5 Stages of Nitrogen Cycle Explained
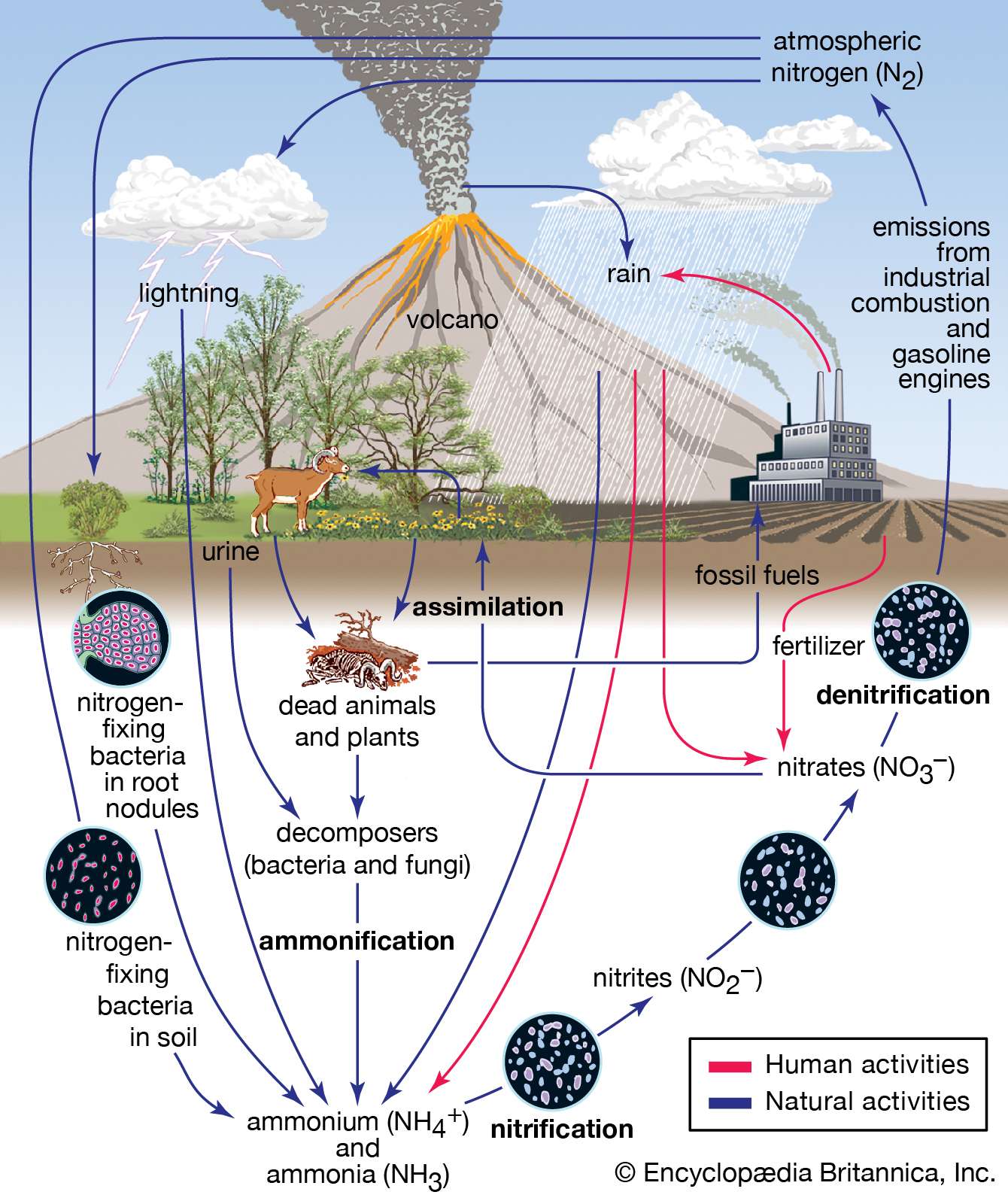
Understanding the Nitrogen Cycle: A Crucial Process for Life on Earth
The nitrogen cycle is a complex process that involves the conversion of nitrogen between its various forms, including nitrogen gas (N2), ammonia (NH3), nitrite (NO2-), and nitrate (NO3-). This cycle is essential for life on Earth, as nitrogen is a critical component of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. In this article, we will delve into the five stages of the nitrogen cycle, exploring the processes that occur at each stage and the importance of this cycle for our ecosystem.
