6 Key Parts of a Microscope to Know
Understanding the Microscope: 6 Key Parts to Know
When it comes to exploring the microscopic world, a microscope is an essential tool. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or hobbyist, knowing the different parts of a microscope is crucial for getting the most out of your observations. In this article, we’ll delve into the six key parts of a microscope that you should be familiar with.
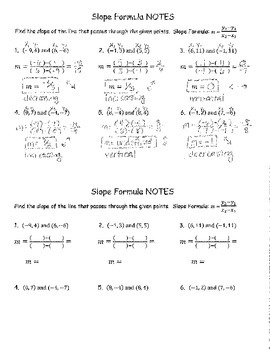
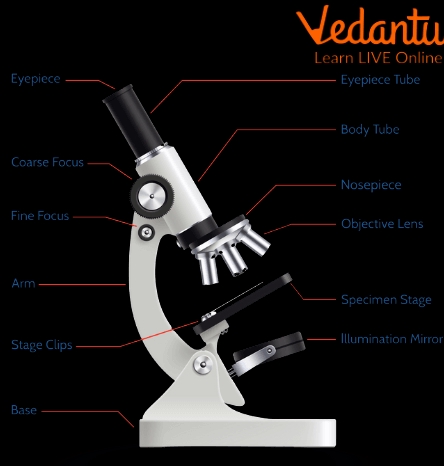
1. Eyepiece (Ocular Lens)
The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, is the part of the microscope that you look directly into to observe your specimen. It’s usually a removable lens that magnifies the image formed by the objective lens. The eyepiece typically has a magnification power of 10x or 15x, but it can vary depending on the type of microscope.
🔍 Note: Always handle the eyepiece with care, as it can be easily damaged.
2. Objective Lens
The objective lens is responsible for collecting light from the specimen and forming an image. It’s usually located at the bottom of the microscope and comes in different magnification powers (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x). The objective lens is the most critical part of the microscope, as it determines the resolution and quality of the image.
- Low-power objective lenses (4x, 10x) are used for observing larger specimens.
- High-power objective lenses (40x, 100x) are used for observing smaller details.
3. Stage
The stage is a flat platform that holds the specimen in place. It’s usually adjustable, allowing you to move the specimen up, down, left, or right to center it under the objective lens. The stage may also have clips or a mechanical stage to secure the specimen.
🔩 Note: Always ensure the stage is clean and free of debris to prevent contamination.
4. Coarse and Fine Focus Knobs
The coarse and fine focus knobs are used to adjust the distance between the objective lens and the specimen. The coarse focus knob makes larger adjustments, while the fine focus knob makes smaller, more precise adjustments.
- Coarse focus knob: Use for initial focusing and making large adjustments.
- Fine focus knob: Use for making small adjustments to fine-tune the focus.
5. Illuminator (Light Source)
The illuminator, also known as the light source, provides the light necessary for observing the specimen. It’s usually located below the stage and can be adjusted to control the intensity of the light.
💡 Note: Always use a diffuser or condenser lens to reduce glare and improve image quality.
6. Arm and Base
The arm and base of the microscope provide stability and support for the entire instrument. The arm connects the microscope head to the base, while the base provides a sturdy foundation for the microscope.
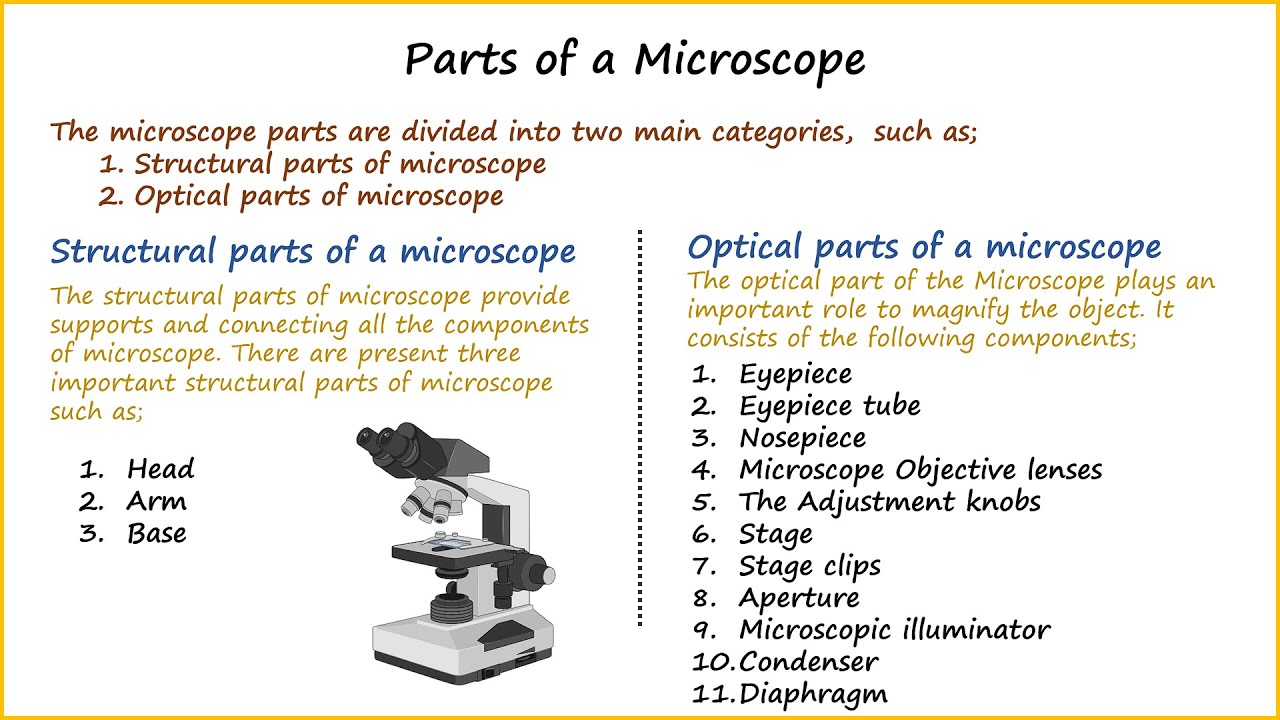
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Arm | Connects the microscope head to the base |
| Base | Provides a sturdy foundation for the microscope |
In conclusion, understanding the different parts of a microscope is essential for effective observation and research. By familiarizing yourself with the eyepiece, objective lens, stage, coarse and fine focus knobs, illuminator, and arm and base, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a skilled microscopist.
What is the purpose of the eyepiece in a microscope?
+The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, magnifies the image formed by the objective lens, allowing the user to observe the specimen being studied.
What is the difference between a coarse and fine focus knob?
+The coarse focus knob makes larger adjustments to the distance between the objective lens and the specimen, while the fine focus knob makes smaller, more precise adjustments.
Why is it important to use a diffuser or condenser lens with a microscope?
+A diffuser or condenser lens helps to reduce glare and improve image quality by controlling the intensity of the light and directing it towards the specimen.