Prokaryote vs Eukaryote: Cell Structure Comparison
Understanding Cell Structure: A Comprehensive Comparison of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and they come in two primary types: prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While both types of cells are essential for life, they exhibit distinct differences in terms of their structure, organization, and function. In this article, we will delve into the world of cells and explore the fundamental differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, focusing on their cell structure.
Prokaryote Cell Structure
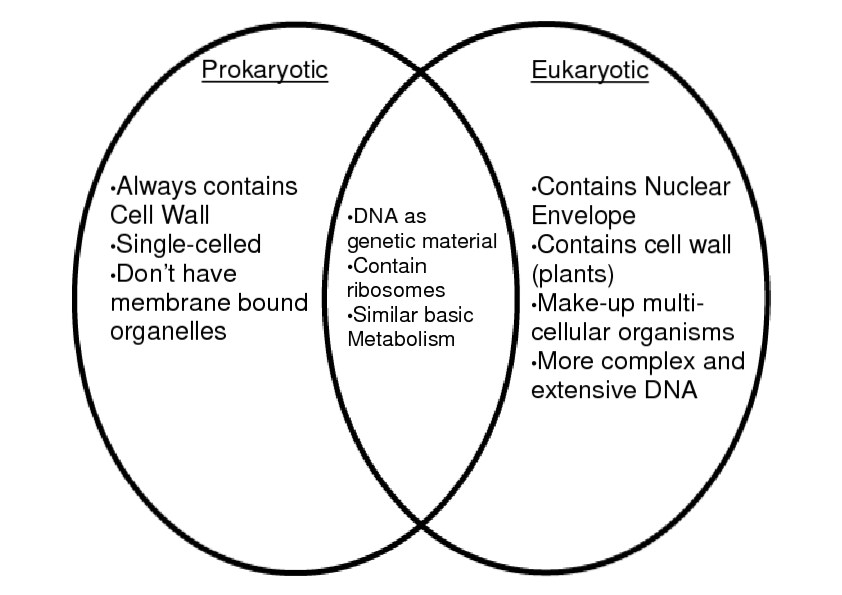
Prokaryotes are the simplest form of cells, and they lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The most well-known prokaryotes are bacteria and archaea. The cell structure of prokaryotes can be summarized as follows:
- Cell Wall: Prokaryotes have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. The cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan (also known as murein) in bacteria and pseudopeptidoglycan in archaea.
- Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a lipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell where metabolic processes take place.
- Nucleoid: The nucleoid is the region where the genetic material (DNA) is located. It is not membrane-bound and is often irregularly shaped.
- Mesosomes: Mesosomes are invaginations of the cell membrane that help in the separation of chromosomes during cell division.
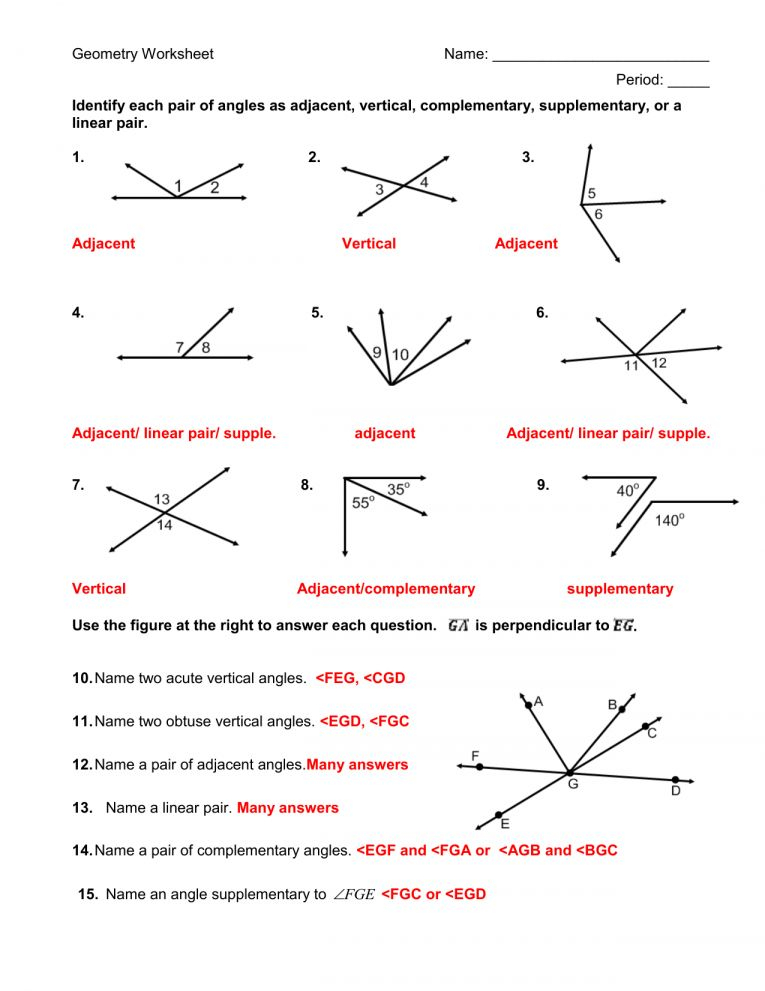
Eukaryote Cell Structure
Eukaryotes are more complex cells that have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The most well-known eukaryotes are plants, animals, fungi, and protists. The cell structure of eukaryotes can be summarized as follows:
- Cell Wall: Eukaryotes have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. The cell wall is composed of cellulose in plants, chitin in fungi, and various materials in other eukaryotes.
