Heating Curve Worksheet Made Easy for Chemistry Students
Understanding Heating Curves: A Comprehensive Guide for Chemistry Students
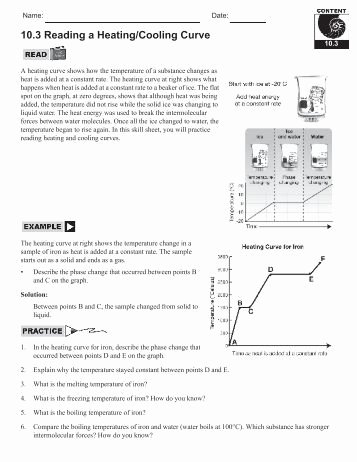
The heating curve is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps students understand the relationship between temperature and heat energy. It’s a graphical representation of the temperature of a substance as it absorbs heat energy. In this article, we’ll break down the heating curve worksheet and provide a step-by-step guide to help chemistry students master this concept.
What is a Heating Curve?
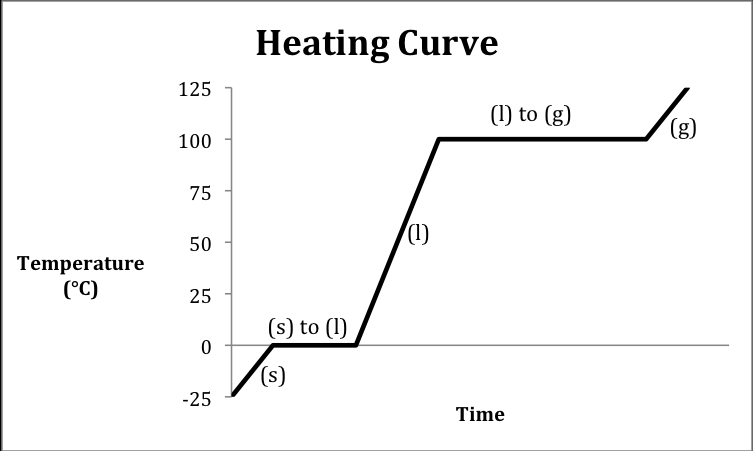
A heating curve is a graph that shows the temperature of a substance as it absorbs heat energy. The curve is typically plotted with temperature on the y-axis and heat energy on the x-axis. The heating curve is divided into several segments, each representing a different phase of the substance, such as solid, liquid, or gas.
Components of a Heating Curve
A typical heating curve consists of the following components:
- Solid-liquid equilibrium: This is the temperature range where the substance changes from solid to liquid.
- Liquid-solid equilibrium: This is the temperature range where the substance changes from liquid to solid.
- Boiling point: This is the temperature at which the substance changes from liquid to gas.
- Melting point: This is the temperature at which the substance changes from solid to liquid.
Interpreting a Heating Curve
Interpreting a heating curve requires understanding the different segments of the curve. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you interpret a heating curve:
- Identify the phase of the substance: Look at the temperature range on the y-axis and determine the phase of the substance.
- Determine the melting point: Identify the temperature at which the substance changes from solid to liquid.
- Determine the boiling point: Identify the temperature at which the substance changes from liquid to gas.
- Calculate the heat of fusion: Calculate the heat energy required to change the substance from solid to liquid.
- Calculate the heat of vaporization: Calculate the heat energy required to change the substance from liquid to gas.
Heating Curve Worksheet
Here’s a sample heating curve worksheet to help you practice interpreting heating curves:
| Substance | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) | Heat of Fusion (kJ/mol) | Heat of Vaporization (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 0 | 100 | 6.01 | 40.66 |
| Ethanol | -114 | 78 | 5.02 | 26.7 |
| Methanol | -98 | 65 | 3.16 | 35.21 |
Using the data provided, answer the following questions:
- What is the melting point of water?
- What is the boiling point of ethanol?
- Calculate the heat of fusion for methanol.
- Calculate the heat of vaporization for water.
📝 Note: Use the data provided in the table to answer the questions.
Tips for Solving Heating Curve Problems
Here are some tips to help you solve heating curve problems:
- Read the problem carefully: Read the problem carefully and identify the key information provided.
- Use the data provided: Use the data provided in the problem to answer the questions.
- Check your units: Make sure to check your units and ensure that they are consistent.
- Practice, practice, practice: Practice solving heating curve problems to improve your understanding of the concept.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Here are some common mistakes to avoid when solving heating curve problems:
- Incorrectly identifying the phase of the substance: Make sure to correctly identify the phase of the substance.
- Miscalculating the heat of fusion or vaporization: Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Not checking units: Make sure to check your units and ensure that they are consistent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding heating curves is essential for chemistry students. By following the steps outlined in this article and practicing with sample problems, you’ll be able to master the concept of heating curves. Remember to read problems carefully, use data provided, check units, and practice regularly to improve your understanding of heating curves.
What is the purpose of a heating curve?
+The purpose of a heating curve is to show the relationship between temperature and heat energy, allowing us to understand the different phases of a substance.
How do I calculate the heat of fusion?
+The heat of fusion is calculated by multiplying the mass of the substance by the latent heat of fusion.
What is the difference between the melting point and boiling point?
+The melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid, while the boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes from liquid to gas.