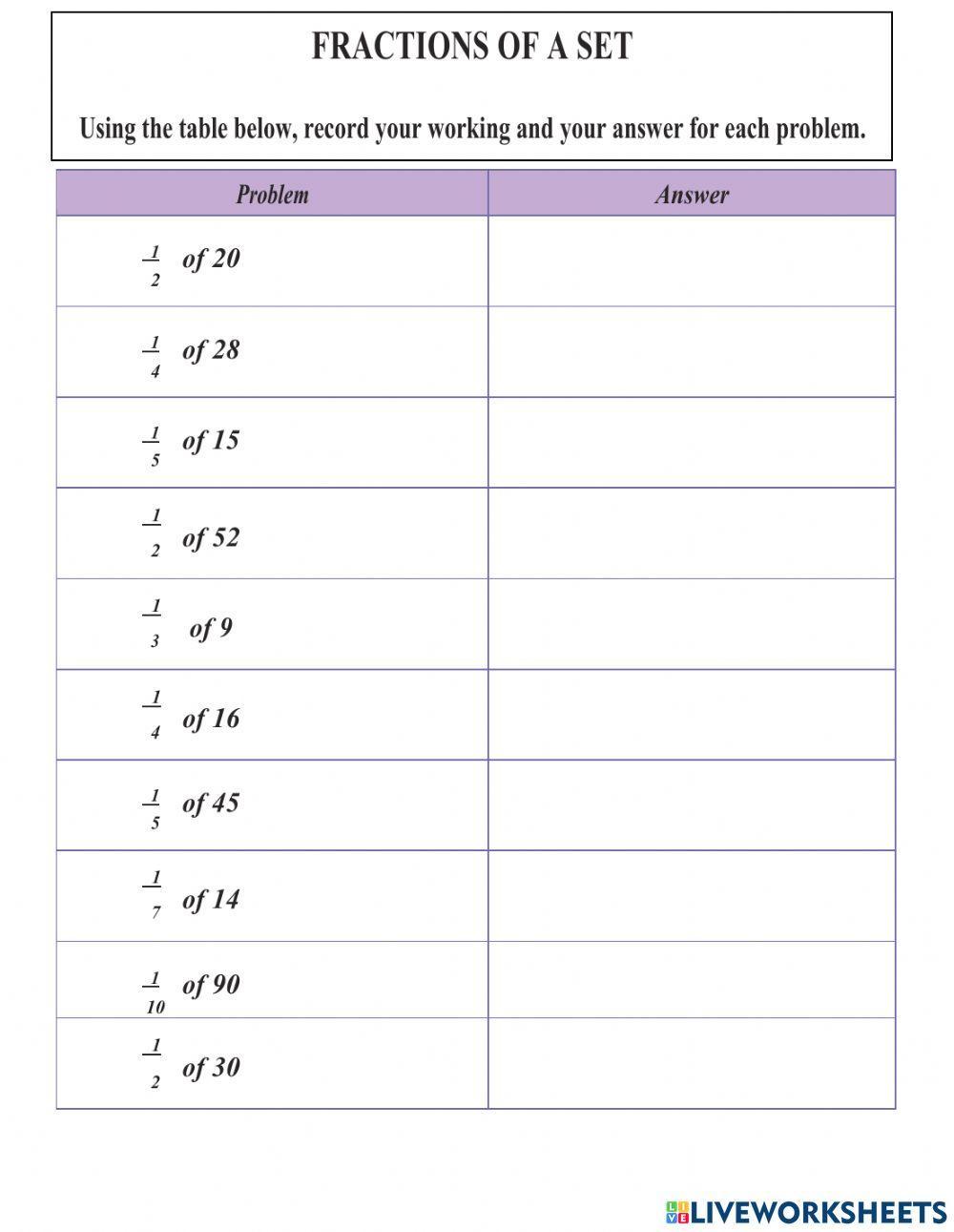
Collision Theory Worksheet: Mastering Chemical Reactions

Understanding Collision Theory
Collision theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how chemical reactions occur. It states that atoms or molecules must collide with each other in order to react. However, not all collisions lead to a reaction. In this worksheet, we will explore the key principles of collision theory and how it applies to chemical reactions.
