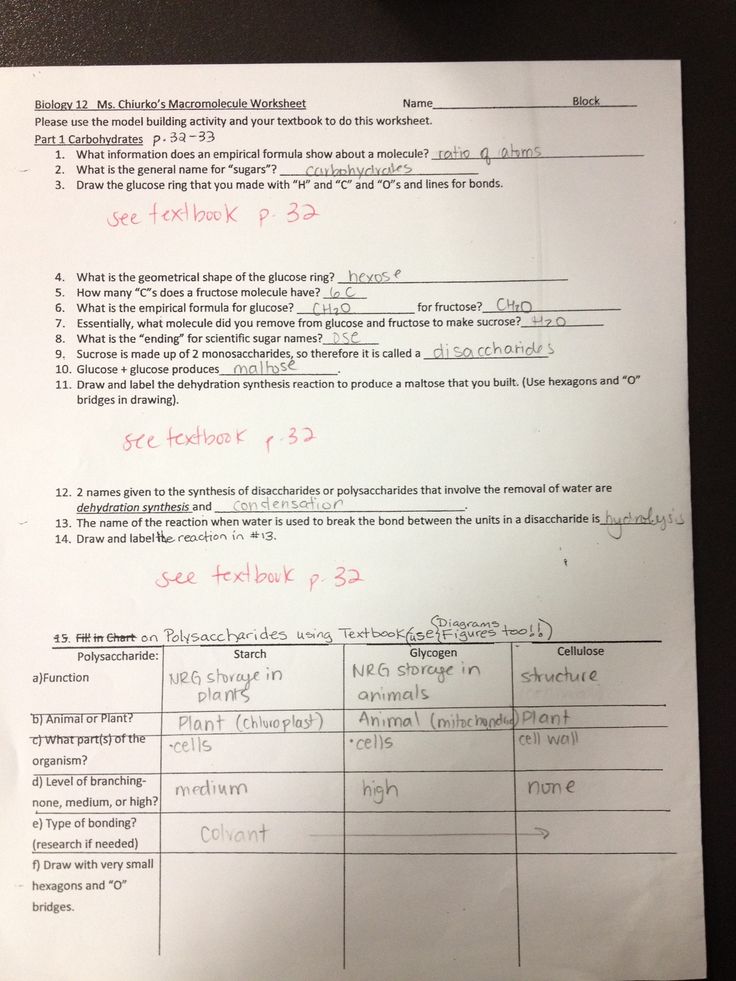
Carbohydrate Worksheet Answer Key
Here is a sample carbohydrate worksheet with answers:

| Food Item | Carbohydrate Content (g) |
|---|---|
| Apple | 25 |
| Banana | 30 |
| White bread | 40 |
| Brown rice | 45 |
| Greek yogurt | 30 |
📝 Note: The carbohydrate content values are approximate and may vary depending on the specific food item and serving size.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, carbohydrates are an essential part of a healthy diet, providing energy, fiber, and various other benefits. By understanding the different types of carbohydrates, their functions, and food sources, we can make informed choices about our diet and maintain optimal health.
What are the main types of carbohydrates?
+The two main types of carbohydrates are simple carbohydrates (sugars) and complex carbohydrates (starches and fibers).
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in the body?
+The primary function of carbohydrates is to provide energy for the body.
Which foods are rich in carbohydrates?
+Carbohydrate-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and dairy products.