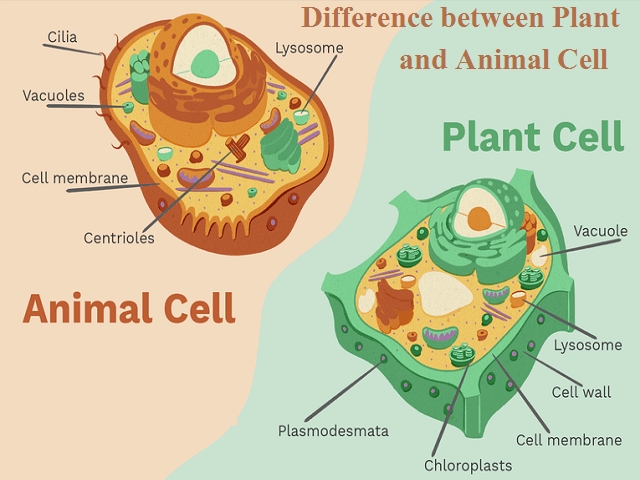
6 Essential Parts of an Animal Cell to Label
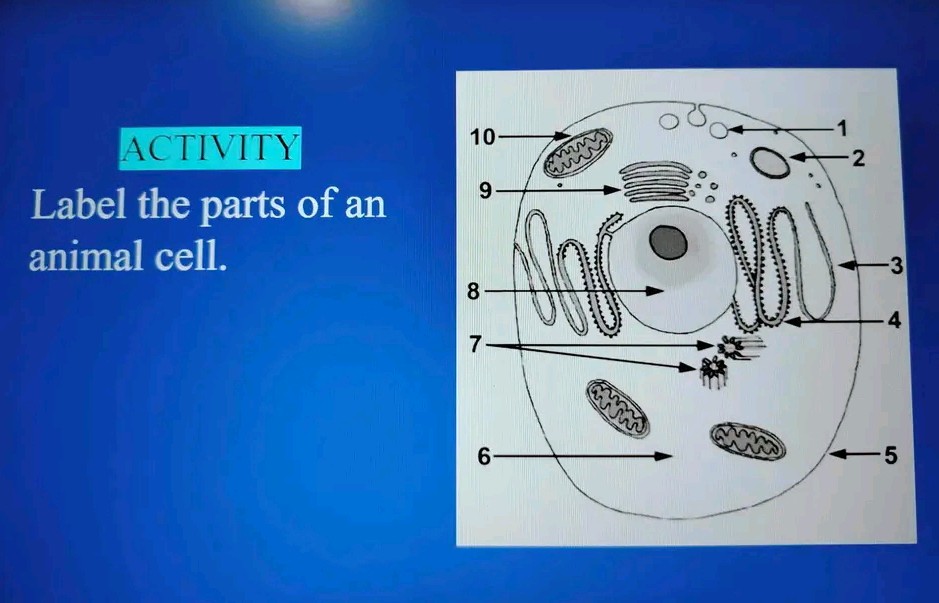
Understanding the Basic Structure of an Animal Cell
Animal cells are the building blocks of life in the animal kingdom, and they are incredibly complex and fascinating. While there are many different types of animal cells, they all share certain basic components. In this article, we will explore the 6 essential parts of an animal cell that you should be able to label.
The Cell Membrane
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It is a thin, semi-permeable membrane that separates the cell from its environment and regulates what enters and leaves the cell. The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with the hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards.
🔬 Note: The cell membrane is not just a passive barrier; it is also involved in cell signaling, cell adhesion, and the transport of molecules in and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane, where many of the cell’s metabolic reactions take place. It is composed of water, salts, sugars, and various organelles, such as mitochondria, ribosomes, and lysosomes. The cytoplasm plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s shape, regulating cell growth and division, and facilitating the movement of materials within the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the cell, where DNA is stored. It is a membrane-bound organelle that contains most of the cell’s genetic material. The nucleus is responsible for controlling cell growth, division, and function, and it plays a critical role in the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next.
🔬 Note: The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which has pores that allow molecules to pass in and out of the nucleus.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouses of the cell, because they generate most of the energy that the cell needs to function. They are membrane-bound organelles that are found in the cytoplasm, and they are responsible for producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that is involved in several important cellular functions, including protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and calcium storage. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which has ribosomes attached to its surface, and smooth ER, which does not.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes. They are responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses. Lysosomes are also involved in cell signaling and the regulation of cell growth and division.
| Organelle | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Separates cell from environment, regulates transport of molecules |
| Cytoplasm | Site of metabolic reactions, maintains cell shape, regulates growth and division |
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material, controls cell growth and division |
| Mitochondria | Generates energy for cell through ATP production |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Involved in protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and calcium storage |
| Lysosomes | Breaks down and recycles cellular waste and foreign substances |
In conclusion, these 6 essential parts of an animal cell are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the various functions of the cell. Understanding the structure and function of these organelles is essential for understanding the biology of animal cells.
What is the main function of the cell membrane?
+The main function of the cell membrane is to separate the cell from its environment and regulate the transport of molecules in and out of the cell.
What is the role of mitochondria in the cell?
+Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for generating most of the energy that the cell needs to function through ATP production.
What is the function of lysosomes in the cell?
+Lysosomes are responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses.
Related Terms:
- Animal cell Worksheet answers
- Animal cell labeling worksheet PDF
- Animal cell with Labels