Mastering EKGs: Practice Worksheets with Answers
Mastering EKGs: Practice Worksheets with Answers
Electrocardiograms (EKGs or ECGs) are a crucial diagnostic tool in cardiology, providing valuable insights into the heart’s electrical activity. Mastering EKG interpretation is essential for healthcare professionals, particularly those working in emergency medicine, critical care, and cardiology. This guide provides practice worksheets with answers to help you improve your EKG interpretation skills.
Understanding the Basics of EKGs
Before diving into practice worksheets, let’s review the basic components of an EKG:
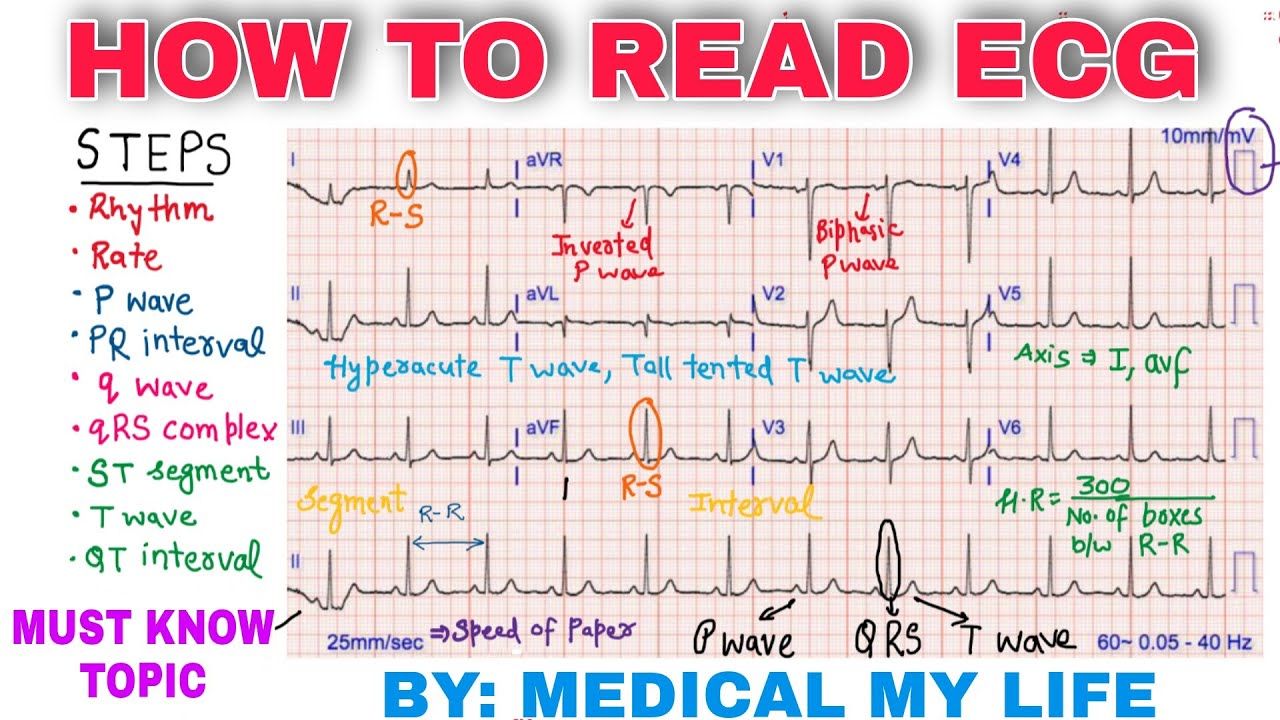
- P wave: Represents the depolarization of the atria
- QRS complex: Represents the depolarization of the ventricles
- T wave: Represents the repolarization of the ventricles
- PR interval: Measures the time between the onset of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex
- QT interval: Measures the time between the start of the QRS complex and the end of the T wave
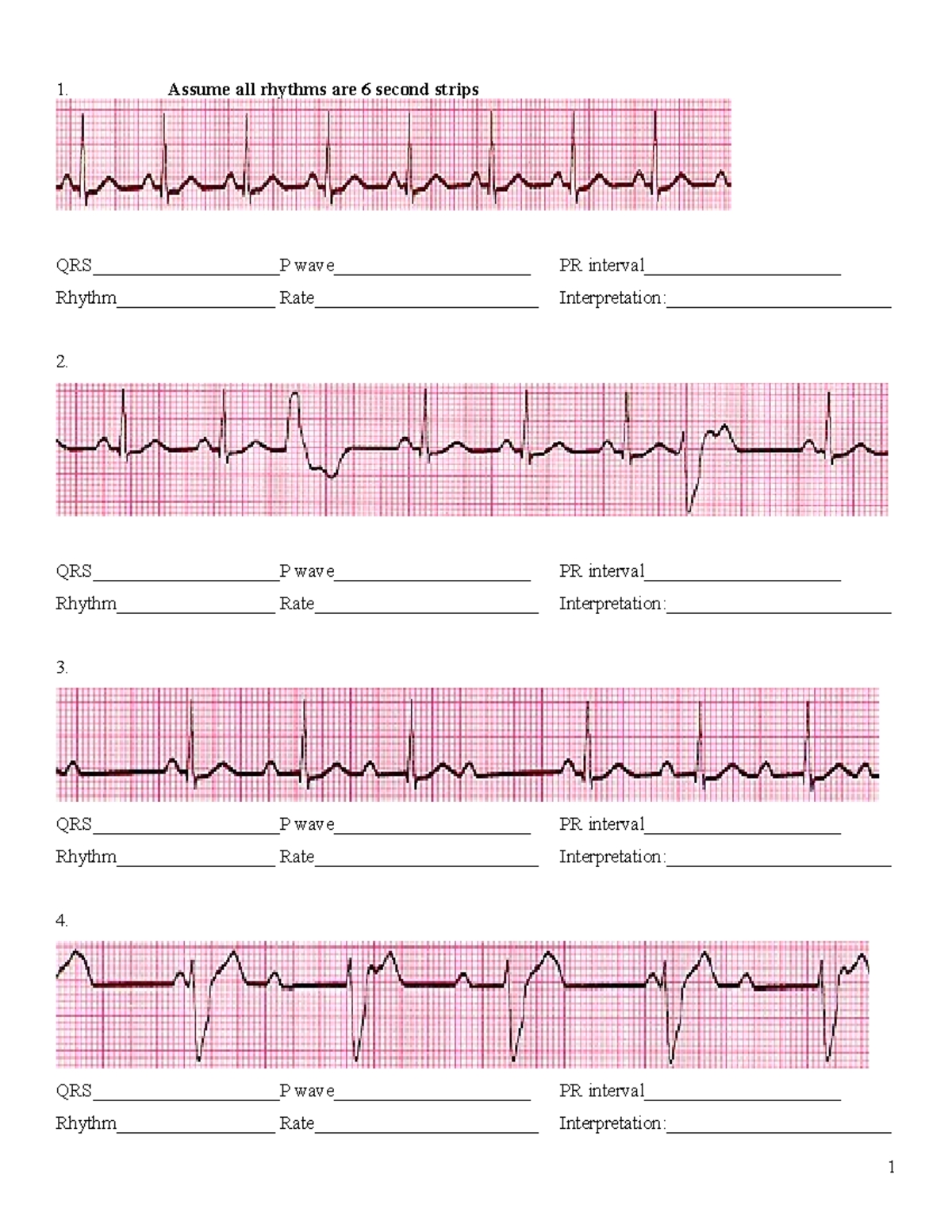
Practice Worksheet 1: Identifying EKG Components
Identify the P wave, QRS complex, T wave, PR interval, and QT interval in the following EKG tracing:
P wave | QRS complex | T wave
-------|--------------|--------
PR interval | QT interval
Answers:
| Component | Location |
|---|---|
| P wave | Small bump before the QRS complex |
| QRS complex | Large bump after the P wave |
| T wave | Small bump after the QRS complex |
| PR interval | Measures the time between the P wave and QRS complex |
| QT interval | Measures the time between the QRS complex and T wave |
Practice Worksheet 2: Interpreting EKG Rhythms
Interpret the following EKG rhythms:
- Sinus rhythm: A normal heart rhythm with a rate of 60-100 beats per minute (bpm)
- Atrial fibrillation: A rapid, irregular heart rhythm with a rate of 100-180 bpm
- Ventricular tachycardia: A rapid, regular heart rhythm with a rate of 100-250 bpm
Rhythm | Rate (bpm) | Interpretation
-------|--------------|---------------
1 | 80 | _______________________
2 | 120 | _______________________
3 | 180 | _______________________
