Photosynthesis and Respiration Worksheet Answer Key

Understanding Photosynthesis and Respiration: A Comprehensive Guide
Photosynthesis and respiration are two fundamental processes that occur in living organisms, enabling them to sustain life. While photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, respiration is the process by which cells generate energy from the food they consume. In this article, we will delve into the world of photosynthesis and respiration, exploring their mechanisms, importance, and the differences between them.
Photosynthesis: The Light-Dependent Reaction
Photosynthesis is a complex process that occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts, which are present in plant cells. The process can be divided into two stages: the light-dependent reaction and the light-independent reaction.
Light-Dependent Reaction:
The light-dependent reaction, also known as the Hill reaction, occurs in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplast. In this stage, light energy is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll and converted into ATP and NADPH.
- Step 1: Light is absorbed by pigments such as chlorophyll, causing an electron to be excited and passed along a series of electron carriers.
- Step 2: The energy from the excited electron is used to pump protons across the thylakoid membrane, creating a proton gradient.
- Step 3: The proton gradient is used to produce ATP through the process of chemiosmosis.
- Step 4: The electrons ultimately reduce NADP+ to form NADPH.
Photosynthesis: The Light-Independent Reaction
The light-independent reaction, also known as the Calvin cycle, occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast. In this stage, CO2 is fixed into glucose using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reaction.
- Step 1: CO2 is fixed into a three-carbon molecule called 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) via the enzyme RuBisCO.
- Step 2: The 3-PGA is reduced to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reaction.
- Step 3: The G3P is used to synthesize glucose and other organic compounds.
Respiration: The Energy-Releasing Process
Respiration is the process by which cells generate energy from the food they consume. There are two main types of respiration: aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration:
Aerobic respiration occurs in the presence of oxygen and is the more efficient of the two types of respiration.
- Step 1: Glucose is converted into pyruvate through the process of glycolysis.
- Step 2: The pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle.
- Step 3: The citric acid cycle produces ATP, NADH, and FADH2 as byproducts.
- Step 4: The electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed through a series of electron carriers, ultimately reducing oxygen to water.
Anaerobic Respiration:
Anaerobic respiration occurs in the absence of oxygen and is less efficient than aerobic respiration.
- Step 1: Glucose is converted into pyruvate through the process of glycolysis.
- Step 2: The pyruvate is converted into lactic acid or ethanol and carbon dioxide.
Comparison of Photosynthesis and Respiration
| Photosynthesis | Respiration | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Light energy | Chemical energy |
| Energy Storage | Glucose | ATP |
| Byproducts | Oxygen and glucose | Carbon dioxide and water |
| Location | Chloroplasts | Mitochondria |
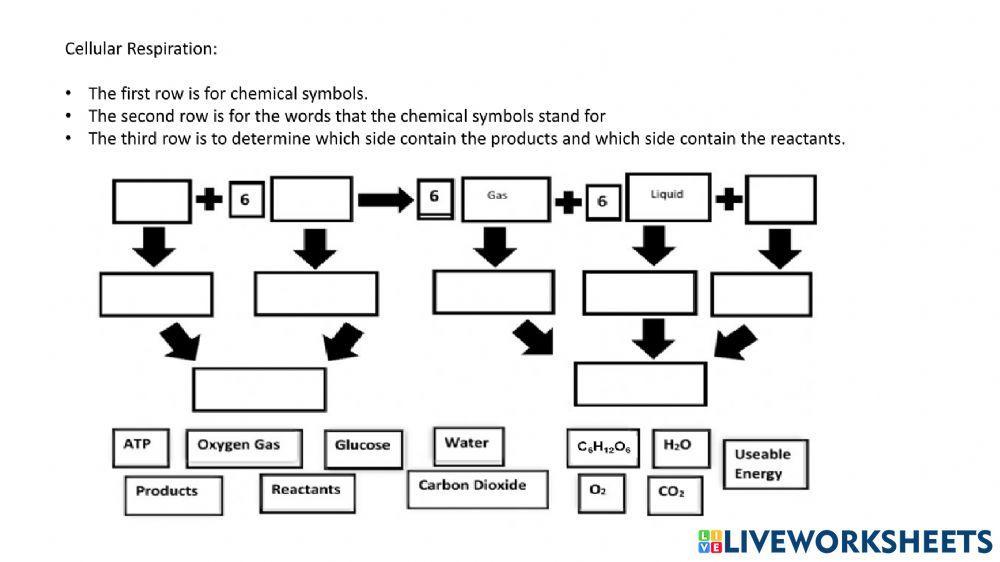
| Equation | 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 | C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP |
💡 Note: While photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, respiration produces carbon dioxide and water.
Importance of Photosynthesis and Respiration
Both photosynthesis and respiration are essential for life on Earth. Photosynthesis provides the energy and organic compounds needed to support life, while respiration generates the energy needed to sustain cellular processes.
- Food Chain: Photosynthesis provides the base of the food chain, supporting herbivores and, in turn, carnivores.
- Oxygen Production: Photosynthesis produces oxygen, which is essential for aerobic respiration.
- Energy Generation: Respiration generates the energy needed to sustain cellular processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, photosynthesis and respiration are two fundamental processes that occur in living organisms. While photosynthesis produces glucose and oxygen, respiration generates energy from the food we consume. Understanding these processes is essential for appreciating the intricate web of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between photosynthesis and respiration?
+
The main difference between photosynthesis and respiration is the source of energy and the byproducts produced. Photosynthesis uses light energy to produce glucose and oxygen, while respiration uses chemical energy to produce ATP and carbon dioxide.
What is the equation for photosynthesis?
+
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
What is the byproduct of anaerobic respiration?
+
The byproduct of anaerobic respiration is lactic acid or ethanol and carbon dioxide.