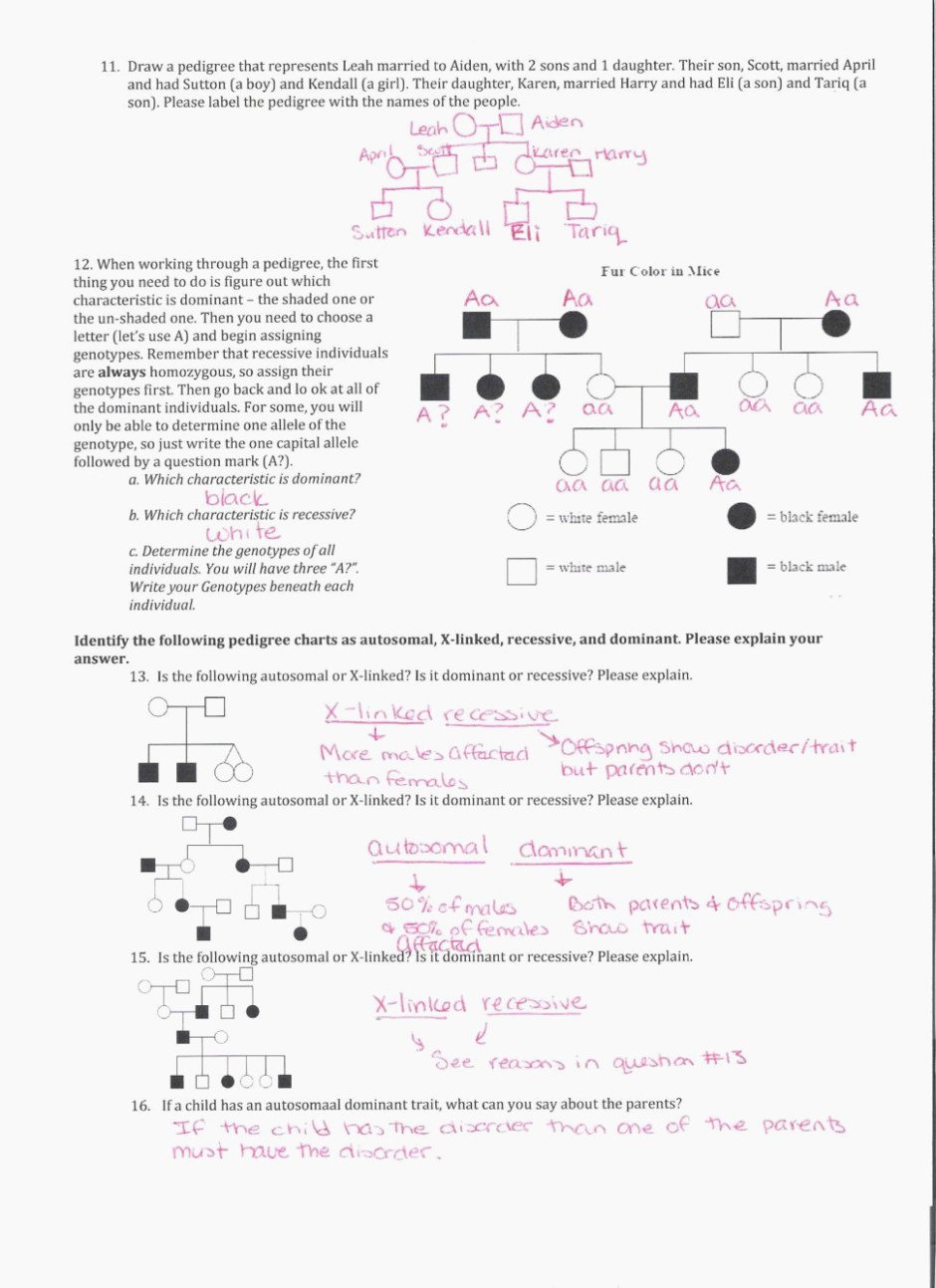
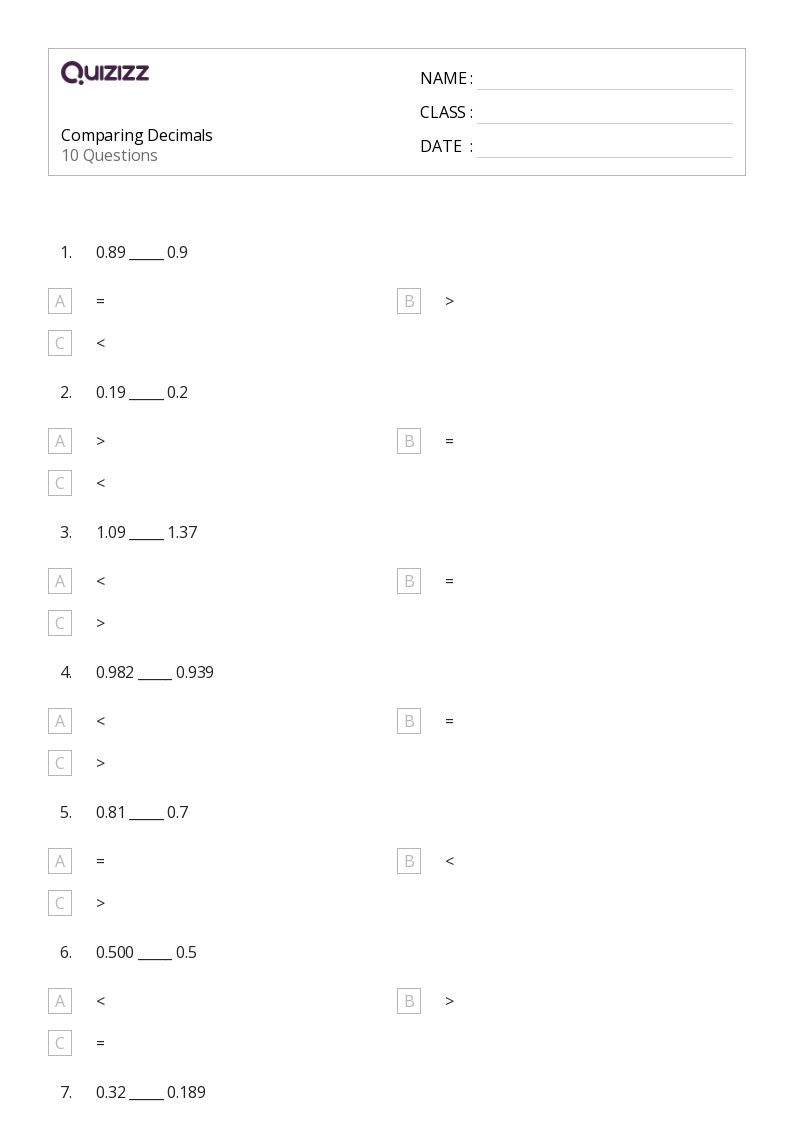
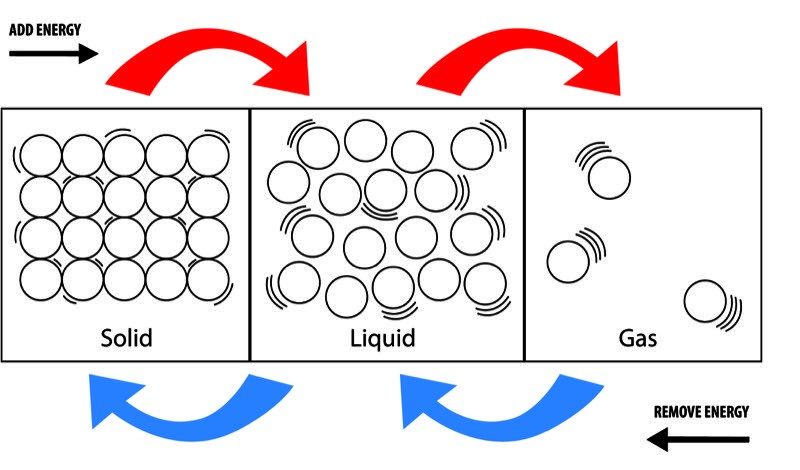
5 Simple Present Exercises to Improve Your Grammar

Understanding the Simple Present Tense
The simple present tense is one of the most fundamental grammatical structures in English, used to describe habits, routines, and general truths. It is essential for clear communication in everyday conversations, writing, and even academic or professional contexts. Mastering the simple present tense can significantly improve your English grammar and comprehension. Here are five simple present exercises to help you enhance your skills:
Exercise 1: Fill in the Blanks
Complete the following sentences using the correct form of the verb in parentheses in the simple present tense:
- I ____________________ (go) to the gym every morning.
- My sister ____________________ (study) English at university.
- We ____________________ (eat) breakfast together as a family.
- They ____________________ (not/be) happy with the new policy.
- It ____________________ (snow) in winter in many parts of the world.
[📝] Note: Pay attention to the subject-verb agreement, ensuring the verb matches the singular or plural form of the subject.
Exercise 2: Sentence Completion
Complete the following sentences with the correct simple present tense form of the verb provided:
- If I ____________________ (win) the lottery, I would buy a house.
- If it ____________________ (rain), we will have to cancel the picnic.
- If she ____________________ (know) the answer, she would tell us.
- If they ____________________ (have) enough money, they would travel the world.
- If he ____________________ (listen) to her advice, he wouldn’t be in trouble.
[📝] Note: Focus on using the correct form of the verb in the simple present tense for hypothetical or uncertain situations.
Exercise 3: Identifying Tense Errors
Identify and correct the errors in tense usage in the following sentences:
- I going to the movies tonight. (Error in verb form)
- She studies English in school, but yesterday she was studying. (Incorrect tense usage)
