Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers

Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet Answers
Genetics is a fascinating field that explores the mysteries of heredity and variation. As you delve into the world of genetics, it’s essential to practice solving problems to reinforce your understanding of key concepts. In this worksheet, we’ll provide answers to genetics practice problems, covering topics from Mendelian inheritance to DNA structure and function.
Mendelian Inheritance
Mendel’s laws of inheritance describe how genes are passed down from one generation to the next. Let’s start with a classic problem:
Problem 1: A pea plant with the genotype “RR” or “Rr” has red flowers, while a plant with the genotype “rr” has white flowers. If a pea plant with the genotype “Rr” is crossed with a plant with the genotype “rr”, what is the probability that the offspring will have red flowers?
Answer: Since the “R” allele is dominant, any plant with the genotype “Rr” or “RR” will have red flowers. The probability of the offspring inheriting the “R” allele from the “Rr” parent is 50% (since the “R” allele has a 50% chance of being passed down). Therefore, the probability that the offspring will have red flowers is 50%.
Punnett Squares
Punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. Let’s try another problem:
Problem 2: A couple has a child with sickle cell anemia, which is caused by a recessive allele “s”. If the father has the genotype “Ss” and the mother has the genotype “ss”, what is the probability that their next child will have sickle cell anemia?
Answer: To solve this problem, we can create a Punnett square:
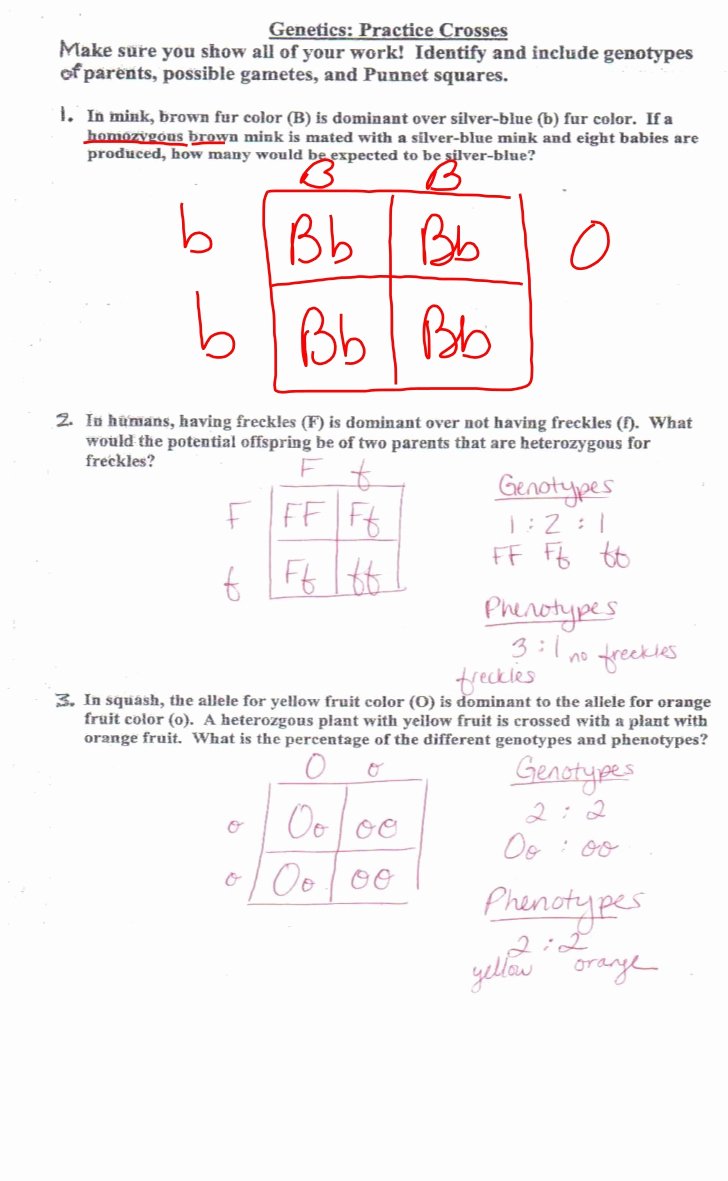
| S | s | |
|---|---|---|
| s | Ss | ss |
| s | Ss | ss |
As we can see, there is a 50% chance that the offspring will inherit the “ss” genotype, which means they will have sickle cell anemia. Therefore, the probability that their next child will have sickle cell anemia is 50%.
DNA Structure and Function
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the molecule that contains the genetic instructions for an organism. Let’s explore a problem related to DNA structure and function:
Problem 3: A segment of DNA has the following sequence: 5’-ATCG-3’. What is the complementary sequence of this DNA segment?
Answer: The complementary sequence is created by pairing each nucleotide with its complementary base:
- A pairs with T
- T pairs with A
- C pairs with G
- G pairs with C
Therefore, the complementary sequence is 3’-TAGC-5’.
Genotype and Phenotype
The genotype of an organism refers to its genetic makeup, while the phenotype refers to its physical characteristics. Let’s examine a problem that connects genotype and phenotype:
Problem 4: A person has the genotype “BB” or “Bb” for the gene that determines eye color, where “B” represents the allele for brown eyes and “b” represents the allele for blue eyes. If this person is crossed with someone who has the genotype “bb”, what is the probability that their offspring will have brown eyes?
Answer: Since the “B” allele is dominant, any offspring with the genotype “BB” or “Bb” will have brown eyes. The probability of the offspring inheriting the “B” allele from the “BB” or “Bb” parent is 100% (since the “B” allele will always be passed down). Therefore, the probability that the offspring will have brown eyes is 100%.
📝 Note: In this problem, we assume that the "B" allele is completely dominant over the "b" allele. In reality, eye color is a complex trait influenced by multiple genes.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
The Hardy-Weinberg principle describes the expected frequencies of different genotypes in a population under certain conditions. Let’s apply this principle to a problem:
Problem 5: A population of rabbits has a gene that determines coat color, with the “B” allele representing brown fur and the “b” allele representing white fur. If the frequency of the “B” allele is 0.6 and the frequency of the “b” allele is 0.4, what is the expected frequency of the “BB” genotype in the population?
Answer: According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle, the expected frequency of the “BB” genotype is equal to the square of the frequency of the “B” allele: (0.6)^2 = 0.36. Therefore, the expected frequency of the “BB” genotype in the population is 36%.
What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype?
+The genotype refers to an organism's genetic makeup, while the phenotype refers to its physical characteristics.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a tool used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
+The Hardy-Weinberg principle describes the expected frequencies of different genotypes in a population under certain conditions.
In conclusion, genetics is a complex and fascinating field that requires practice to master. By working through these practice problems, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of key concepts, from Mendelian inheritance to DNA structure and function. Remember to apply the principles and tools you’ve learned to solve problems and analyze data.