5 Ways to Master Solid Liquid Gas
Understanding the Basics of Solid, Liquid, and Gas
The three main states of matter - solid, liquid, and gas - are fundamental concepts in physics and chemistry. Mastering these concepts is crucial for understanding various natural phenomena and industrial processes. In this article, we will explore five ways to deepen your understanding of solid, liquid, and gas, making you a master of these essential states of matter.
1. Visualize the Molecular Structure
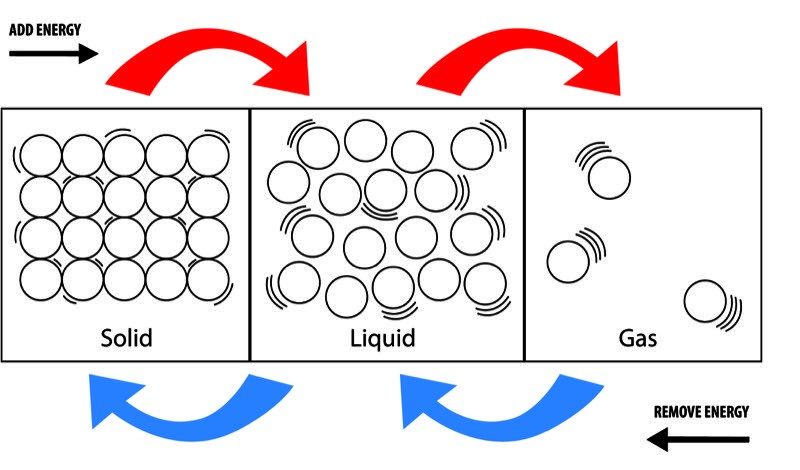
To grasp the differences between solid, liquid, and gas, it’s essential to understand the molecular structure of each state. Imagine a jar of marbles, where each marble represents a molecule.
- In a solid, the marbles are closely packed and have a fixed position in space. The molecules are arranged in a regular, three-dimensional pattern, giving the solid its shape and volume.
- In a liquid, the marbles are close together but are free to move past each other. The molecules are not rigidly fixed, allowing the liquid to flow and take the shape of its container.
- In a gas, the marbles are widely spaced and are free to move in any direction. The molecules are not fixed and can spread out, filling their container.
Visualizing the molecular structure helps you understand the unique properties of each state, such as the rigidity of solids, the fluidity of liquids, and the expansive nature of gases.
2. Experiment with Phase Transitions
Phase transitions occur when a substance changes from one state of matter to another, such as from solid to liquid (melting) or from liquid to gas (vaporization). Conduct simple experiments to observe phase transitions:
- Melting: Place an ice cube in a bowl and observe how it changes from a solid to a liquid as it absorbs heat.
- Vaporization: Boil water in a pot and watch as the liquid turns into steam (a gas).
- Condensation: Hold a cold glass over the steam and observe how the gas changes back into a liquid.
These experiments help you understand the conditions necessary for phase transitions and the energy changes involved.
3. Understand the Role of Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive and repulsive forces between molecules that determine the state of matter. Learn about the different types of intermolecular forces:
- Hydrogen bonding: A strong force between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine).
- Dipole-dipole forces: Forces between molecules with a permanent electric dipole moment.
- London dispersion forces: Weak forces between non-polar molecules.
Understanding intermolecular forces helps you explain the physical properties of substances, such as their melting and boiling points, viscosity, and solubility.
4. Learn about Real-World Applications
The concepts of solid, liquid, and gas have numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Materials science: Understanding the properties of solids, liquids, and gases is crucial for developing new materials with specific characteristics, such as strength, conductivity, or optical properties.
- Chemical engineering: Knowledge of phase transitions and intermolecular forces is essential for designing and optimizing chemical processes, such as distillation, crystallization, and extraction.
- Environmental science: Understanding the behavior of gases, liquids, and solids is vital for addressing environmental issues, such as climate change, air and water pollution, and waste management.
Exploring real-world applications helps you appreciate the significance of solid, liquid, and gas in everyday life.
5. Practice Problem-Solving
Practice solving problems related to solid, liquid, and gas to reinforce your understanding:
- Calculate the density of a substance: Use the formula density = mass / volume to calculate the density of a solid, liquid, or gas.
- Determine the state of matter: Given a set of conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.), determine whether a substance is a solid, liquid, or gas.
- Predict phase transitions: Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and phase transitions to predict how a substance will behave under different conditions.
Regular practice helps solidify your understanding of solid, liquid, and gas, making you more confident and proficient in your knowledge.
🤔 Note: Mastering solid, liquid, and gas requires a combination of theoretical knowledge, practical experience, and problem-solving skills. By following these five ways, you'll be well on your way to becoming a master of these essential states of matter.
In conclusion, mastering solid, liquid, and gas requires a deep understanding of the molecular structure, phase transitions, intermolecular forces, real-world applications, and problem-solving skills. By following these five ways, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental concepts and be able to apply them in various contexts.
What is the difference between a solid, liquid, and gas?
+A solid has a fixed shape and volume, a liquid takes the shape of its container and has a fixed volume, and a gas has neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume.
What are intermolecular forces?
+Intermolecular forces are the attractive and repulsive forces between molecules that determine the state of matter.
What is the purpose of understanding solid, liquid, and gas?
+Understanding solid, liquid, and gas is essential for understanding various natural phenomena and industrial processes, and has numerous practical applications in fields such as materials science, chemical engineering, and environmental science.
Related Terms:
- Materi
- Tabel Periodik
- Kimia
- Air
- Wujud materi
- solid, liquid gas worksheet pdf