Mastering Voltage, Current, and Resistance with Ease
Understanding the Basics of Electricity
Electricity is a fundamental part of our daily lives, and understanding its basic principles is crucial for anyone interested in electronics, engineering, or physics. Voltage, current, and resistance are the three essential components of electricity, and grasping their relationships and behaviors is key to mastering the subject. In this article, we will delve into the world of electricity, exploring the definitions, formulas, and practical applications of voltage, current, and resistance.
Voltage: The Driving Force of Electricity
Voltage, also known as electric potential difference, is the driving force behind the flow of electric current. It is measured in volts (V) and is defined as the potential difference between two points in a circuit. Voltage is created by a source of electromotive force (EMF), such as a battery or a generator.
Key Points to Remember:
- Voltage is the “pressure” that drives electric current through a circuit.
- Voltage is measured in volts (V).
- Voltage is created by a source of electromotive force (EMF).
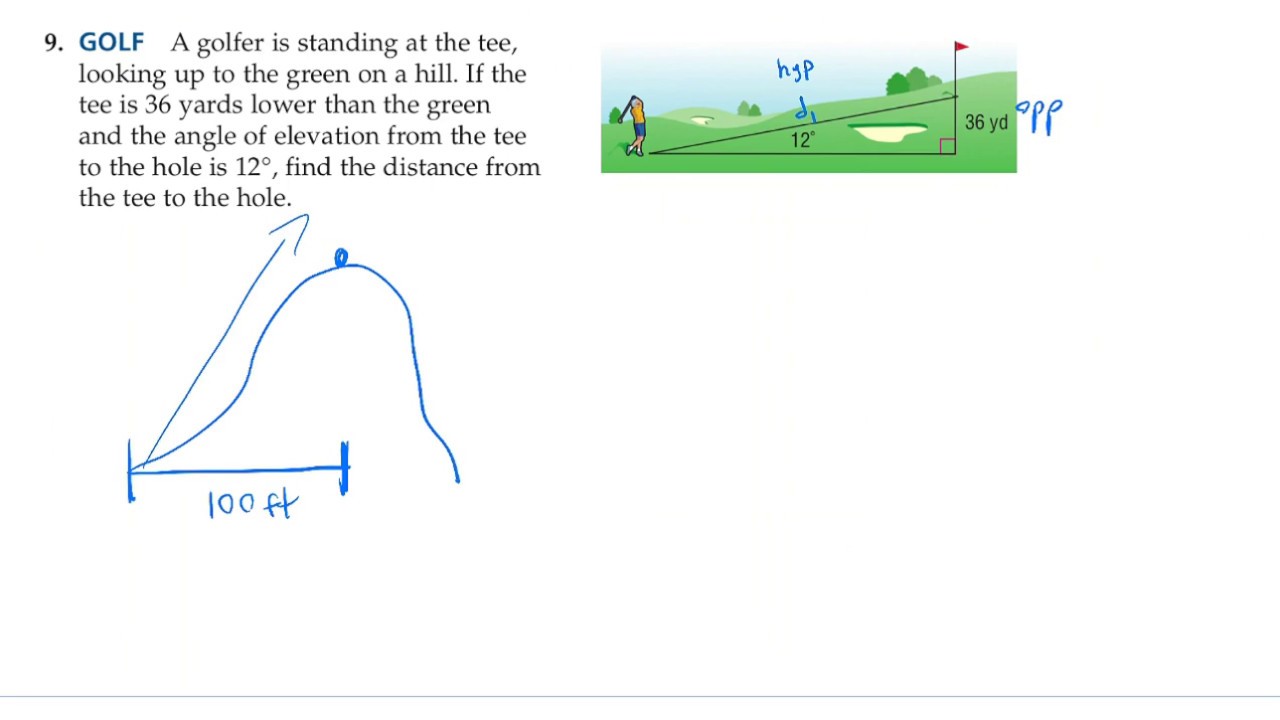
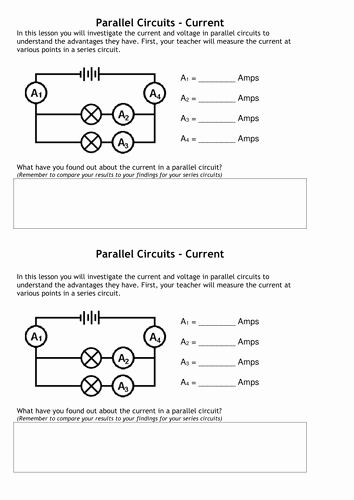
Current: The Flow of Electric Charge
Electric current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. It is measured in amperes (A) and is defined as the rate of flow of electric charge. Current is the result of voltage applied across a conductor and is affected by the resistance of the conductor.
Key Points to Remember:
- Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor.
- Current is measured in amperes (A).
- Current is affected by the resistance of the conductor.
Resistance: The Opposition to Electric Flow
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current through a conductor. It is measured in ohms (Ω) and is defined as the ratio of voltage to current. Resistance depends on the material, size, and shape of the conductor.
Key Points to Remember:
- Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electric current.
- Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
- Resistance depends on the material, size, and shape of the conductor.
Ohm's Law: The Relationship Between Voltage, Current, and Resistance
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance. It states that voltage (V) is equal to current (I) multiplied by resistance ®.
Ohm’s Law Formula:
V = I × R
Key Points to Remember:
- Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance.
- Ohm’s Law is expressed as V = I × R.
Practical Applications of Voltage, Current, and Resistance
Understanding voltage, current, and resistance is crucial for designing and building electronic circuits. Here are some practical applications of these concepts:
- Electric Power: Electric power is the product of voltage and current. It is measured in watts (W) and is used to calculate the energy consumed by a device.
- Electronic Devices: Electronic devices, such as smartphones and laptops, rely on voltage, current, and resistance to function. Understanding these concepts is essential for designing and building electronic circuits.
- Circuit Analysis: Circuit analysis is the process of analyzing electronic circuits to determine their behavior. Understanding voltage, current, and resistance is crucial for circuit analysis.
💡 Note: Electric circuits can be complex and involve multiple components. Understanding voltage, current, and resistance is essential for designing and building electronic circuits.
Conclusion
Mastering voltage, current, and resistance is essential for anyone interested in electronics, engineering, or physics. Understanding the relationships and behaviors of these components is key to designing and building electronic circuits. By applying the concepts of voltage, current, and resistance, you can analyze and troubleshoot electronic circuits, design new devices, and push the boundaries of innovation.
What is the unit of measurement for voltage?
+The unit of measurement for voltage is volts (V).
What is the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance?
+The relationship between voltage, current, and resistance is described by Ohm’s Law, which states that voltage (V) is equal to current (I) multiplied by resistance ®. The formula is V = I × R.
What is the practical application of understanding voltage, current, and resistance?
+Understanding voltage, current, and resistance is essential for designing and building electronic circuits, analyzing and troubleshooting electronic devices, and pushing the boundaries of innovation.