- Cell Membrane: The cell membrane is a lipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell where metabolic processes take place.
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the membrane-bound organelle that contains the genetic material (DNA). It is often spherical in shape and has a distinct nuclear envelope.
- Mitochondria: Mitochondria are organelles responsible for generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The ER is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that help in protein synthesis and transport.
- Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a complex of flattened sacs and tubules that help in protein modification and secretion.
- Lysosomes: Lysosomes are organelles responsible for cellular digestion and recycling of materials.
Key Differences between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
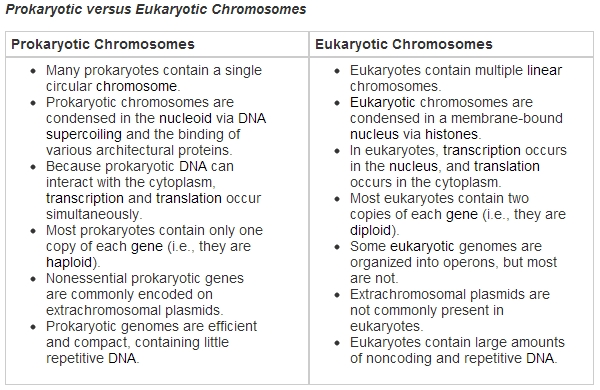
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus | True nucleus |
| Cell Wall | Peptidoglycan or pseudopeptidoglycan | Cellulose, chitin, or other materials |
| Membrane-bound Organelles | No | Yes (e.g., mitochondria, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes) |
| Cell Size | Typically small (1-10 μm) | Typically large (10-100 μm) |
| Genetic Material | Single circular DNA molecule | Linear DNA molecules with histone proteins |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis and meiosis |
📝 Note: The table highlights the main differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but it is not an exhaustive list of characteristics.
Evolutionary Significance of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are thought to have evolved around 3.5 billion years ago, during a time when the Earth’s atmosphere was still forming. They were the first cells to exist on our planet and played a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s ecosystem. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, evolved around 2.1 billion years ago, and their development is believed to have been influenced by the presence of oxygen in the atmosphere.
The evolution of eukaryotes marked a significant milestone in the history of life on Earth, as it led to the development of complex multicellular organisms. The diversity of eukaryotes has allowed them to occupy a wide range of ecological niches, from the simplest protists to complex plants and animals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prokaryotes and eukaryotes are two distinct types of cells that differ significantly in terms of their structure, organization, and function. While prokaryotes are simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, eukaryotes are more complex and have a true nucleus and other organelles. Understanding the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is essential for appreciating the diversity of life on Earth and the evolutionary processes that have shaped our planet.
What is the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
+The main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the presence of a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotes, which are absent in prokaryotes.
Which type of cell is more complex?
+Eukaryotes are more complex than prokaryotes due to the presence of membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus.
What is the evolutionary significance of prokaryotes?
+Prokaryotes are thought to have evolved around 3.5 billion years ago and played a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s ecosystem. They were the first cells to exist on our planet.