Stage 1: Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen gas (N2) is converted into a usable form, such as ammonia (NH3) or nitrate (NO3-). This process is carried out by certain microorganisms, such as bacteria and cyanobacteria, which have the enzyme nitrogenase. Nitrogenase catalyzes the conversion of N2 into NH3, which can then be used by plants and other organisms.
💡 Note: Nitrogen fixation is a critical process, as it allows nitrogen to be converted into a form that can be used by living organisms.
Stage 2: Assimilation
Assimilation is the process by which plants and other organisms take up nitrogen from the soil or atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds, such as amino acids. This process is carried out by enzymes, such as glutamine synthetase, which convert ammonia (NH3) into glutamine.
- Key enzymes involved in assimilation:
- Glutamine synthetase
- Glutamate synthase
- Importance of assimilation:
- Allows plants to synthesize amino acids
- Essential for plant growth and development
Stage 3: Ammonification
Ammonification is the process by which microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, break down organic matter and release ammonia (NH3) into the environment. This process is carried out by enzymes, such as proteases and peptidases, which break down proteins and peptides into amino acids.
- Key enzymes involved in ammonification:
- Proteases
- Peptidases
- Importance of ammonification:
- Releases nitrogen back into the environment
- Essential for nutrient cycling
Stage 4: Nitrification
Nitrification is the process by which ammonia (NH3) is converted into nitrite (NO2-) and then into nitrate (NO3-). This process is carried out by certain microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, which have the enzyme ammonia monooxygenase. Nitrification is an important process, as it allows nitrogen to be converted into a form that can be used by plants.
- Key enzymes involved in nitrification:
- Ammonia monooxygenase
- Nitrite oxidase
- Importance of nitrification:
- Converts ammonia into a usable form for plants
- Essential for plant growth and development
Stage 5: Denitrification
Denitrification is the process by which nitrate (NO3-) is converted back into nitrogen gas (N2). This process is carried out by certain microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, which have the enzyme nitrate reductase. Denitrification is an important process, as it allows nitrogen to be converted back into a form that can be used by microorganisms.
- Key enzymes involved in denitrification:
- Nitrate reductase
- Nitrite reductase
- Importance of denitrification:
- Converts nitrate back into nitrogen gas
- Essential for nutrient cycling
Conclusion
In summary, the nitrogen cycle is a complex process that involves the conversion of nitrogen between its various forms. The five stages of the nitrogen cycle, including nitrogen fixation, assimilation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification, are essential for life on Earth. Understanding the nitrogen cycle is critical for managing ecosystems and ensuring the health of our planet.
What is the importance of the nitrogen cycle?
+The nitrogen cycle is essential for life on Earth, as it allows nitrogen to be converted between its various forms, making it available for use by living organisms.
Which stage of the nitrogen cycle is carried out by plants?
+Assimilation is the stage of the nitrogen cycle that is carried out by plants, where they take up nitrogen from the soil or atmosphere and convert it into organic compounds.
What is the enzyme responsible for nitrogen fixation?
+Nitrogenase is the enzyme responsible for nitrogen fixation, which catalyzes the conversion of N2 into NH3.
Related Terms:
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet PDF
- Nitrogen cycle Worksheet answers PDF
- Nitrogen cycle questions and Answers
- Nitrogen cycle worksheet high school
- Free nitrogen cycle worksheet
- Nitrogen cycle diagram