Mastering Angles: Reading a Protractor Made Easy
Understanding Angles: The Basics
Angles are a fundamental concept in geometry and trigonometry, and being able to read a protractor accurately is a crucial skill for anyone interested in mathematics, architecture, engineering, or design. In this article, we will explore the basics of angles, how to read a protractor, and provide tips and tricks to make angle measurement a breeze.
What is a Protractor?
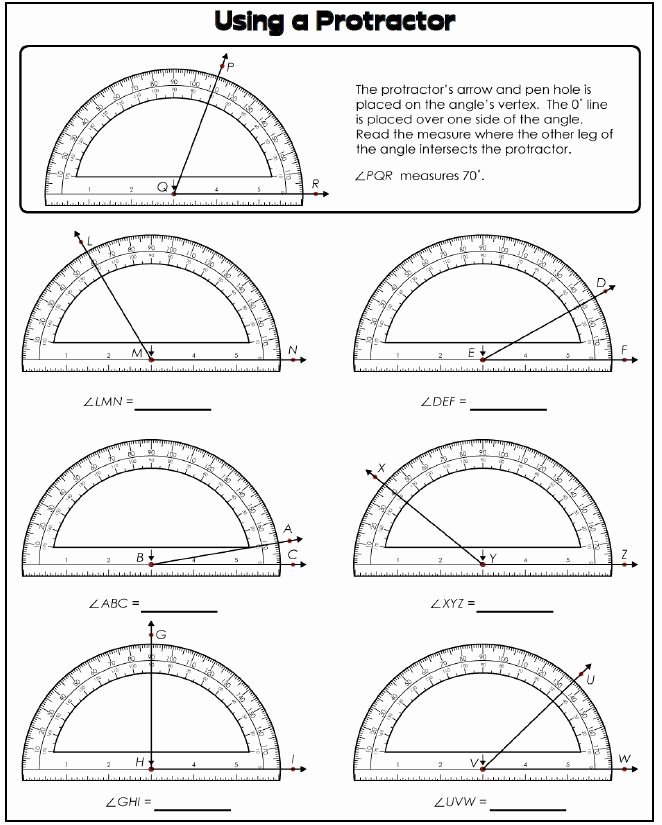
A protractor is a circular or semi-circular tool used to measure angles in degrees. It consists of a circular or semi-circular scale with markings to indicate degrees, minutes, and seconds. Protractors can be found in various forms, including digital and analog versions.
Types of Angles
Before we dive into reading a protractor, let’s quickly review the different types of angles:
- Acute Angle: An angle less than 90 degrees.
- Right Angle: An angle exactly equal to 90 degrees.
- Obtuse Angle: An angle greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
- Straight Angle: An angle exactly equal to 180 degrees.
- Reflex Angle: An angle greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees.
Reading a Protractor: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s move on to reading a protractor:
Step 1: Identify the Type of Protractor
Before you start measuring angles, make sure you know what type of protractor you’re using. Is it a circular or semi-circular protractor? Is it a digital or analog protractor?
Step 2: Align the Protractor
Place the protractor on the angle you want to measure, making sure the vertex of the angle (the point where the two lines meet) aligns with the center of the protractor.
Step 3: Identify the Degree Markings
Look for the degree markings on the protractor. These markings will indicate the angle measurement in degrees.
Step 4: Measure the Angle
To measure the angle, rotate the protractor until the line that forms the angle aligns with the degree markings. Take note of the degree measurement where the line intersects the protractor.
📝 Note: When measuring angles, make sure to read the degree markings from the center of the protractor outwards.
Step 5: Determine the Angle Type
Once you’ve measured the angle, determine the type of angle it is (acute, right, obtuse, straight, or reflex).
Example: Measuring an Angle
Let’s say you want to measure an angle that forms a triangle with two sides. Place the protractor on the angle, aligning the vertex with the center of the protractor. Rotate the protractor until the line that forms the angle aligns with the degree markings. Let’s say the line intersects the protractor at 120 degrees. Since the angle is greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees, it’s an obtuse angle.
Tips and Tricks for Reading a Protractor
Here are some tips and tricks to help you master reading a protractor:
- Always align the vertex of the angle with the center of the protractor.
- Use a ruler or straightedge to help you draw accurate lines and angles.
- When measuring angles, use a pencil mark to indicate the degree measurement.
- Practice, practice, practice! The more you practice reading a protractor, the more comfortable you’ll become.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when reading a protractor:
- Not aligning the vertex of the angle with the center of the protractor.
- Not reading the degree markings from the center of the protractor outwards.
- Not determining the type of angle (acute, right, obtuse, straight, or reflex).
📝 Note: Avoid these common mistakes by practicing regularly and double-checking your measurements.
Conclusion
Mastering angles and reading a protractor is a fundamental skill that requires practice and patience. By following these steps and tips, you’ll become more confident and accurate in your ability to measure angles. Remember to always align the vertex of the angle with the center of the protractor, read the degree markings from the center outwards, and determine the type of angle.
What is the difference between a circular and semi-circular protractor?
+
A circular protractor measures angles from 0 to 360 degrees, while a semi-circular protractor measures angles from 0 to 180 degrees.
How do I determine the type of angle?
+
To determine the type of angle, measure the angle using a protractor and then determine if it’s acute (less than 90 degrees), right (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse (greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees), straight (exactly 180 degrees), or reflex (greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees).
Can I use a digital protractor to measure angles?
+
Yes, digital protractors can be used to measure angles. They often provide more accurate measurements and can be easier to use than analog protractors.
Related Terms:
- Reading a protractor worksheet PDF
- Reading a protractor worksheet answers
- Angles worksheet with answers
- Measuring angles Worksheet
- Basic geometry worksheets