Long Division Step By Step Worksheet
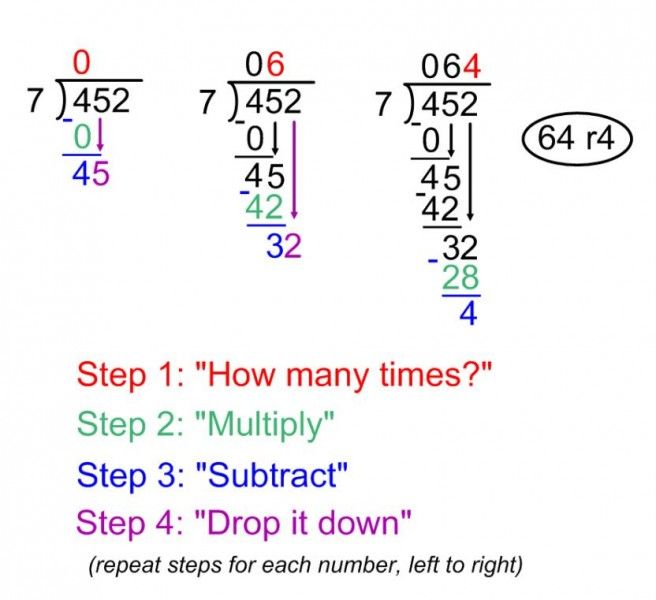
Mastering Long Division: A Step-by-Step Guide
Long division is a fundamental concept in mathematics that can seem intimidating at first, but with practice and patience, it can become second nature. In this article, we will break down the long division process into manageable steps, providing a comprehensive guide to help you master this essential math skill.
Understanding the Long Division Format
Before we dive into the step-by-step process, let’s take a look at the long division format:
| Dividend (Number being divided) | ÷ | Divisor (Number by which we are dividing) |
| Quotient (Result of division) | Remainder (Amount left over) |
Step 1: Write the Problem
Start by writing the dividend (the number being divided) on top of a line, and the divisor (the number by which we are dividing) below it.
Step 2: Divide the First Digit
Divide the first digit of the dividend by the divisor, and write the result below the line.
📝 Note: If the first digit of the dividend is smaller than the divisor, bring down the next digit and repeat the process.
Step 3: Multiply and Subtract
Multiply the result from Step 2 by the divisor, and subtract the product from the dividend.
Step 4: Bring Down the Next Digit
Bring down the next digit of the dividend, and repeat the process from Step 2.
Step 5: Repeat Steps 2-4
Continue repeating Steps 2-4 until you have used up all the digits of the dividend.
Step 6: Write the Remainder
The final result is the quotient (result of division), and the remainder (amount left over).
Example Problem
Let’s work through an example problem to illustrate the long division process:
Problem: 432 ÷ 12 =?
Step 1: Write the problem
| 432 | ÷ | 12 |
| Quotient | Remainder |
Step 2: Divide the first digit
4 ÷ 12 = 0 with a remainder of 4
Step 3: Multiply and subtract
0 × 12 = 0 4 - 0 = 4
Step 4: Bring down the next digit
Bring down the next digit (3)
43 ÷ 12 = 3 with a remainder of 7
Step 5: Repeat Steps 2-4
Multiply and subtract
3 × 12 = 36 43 - 36 = 7
Bring down the next digit (2)
72 ÷ 12 = 6 with a remainder of 0
Step 6: Write the remainder
The final result is:
Quotient: 36 Remainder: 0
Therefore, 432 ÷ 12 = 36.
Tips and Tricks
- Always check your work by multiplying the quotient by the divisor and adding the remainder.
- Use a consistent method for writing the problem, such as writing the dividend on top of a line and the divisor below it.
- Practice, practice, practice! The more you practice long division, the more comfortable you will become with the process.
What is the purpose of long division?
+Long division is used to divide a large number (dividend) by a smaller number (divisor) to find the quotient and remainder.
Why is long division important?
+Long division is an essential math skill that is used in a variety of real-world applications, such as finance, science, and engineering.
How can I improve my long division skills?
+Practice regularly, use online resources or worksheets, and watch video tutorials to improve your long division skills.
In conclusion, long division is a valuable math skill that can be mastered with practice and patience. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can improve your understanding of long division and become more confident in your math abilities.
Related Terms:
- Long division with boxes worksheet
- Long division steps printable free
- Long division worksheets PDF
- Step by step division worksheets
- Long division worksheets grade 6