Atomic Dimensions Worksheet
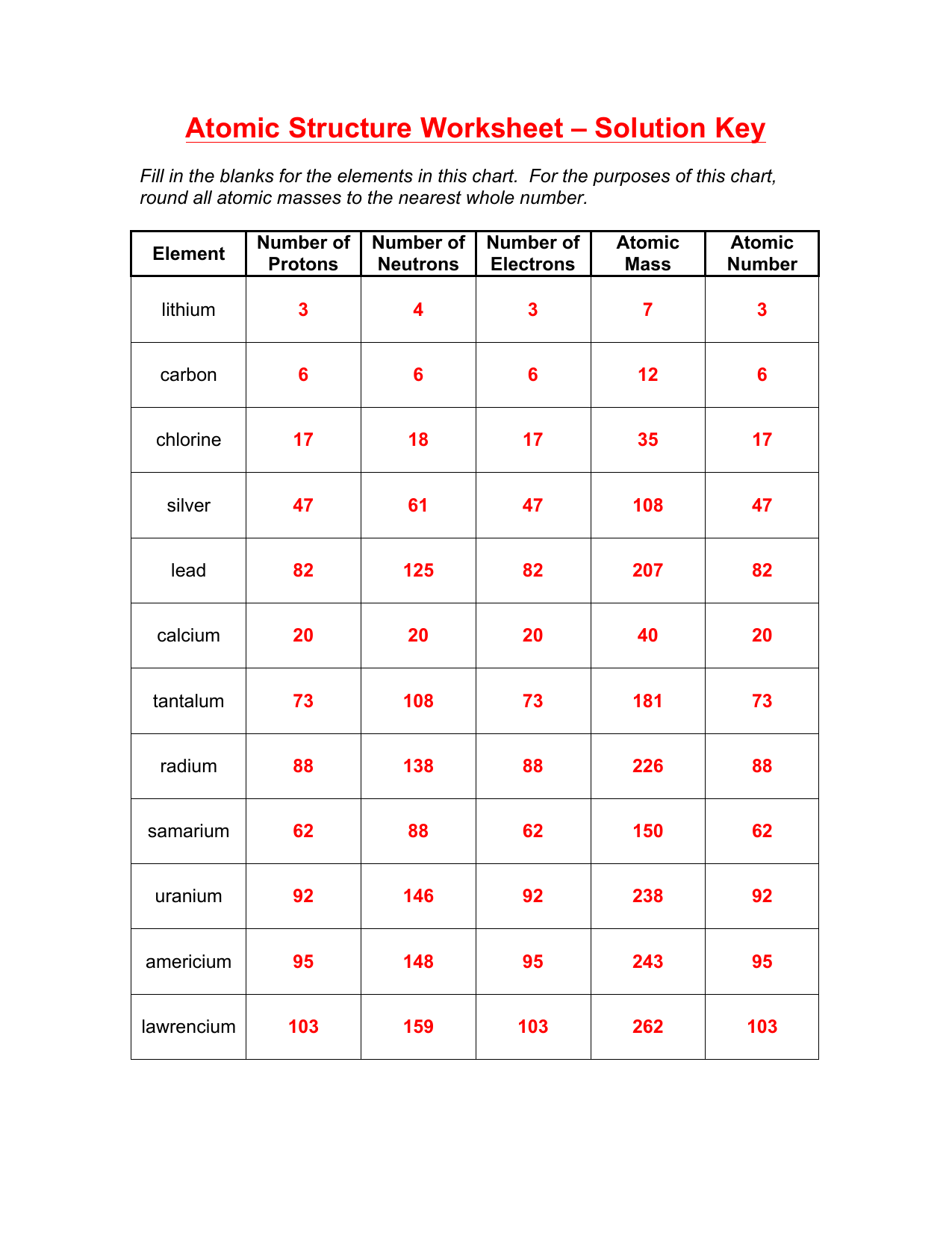
Atomic Dimensions: Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms are the fundamental constituents of matter, and their dimensions play a crucial role in determining the properties of elements and compounds. In this worksheet, we will delve into the world of atomic dimensions, exploring the different aspects of atomic size and its significance in chemistry.
What is Atomic Radius?
The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron in its ground state. It is a measure of the size of an atom, and it varies depending on the element. The atomic radius is typically measured in picometers (pm) or angstroms (Å).
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius
Several factors influence the atomic radius of an element:
• Atomic number: As the atomic number increases, the number of protons in the nucleus also increases, which leads to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. This results in a decrease in atomic radius. • Electron shielding: The presence of inner electrons can shield the outer electrons from the attractive force of the nucleus, leading to an increase in atomic radius. • Electronegativity: Elements with high electronegativity values tend to have smaller atomic radii due to the strong attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
Types of Atomic Radius
There are three types of atomic radius:
• Covalent radius: The covalent radius is the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the point where the electron cloud meets the electron cloud of another atom in a covalent bond. • Metallic radius: The metallic radius is the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the point where the electron cloud meets the electron cloud of another atom in a metallic bond. • Van der Waals radius: The van der Waals radius is the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the point where the electron cloud meets the electron cloud of another atom in a van der Waals bond.
Periodic Trends in Atomic Radius
The atomic radius of elements follows periodic trends:
• Down a group: The atomic radius increases down a group due to the addition of new energy levels, which increases the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons. • Across a period: The atomic radius decreases across a period due to the increase in atomic number, which leads to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons.
