Solving Monohybrid Crosses Made Easy Worksheet Answers

Understanding Monohybrid Crosses: A Step-by-Step Guide
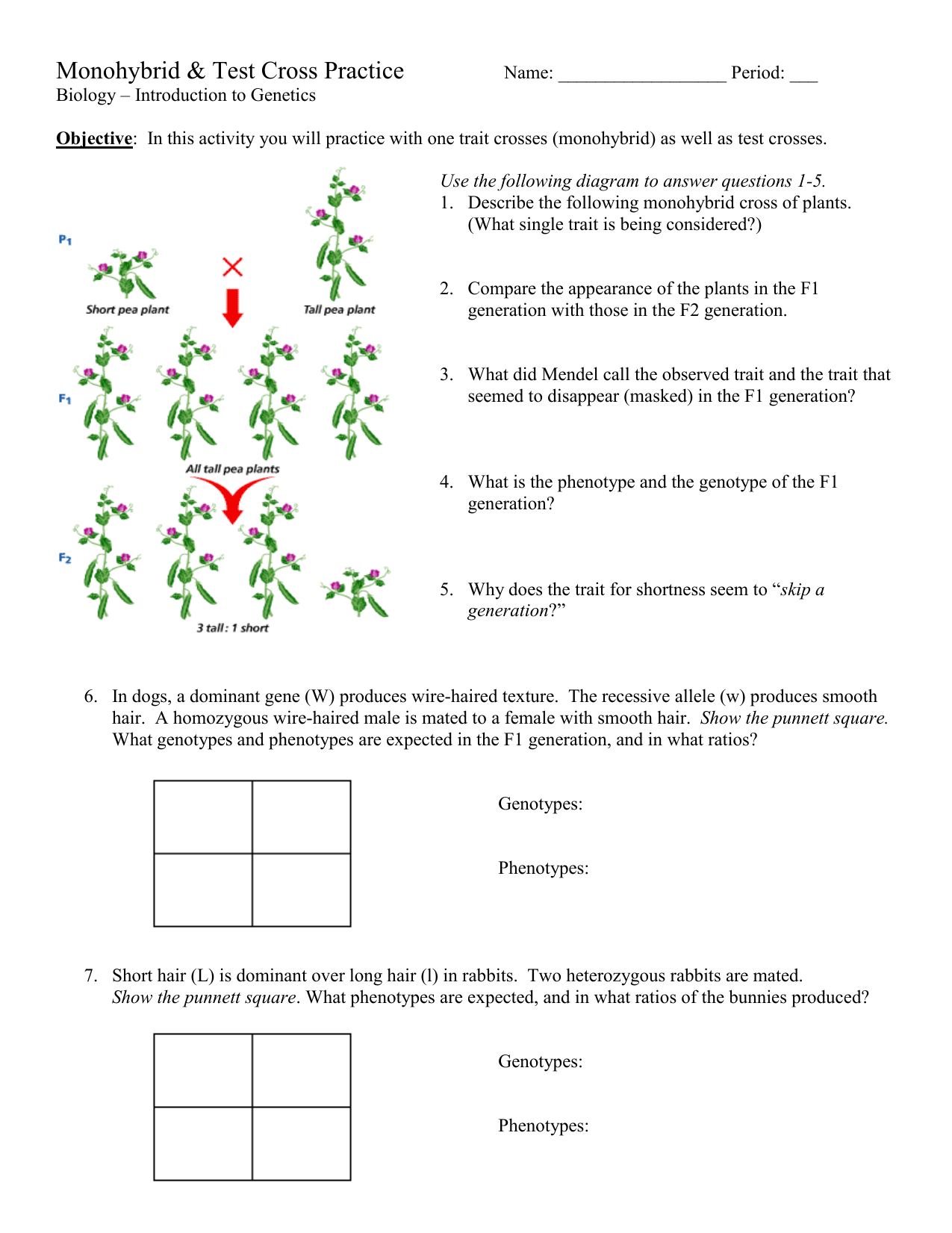
Monohybrid crosses are a fundamental concept in genetics, and understanding them is crucial for students of biology and genetics. A monohybrid cross involves the cross-breeding of two organisms that differ in a single gene, resulting in offspring with a combination of traits. In this article, we will break down the process of solving monohybrid crosses and provide a worksheet with answers to help you practice.