- They have eaten breakfast already, but this morning they eat. (Incorrect tense usage)
- We will go to the park, but now we going. (Error in verb form)
- It snows every winter, but last winter it snow. (Incorrect tense usage)
Exercise 4: Sentence Transformation
Transform the following sentences into the simple present tense:
- By next year, I will have graduated. (Future perfect tense)
- They were playing soccer when I arrived. (Past continuous tense)
- If I had more money, I would travel. (Conditional tense)
- She has been studying English for three years. (Present perfect continuous tense)
- We are not going to the concert tonight. (Present continuous tense)
[📝] Note: Pay attention to changing the verb form, auxiliary verbs, and any necessary rephrasing to maintain the original meaning.
Exercise 5: Writing Short Paragraphs
Write short paragraphs (about 100-150 words) describing your daily routine, habits, or general truths about the world, using the simple present tense throughout:
- Describe what you typically do on a Sunday morning.
- Explain the process of how a specific type of plant grows.
- Discuss the daily routine of a fictional character, including what they eat, where they go, and how they spend their time.
[📝] Note: Use a variety of verb forms in the simple present tense and ensure correct subject-verb agreement throughout your paragraphs.
By completing these exercises, you will significantly improve your understanding and usage of the simple present tense, enhancing your English grammar skills. Practice regularly to become more comfortable and confident in your ability to communicate effectively.
What is the simple present tense used for?
+The simple present tense is used to describe habits, routines, and general truths about the world.
How do I form the simple present tense?
+The simple present tense is formed using the base form of the verb for singular subjects (I, you, we, they) and adding -s or -es for plural subjects (he, she, it).
What are some common mistakes in using the simple present tense?
+Common mistakes include incorrect verb form usage, subject-verb agreement errors, and using the wrong tense for the context.