Master Hydrocarbon Names in 5 Easy Steps
Mastering Hydrocarbon Names in 5 Easy Steps
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon atoms. They can be found in various forms, such as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons. Mastering the naming of hydrocarbons is crucial for any student of organic chemistry. In this blog post, we will break down the process of naming hydrocarbons into 5 easy steps.
Step 1: Identify the Type of Hydrocarbon
The first step in naming a hydrocarbon is to identify the type of hydrocarbon it is. There are several types of hydrocarbons, including:
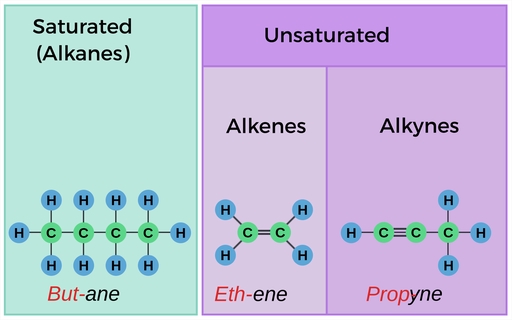
- Alkanes: Saturated hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms.
- Alkenes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
- Alkynes: Unsaturated hydrocarbons with one or more triple bonds between carbon atoms.
- Aromatic hydrocarbons: Hydrocarbons with a planar, ring-shaped molecule and alternating double and single bonds.
🔍 Note: Aromatic hydrocarbons are a special type of hydrocarbon that follows a different set of naming rules.
Step 2: Determine the Parent Chain
Once you have identified the type of hydrocarbon, the next step is to determine the parent chain. The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule. The parent chain can be either linear or branched.
- Linear parent chain: A straight chain of carbon atoms.
- Branched parent chain: A chain of carbon atoms with one or more branches.
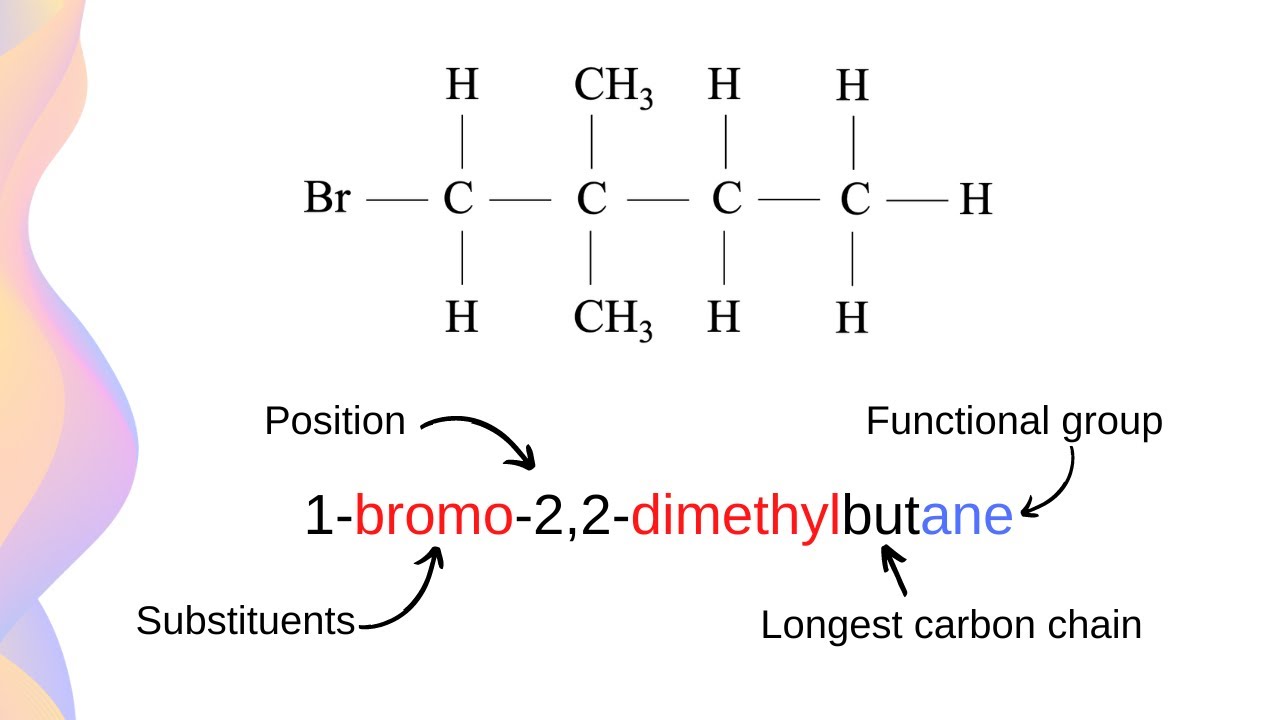
Step 3: Identify and Number the Substituents
Substituents are groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain. In hydrocarbons, substituents can be alkyl groups, halogen atoms, or other functional groups. The next step is to identify and number the substituents.
- Alkyl groups: Groups of carbon and hydrogen atoms that are attached to the parent chain.
- Halogen atoms: Atoms such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine that are attached to the parent chain.
Step 4: Name the Substituents
Once you have identified and numbered the substituents, the next step is to name them. The name of the substituent is based on the number of carbon atoms in the group.
- Methyl group: A group with one carbon atom (CH3).
- Ethyl group: A group with two carbon atoms (C2H5).
- Propyl group: A group with three carbon atoms (C3H7).
📝 Note: When naming substituents, the suffix "-yl" is used to indicate that the group is attached to the parent chain.
Step 5: Combine the Parent Chain and Substituents
The final step is to combine the parent chain and the substituents to form the complete name of the hydrocarbon. The name of the hydrocarbon is based on the type of hydrocarbon, the length of the parent chain, and the number and type of substituents.
- Alkanes: The suffix “-ane” is used to indicate that the hydrocarbon is an alkane.
- Alkenes: The suffix “-ene” is used to indicate that the hydrocarbon is an alkene.
- Alkynes: The suffix “-yne” is used to indicate that the hydrocarbon is an alkyne.
| Hydrocarbon Type | Parent Chain | Substituents | Complete Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkane | CH3CH2CH2CH3 | Methyl group | 2-Methylpropane |
| Alkene | CH2CHCH3 | Ethyl group | 2-Ethyl-1-butene |
| Alkyne | CHCHCCH3 | Propyl group | 3-Propyl-1-butyne |
To summarize, naming hydrocarbons involves identifying the type of hydrocarbon, determining the parent chain, identifying and numbering the substituents, naming the substituents, and combining the parent chain and substituents to form the complete name.
What is the difference between an alkane and an alkene?
+Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms, while alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with one or more double bonds between carbon atoms.
How do you name a hydrocarbon with multiple substituents?
+When naming a hydrocarbon with multiple substituents, the substituents are listed in alphabetical order, and the parent chain is numbered to indicate the position of each substituent.
What is the purpose of the IUPAC naming system?
+The IUPAC naming system provides a standardized way of naming chemical compounds, including hydrocarbons, to ensure consistency and clarity in communication among chemists.