What is a Monohybrid Cross?
A monohybrid cross is a type of genetic cross that involves the cross-breeding of two organisms that differ in a single gene. This gene is responsible for a specific trait, such as flower color, seed shape, or height. The cross is designed to study the inheritance of this trait and to determine the genotype and phenotype of the offspring.
Key Terms to Understand
Before we dive into solving monohybrid crosses, it’s essential to understand some key terms:
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism, represented by letters (e.g., BB, Bb, or bb).
- Phenotype: The physical expression of the genotype (e.g., tall or short).
- Allele: A variant of a gene that occupies a specific location on a chromosome.
- Dominant: An allele that will be expressed if an organism has one or two copies of the allele.
- Recessive: An allele that will only be expressed if an organism has two copies of the allele.
Steps to Solve a Monohybrid Cross
To solve a monohybrid cross, follow these steps:
- Determine the genotype of the parents: Identify the genotype of the two parents, using letters to represent the alleles.
- Determine the possible genotypes of the offspring: Use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype of the offspring: Use the genotype to determine the phenotype of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of each phenotype: Calculate the probability of each phenotype by counting the number of offspring with each phenotype and dividing by the total number of offspring.
Example 1: Solving a Monohybrid Cross
Let’s consider an example of a monohybrid cross between two pea plants. One parent is tall (T) and the other is short (t).
Step 1: Determine the genotype of the parents
Parent 1: TT (homozygous dominant) Parent 2: tt (homozygous recessive)
Step 2: Determine the possible genotypes of the offspring
Use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring:
| T | t | |
|---|---|---|
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | Tt | tt |
Step 3: Determine the phenotype of the offspring
Use the genotype to determine the phenotype of the offspring:
- TT: tall
- Tt: tall
- tt: short
Step 4: Calculate the probability of each phenotype
Count the number of offspring with each phenotype and divide by the total number of offspring:
- Tall: 3⁄4
- Short: 1⁄4
Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to a sample worksheet:
- What is the genotype of the offspring in a cross between a homozygous dominant parent (BB) and a homozygous recessive parent (bb)?
Answer: Bb
- What is the phenotype of the offspring in a cross between a tall parent (T) and a short parent (t)?
Answer: Tall (3⁄4) and short (1⁄4)
- What is the probability of a tall offspring in a cross between a homozygous dominant parent (TT) and a heterozygous parent (Tt)?
Answer: 3⁄4
👉 Note: Remember to always use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring, and then use the genotype to determine the phenotype.
Conclusion
Solving monohybrid crosses is a crucial skill in genetics, and with practice, you can become proficient in solving these types of problems. Remember to always determine the genotype of the parents, use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring, and then use the genotype to determine the phenotype. With these steps and practice, you’ll be solving monohybrid crosses like a pro!
What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype?
+The genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism, represented by letters (e.g., BB, Bb, or bb). The phenotype is the physical expression of the genotype (e.g., tall or short).
What is a Punnett square, and how is it used in solving monohybrid crosses?
+A Punnett square is a diagram used to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring in a genetic cross. It is used to predict the probability of each genotype and phenotype in the offspring.
What is the difference between a dominant and a recessive allele?
+A dominant allele is an allele that will be expressed if an organism has one or two copies of the allele. A recessive allele is an allele that will only be expressed if an organism has two copies of the allele.
Related Terms:
- Monohybrid Cross Practice Worksheet
- Monohybrid Cross Worksheet PDF
- Monohybrid cross problems with Answers