Key Principles of Collision Theory
There are three main principles of collision theory:
- Collision Frequency: The frequency at which atoms or molecules collide with each other. This depends on the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, and the surface area of the reactants.
- Collision Energy: The energy required for a collision to be effective. This depends on the activation energy of the reaction, which is the minimum energy required for the reaction to occur.
- Orientation: The orientation of the atoms or molecules during a collision. The reactants must be oriented in a specific way for the reaction to occur.
Factors Affecting Collision Frequency
Several factors can affect the collision frequency:
- Concentration: Increasing the concentration of reactants increases the collision frequency.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the reactants, leading to more frequent collisions.
- Surface Area: Increasing the surface area of the reactants increases the chance of collisions.
Factors Affecting Collision Energy
Several factors can affect the collision energy:
- Activation Energy: The minimum energy required for the reaction to occur. If the collision energy is less than the activation energy, the reaction will not occur.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature increases the kinetic energy of the reactants, making it more likely for collisions to have sufficient energy.
Effective Collisions
Not all collisions are effective. For a collision to be effective, the following conditions must be met:
- The collision energy must be greater than or equal to the activation energy.
- The reactants must be oriented in a specific way.
- The collision must occur at a specific point on the reactant molecules.
Calculating Collision Frequency
Collision frequency can be calculated using the following formula:
Collision Frequency = (Number of Collisions per Unit Time) / (Number of Molecules per Unit Volume)
This can be represented mathematically as:
Z = (N / V) * (π * d^2 * v)
Where:
- Z is the collision frequency
- N is the number of molecules per unit volume
- V is the volume of the reaction vessel
- d is the diameter of the molecules
- v is the velocity of the molecules
Example Problems
- Calculate the collision frequency of a gas at room temperature (25°C) and atmospheric pressure (1 atm) if the number of molecules per unit volume is 2.5 x 10^25 molecules/m^3.
Solution:
Z = (2.5 x 10^25 molecules/m^3) * (π * (2 x 10^-10 m)^2 * (500 m/s))
Z = 1.57 x 10^31 collisions/m^3/s
- A reaction requires an activation energy of 50 kJ/mol. If the collision energy is 40 kJ/mol, will the reaction occur?
Solution:
No, the collision energy is less than the activation energy, so the reaction will not occur.
🚨 Note: The activation energy is the minimum energy required for the reaction to occur. If the collision energy is less than the activation energy, the reaction will not occur.
Real-World Applications
Collision theory has many real-world applications:
- Catalysis: Catalysts work by increasing the collision frequency or reducing the activation energy, making reactions occur faster and more efficiently.
- Chemical Synthesis: Understanding collision theory is crucial in designing chemical synthesis reactions, where reactants must collide with each other in a specific way to form the desired product.
- Materials Science: Collision theory is used to design materials with specific properties, such as conductivity or strength.
What is collision theory?
+Collision theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how chemical reactions occur. It states that atoms or molecules must collide with each other in order to react.
What are the key principles of collision theory?
+The key principles of collision theory are collision frequency, collision energy, and orientation.
What factors affect collision frequency?
+Concentration, temperature, and surface area affect collision frequency.
In conclusion, collision theory is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how chemical reactions occur. Understanding the key principles of collision theory, including collision frequency, collision energy, and orientation, is crucial in designing chemical synthesis reactions and predicting the outcome of reactions. By applying collision theory, scientists can design more efficient reactions and materials with specific properties.
Related Terms:
- Collision theory Worksheet answer Key
- Collision theory Worksheet Answers PDF
- Collision drive reactions Worksheet answers