Importance of Atomic Radius in Chemistry
The atomic radius plays a crucial role in determining various chemical properties, such as:
• Reactivity: Elements with smaller atomic radii tend to be more reactive due to the stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons. • Electronegativity: Elements with smaller atomic radii tend to have higher electronegativity values. • Bonding: The atomic radius influences the type of bond formed between atoms.
🔍 Note: The atomic radius is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding its trends and factors is essential for predicting chemical properties and behavior.
Calculating Atomic Radius
The atomic radius can be calculated using the following formula:
r = (n × l) / (Z × k)
where:
• r = atomic radius • n = principal quantum number • l = azimuthal quantum number • Z = atomic number • k = constant
Table of Atomic Radii
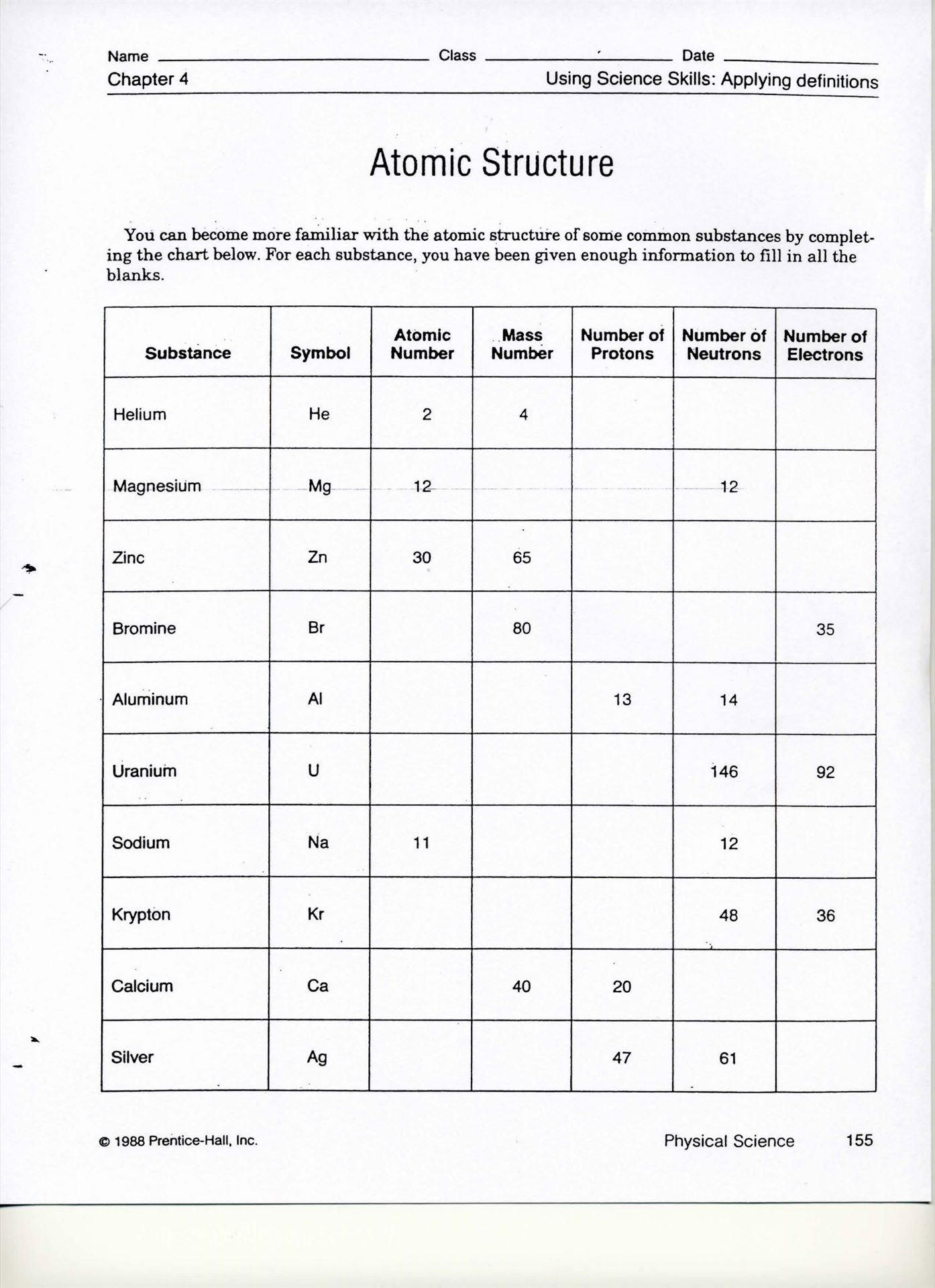
| Element | Atomic Radius (pm) |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 37 |
| Helium | 31 |
| Lithium | 152 |
| Beryllium | 112 |
| Boron | 87 |
📝 Note: The atomic radii values are approximate and may vary depending on the source.
In conclusion, atomic dimensions play a vital role in understanding the properties of elements and compounds. By grasping the concepts of atomic radius, its factors, and periodic trends, we can better appreciate the intricate world of chemistry.
What is the definition of atomic radius?
+The atomic radius is the distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outermost electron in its ground state.
What are the factors that affect atomic radius?
+The factors that affect atomic radius include atomic number, electron shielding, and electronegativity.
What are the types of atomic radius?
+The types of atomic radius include covalent radius, metallic radius, and van der Waals radius.
Related Terms:
- Atomic Structure Worksheet pdf
- Isotope practice worksheet
- Igcse atomic structure worksheet pdf
- Periodic table practice worksheet