Mitosis vs Meiosis: Understanding Cell Division
Cell Division: The Foundation of Life
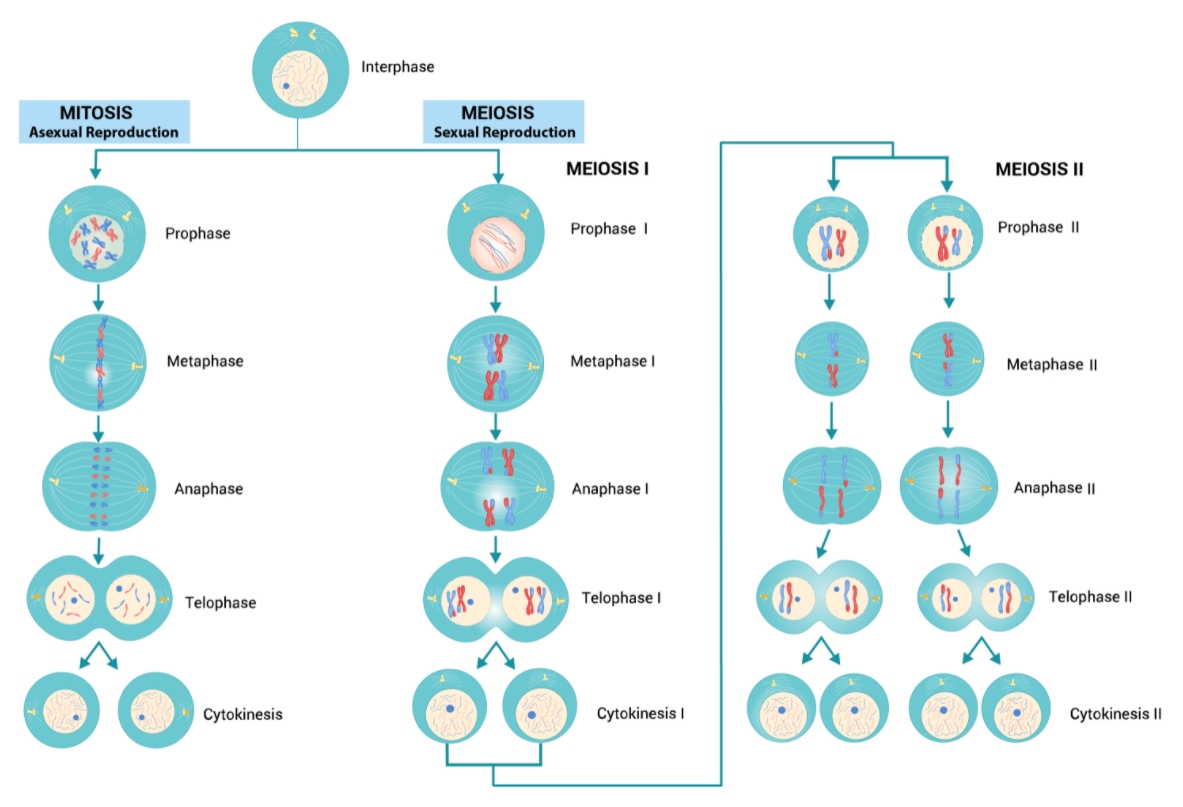
Cell division is a fundamental process that occurs in all living organisms, from single-celled bacteria to complex multicellular organisms like humans. It is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. In this article, we will explore the differences between mitosis and meiosis, and examine the importance of each process in the life cycle of organisms.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It is a crucial process that occurs in all multicellular organisms, allowing for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. During mitosis, the cell’s DNA is replicated, and the chromosomes are divided equally between the two daughter cells.
The Stages of Mitosis
Mitosis consists of four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
- Prophase: The chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes line up at the center of the cell, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin.
🔍 Note: Mitosis is essential for the growth and development of multicellular organisms, as it allows for the production of new cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
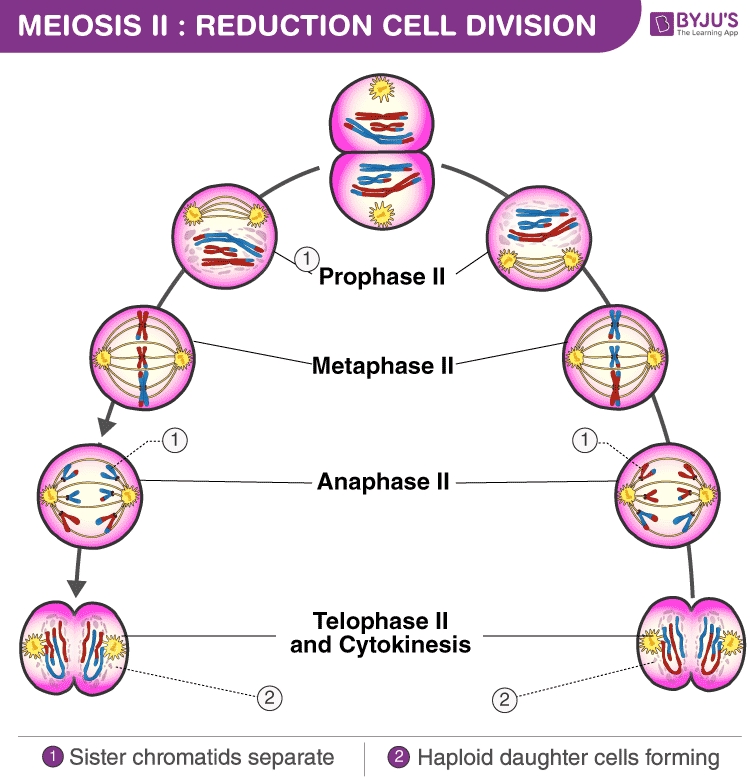
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is the process of cell division that results in four non-identical daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, such as egg and sperm cells. During meiosis, the cell’s DNA is replicated, and the chromosomes are divided unequally between the four daughter cells.
The Stages of Meiosis
Meiosis consists of two successive cell divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II.
- Meiosis I: The homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over.
- Meiosis II: The sister chromatids separate, resulting in four non-identical daughter cells.
🔍 Note: Meiosis is essential for the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) that are necessary for sexual reproduction.
| Cell Division Type | Number of Daughter Cells | Number of Chromosomes per Daughter Cell | Genetic Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitosis | 2 | Same as parent cell | Genetically identical |
| Meiosis | 4 | Half the number of parent cell | Non-identical |
Key Differences between Mitosis and Meiosis
- Number of daughter cells: Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical daughter cells.
- Number of chromosomes: Mitosis results in daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while meiosis results in daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes.
- Genetic identity: Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces non-identical daughter cells.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mitosis and meiosis are two distinct types of cell division that play critical roles in the life cycle of organisms. Mitosis is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues, while meiosis is necessary for the production of gametes that are necessary for sexual reproduction. Understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis is crucial for appreciating the complexities of cellular biology and the importance of these processes in the functioning of living organisms.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced. Mitosis produces two daughter cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical daughter cells.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
+The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) that are necessary for sexual reproduction.
What is the result of mitosis?
+The result of mitosis is two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.