Evolution Evidence Worksheet Answers
Understanding the Evidence for Evolution
Evolution is the scientifically supported theory that all species of life have developed from a common ancestor through the process of variation, mutation, genetic drift, and natural selection. The evidence for evolution is vast and comes from multiple fields of study, including biology, genetics, paleontology, and geology.
Biological Evidence
One of the key pieces of evidence for evolution is the presence of homologous structures in different species. Homologous structures are body parts that are similar in different species, indicating a common ancestor. For example:
- The forelimbs of vertebrates (such as humans, birds, and whales) have a similar bone structure, despite being used for different purposes (e.g., walking, flying, swimming).
- The eye structure of octopuses and humans is similar, despite being in different phyla.
🔍 Note: Homologous structures provide strong evidence for evolution, as they suggest that different species share a common ancestor.
Genetic Evidence
Genetic evidence also supports evolution. The genetic code is the set of rules that dictates how DNA is translated into proteins. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that it is similar in all living organisms. This suggests that all life on Earth shares a common ancestor.
- The genetic code is similar in humans, chimpanzees, and bacteria, indicating a shared ancestry.
- DNA sequencing has revealed that humans and chimpanzees share nearly 99% of their DNA, confirming their close evolutionary relationship.
Paleontological Evidence
Fossil records provide significant evidence for evolution. Fossils of ancient organisms show a clear pattern of gradual changes over time, indicating the evolution of new species.
- Transitional fossils, such as Tiktaalik and Archaeopteryx, exhibit characteristics of both the ancestral and descendant groups, providing evidence for the gradual evolution of new species.
- The fossil record shows a clear pattern of gradual changes in life forms over time, with older fossils showing more primitive characteristics and newer fossils showing more advanced characteristics.
Geological Evidence
Geological evidence also supports evolution. The Earth’s geology provides a record of the history of life on Earth, with older rocks containing fossils of more primitive organisms and newer rocks containing fossils of more advanced organisms.
- Rock layers show a clear pattern of layering, with older rocks buried beneath newer rocks, indicating the gradual accumulation of sediments over time.
- Geologic time scale provides a framework for understanding the history of life on Earth, with different eons and eras corresponding to different stages in the evolution of life.
Observational Evidence
Observational evidence for evolution comes from studies of natural populations and experiments.
- Natural selection has been observed in action, with populations adapting to changing environments over time.
- Artificial selection experiments have demonstrated the power of selection in shaping the evolution of populations.
Comparative Anatomy Evidence
Comparative anatomy provides evidence for evolution by showing that different species share similar body structures, despite differences in their function.
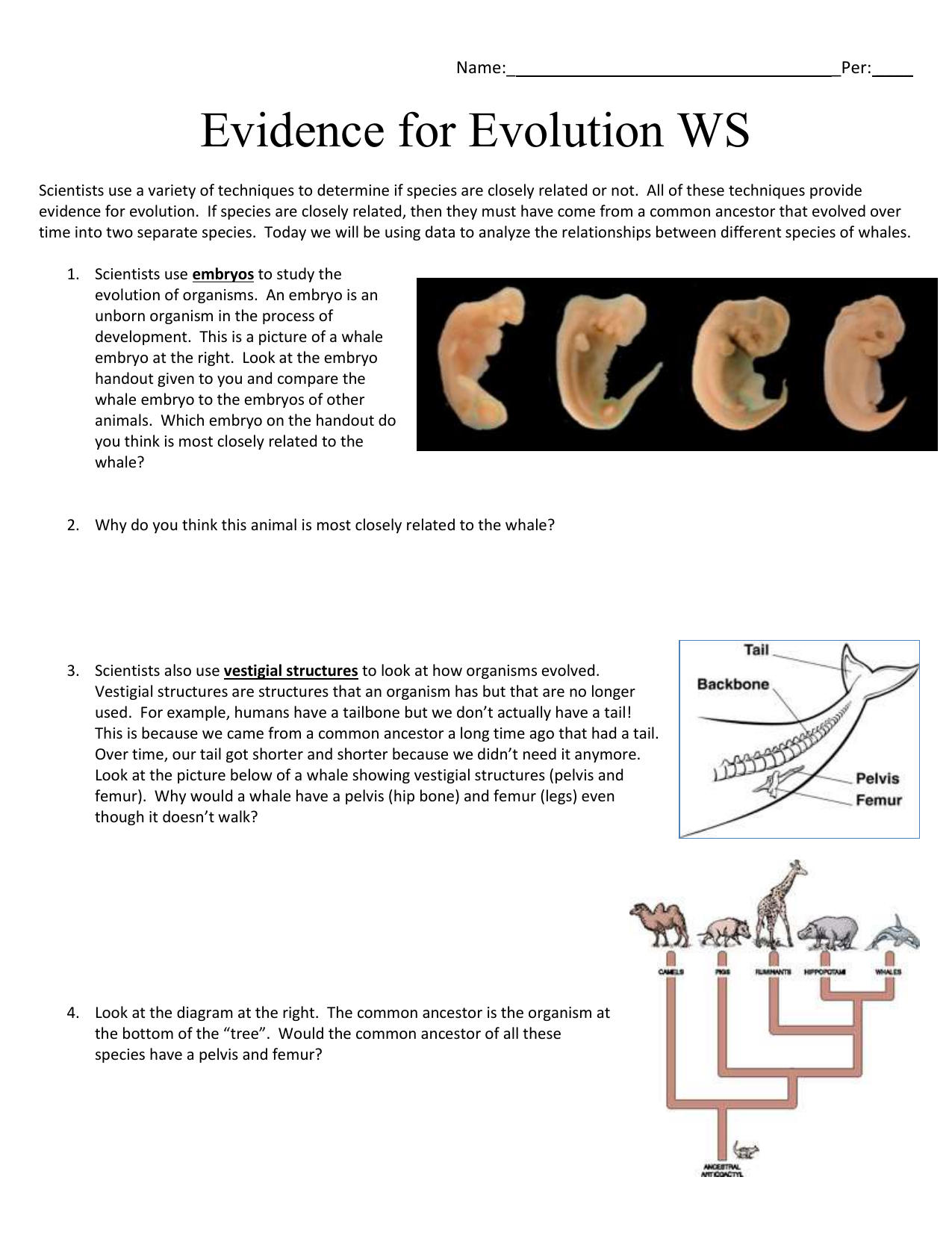
- Vestigial structures, such as the human appendix and the whale pelvis, are remnants of ancestral traits that have lost their original function.
- Embryonic development shows that different species share similar embryonic structures, indicating a shared ancestry.
🔍 Note: Comparative anatomy provides strong evidence for evolution, as it shows that different species share similar body structures, despite differences in their function.
What is the main evidence for evolution?
+The main evidence for evolution comes from multiple fields of study, including biology, genetics, paleontology, and geology. This includes homologous structures, genetic code, fossil records, geological evidence, observational evidence, and comparative anatomy.
What is the genetic code?
+The genetic code is the set of rules that dictates how DNA is translated into proteins. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that it is similar in all living organisms.
What are transitional fossils?
+Transitional fossils are fossils of ancient organisms that exhibit characteristics of both the ancestral and descendant groups, providing evidence for the gradual evolution of new species.
The evidence for evolution is overwhelming and comes from multiple fields of study. By understanding the different types of evidence, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the scientific theory of evolution and how it explains the diversity of life on Earth.
Related Terms:
- Evidence for evolution Worksheet PDF
- Evidence of evolution activity