Answers:
| Rhythm | Rate (bpm) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | Sinus rhythm |
| 2 | 120 | Atrial fibrillation |
| 3 | 180 | Ventricular tachycardia |
Practice Worksheet 3: Identifying EKG Abnormalities
Identify the EKG abnormalities in the following tracings:
- Left bundle branch block: A widening of the QRS complex with a leftward shift
- Right bundle branch block: A widening of the QRS complex with a rightward shift
- ST segment elevation: An elevation of the ST segment above the baseline
Abnormality | Location | Description
------------|------------|-------------
1 | QRS complex | _______________________
2 | ST segment | _______________________
3 | P wave | _______________________
Answers:
| Abnormality | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | QRS complex | Left bundle branch block |
| 2 | ST segment | ST segment elevation |
| 3 | P wave | Right bundle branch block |
💡 Note: These practice worksheets are designed to help you develop your EKG interpretation skills. However, it's essential to remember that EKG interpretation requires a comprehensive understanding of cardiac anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology.
What is the purpose of an EKG?
+An EKG is used to diagnose and monitor various heart conditions, including arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, and cardiac chamber enlargement.
What is the normal range for an EKG?
+The normal range for an EKG varies depending on the parameter being measured. However, a normal heart rate is typically between 60-100 beats per minute.
Can EKGs detect all heart conditions?
+No, EKGs are not foolproof and may not detect all heart conditions. Other diagnostic tests, such as echocardiograms and cardiac stress tests, may be necessary to confirm a diagnosis.
In conclusion, mastering EKG interpretation is a complex process that requires practice and dedication. These practice worksheets are designed to help you develop your skills and improve your ability to interpret EKGs accurately. Remember to always consult with a qualified healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns about EKG interpretation.