Solubility Curve Worksheet Answer Key Solutions Made Easy
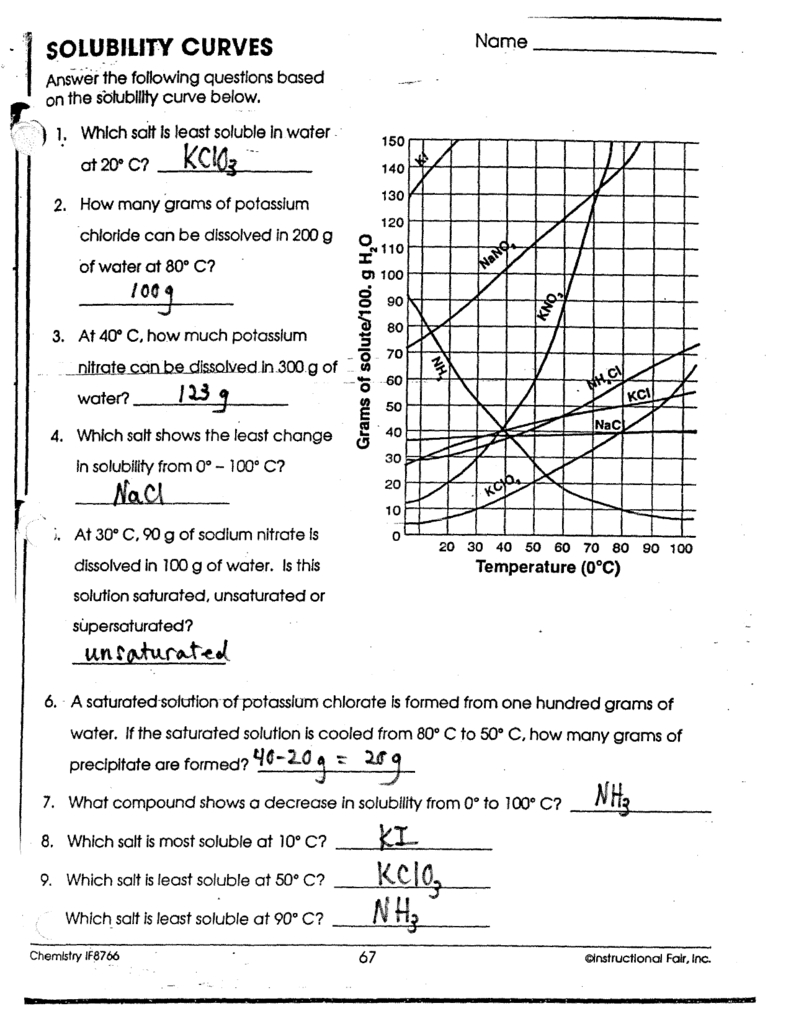
Understanding Solubility Curves: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to chemistry, solubility curves are an essential concept to grasp, especially for students and professionals alike. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of solubility curves, exploring what they are, how to read them, and how to apply the knowledge in real-world scenarios.
What is a Solubility Curve?
A solubility curve is a graphical representation of the solubility of a substance in a given solvent at various temperatures. It is a vital tool used to determine the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a solvent at a specific temperature. The curve is typically plotted with temperature on the x-axis and solubility on the y-axis.
Key Components of a Solubility Curve
To accurately read and interpret a solubility curve, it’s crucial to understand its key components:
- Solubility: The maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature.
- Temperature: The temperature at which the solubility is measured.
- Saturation point: The point at which the solution becomes saturated, and no more solute can dissolve.
How to Read a Solubility Curve
Reading a solubility curve can seem daunting at first, but with practice, it becomes second nature. Here are the steps to follow:
- Identify the substance and solvent: Note the substance and solvent being used in the experiment.
- Locate the temperature: Find the temperature on the x-axis and draw a vertical line up to the curve.
- Determine the solubility: Read the solubility value from the y-axis where the line intersects the curve.
Types of Solubility Curves
There are several types of solubility curves, including:
- Normal solubility curve: A curve that increases steadily as temperature increases.
- Inverted solubility curve: A curve that decreases as temperature increases.
- S-shaped solubility curve: A curve that initially increases, then decreases, and finally increases again as temperature increases.
Factors Affecting Solubility Curves
Several factors can influence the shape and position of a solubility curve, including:
- Temperature: Changes in temperature can alter the solubility of a substance.
- Pressure: Increased pressure can affect the solubility of gases.
- Presence of impurities: Impurities can alter the solubility of a substance.
📝 Note: Solubility curves can be affected by various factors, and it's essential to consider these factors when interpreting the data.
Applications of Solubility Curves
Solubility curves have numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceutical industry: Solubility curves are used to determine the solubility of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
- Food industry: Solubility curves are used to optimize the production of food products, such as sugar and salt.
- Environmental monitoring: Solubility curves are used to monitor the levels of pollutants in water and air.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding solubility curves is crucial in various fields, from pharmaceuticals to environmental monitoring. By grasping the concept of solubility curves and how to read them, professionals and students can make informed decisions and optimize processes.
Solubility Curve Worksheet Answer Key

| Substance | Temperature (°C) | Solubility (g/100 mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Sugar | 20 | 65 |
| Salt | 20 | 35 |
| Sugar | 40 | 80 |
| Salt | 40 | 40 |
Using the solubility curve, answer the following questions:
- What is the solubility of sugar at 20°C?
- What is the solubility of salt at 40°C?
- How does the solubility of sugar change as the temperature increases from 20°C to 40°C?
Answers:
- The solubility of sugar at 20°C is 65 g/100 mL.
- The solubility of salt at 40°C is 40 g/100 mL.
- The solubility of sugar increases from 65 g/100 mL to 80 g/100 mL as the temperature increases from 20°C to 40°C.
What is the purpose of a solubility curve?
+A solubility curve is used to determine the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature.
How does temperature affect solubility?
+Temperature can affect the solubility of a substance. In general, an increase in temperature leads to an increase in solubility.
What are the different types of solubility curves?
+There are three main types of solubility curves: normal, inverted, and S-shaped.
Related Terms:
- Solubility curve Worksheet PDF
- Solubility curve questions and answers
- Solubility curve Worksheet Answers PDF
- Solubility curve PDF
- Saturated solubility