Motion Graphs Worksheet Answers
Motion Graphs: Understanding the Basics
Motion graphs are a fundamental concept in physics that helps us visualize and analyze the motion of objects. In this article, we will delve into the world of motion graphs, exploring the different types, how to read them, and providing answers to common worksheet questions.
What is a Motion Graph?
A motion graph is a graphical representation of an object’s motion, typically displaying the object’s position, velocity, and acceleration over time. These graphs are essential tools in physics, allowing us to analyze and understand complex motion.
Types of Motion Graphs
There are three primary types of motion graphs:
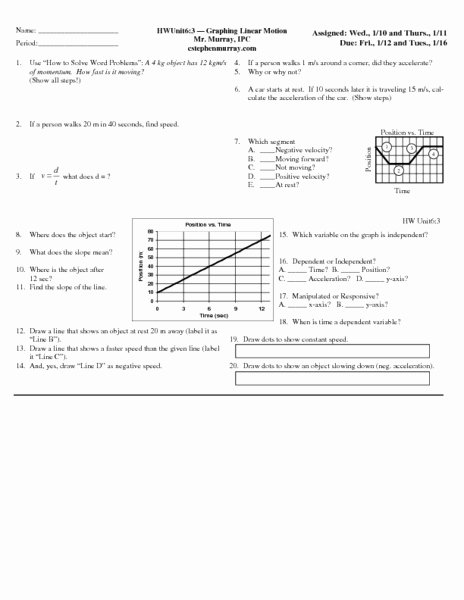
- Position-Time Graphs: These graphs display the object’s position over time, typically on the x-axis.
- Velocity-Time Graphs: These graphs display the object’s velocity over time, typically on the x-axis.
- Acceleration-Time Graphs: These graphs display the object’s acceleration over time, typically on the x-axis.
How to Read a Motion Graph
Reading a motion graph can seem intimidating, but with practice, you’ll become proficient in no time. Here are some essential tips:
- Position-Time Graphs:
- The x-axis represents time.
- The y-axis represents position.
- A straight line indicates constant velocity.
- A curved line indicates changing velocity.
- Velocity-Time Graphs:
- The x-axis represents time.
- The y-axis represents velocity.
- A straight line indicates constant acceleration.
- A curved line indicates changing acceleration.
- Acceleration-Time Graphs:
- The x-axis represents time.
- The y-axis represents acceleration.
- A straight line indicates constant jerk (change in acceleration).
- A curved line indicates changing jerk.
Motion Graphs Worksheet Answers
Now, let’s move on to some common worksheet questions and answers.
📝 Note: The following questions and answers are based on a fictional worksheet. Please adjust according to your specific worksheet.
Question 1: What does a straight line on a position-time graph indicate?
Answer: A straight line on a position-time graph indicates constant velocity.
Question 2: What does a curved line on a velocity-time graph indicate?
Answer: A curved line on a velocity-time graph indicates changing acceleration.
Question 3: What is the slope of a position-time graph?
Answer: The slope of a position-time graph represents the object’s velocity.
Question 4: What does the area under a velocity-time graph represent?
Answer: The area under a velocity-time graph represents the object’s displacement.
Question 5: What is the difference between a position-time graph and a velocity-time graph?
Answer: A position-time graph displays the object’s position over time, while a velocity-time graph displays the object’s velocity over time.
Motion Graphs Table
| Graph Type | X-Axis | Y-Axis | Straight Line | Curved Line |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position-Time | Time | Position | Constant Velocity | Changing Velocity |
| Velocity-Time | Time | Velocity | Constant Acceleration | Changing Acceleration |
| Acceleration-Time | Time | Acceleration | Constant Jerk | Changing Jerk |
📝 Note: This table summarizes the key characteristics of each graph type. Use it as a reference when working with motion graphs.
In conclusion, motion graphs are powerful tools in physics that help us visualize and analyze complex motion. By understanding the different types of motion graphs and how to read them, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle a wide range of problems. Remember to practice regularly, and don’t hesitate to reach out if you have any questions or need further clarification.
What is the main purpose of a motion graph?
+The main purpose of a motion graph is to visualize and analyze an object’s motion, displaying its position, velocity, and acceleration over time.
What does a straight line on a velocity-time graph indicate?
+A straight line on a velocity-time graph indicates constant acceleration.
What is the slope of a velocity-time graph?
+The slope of a velocity-time graph represents the object’s acceleration.