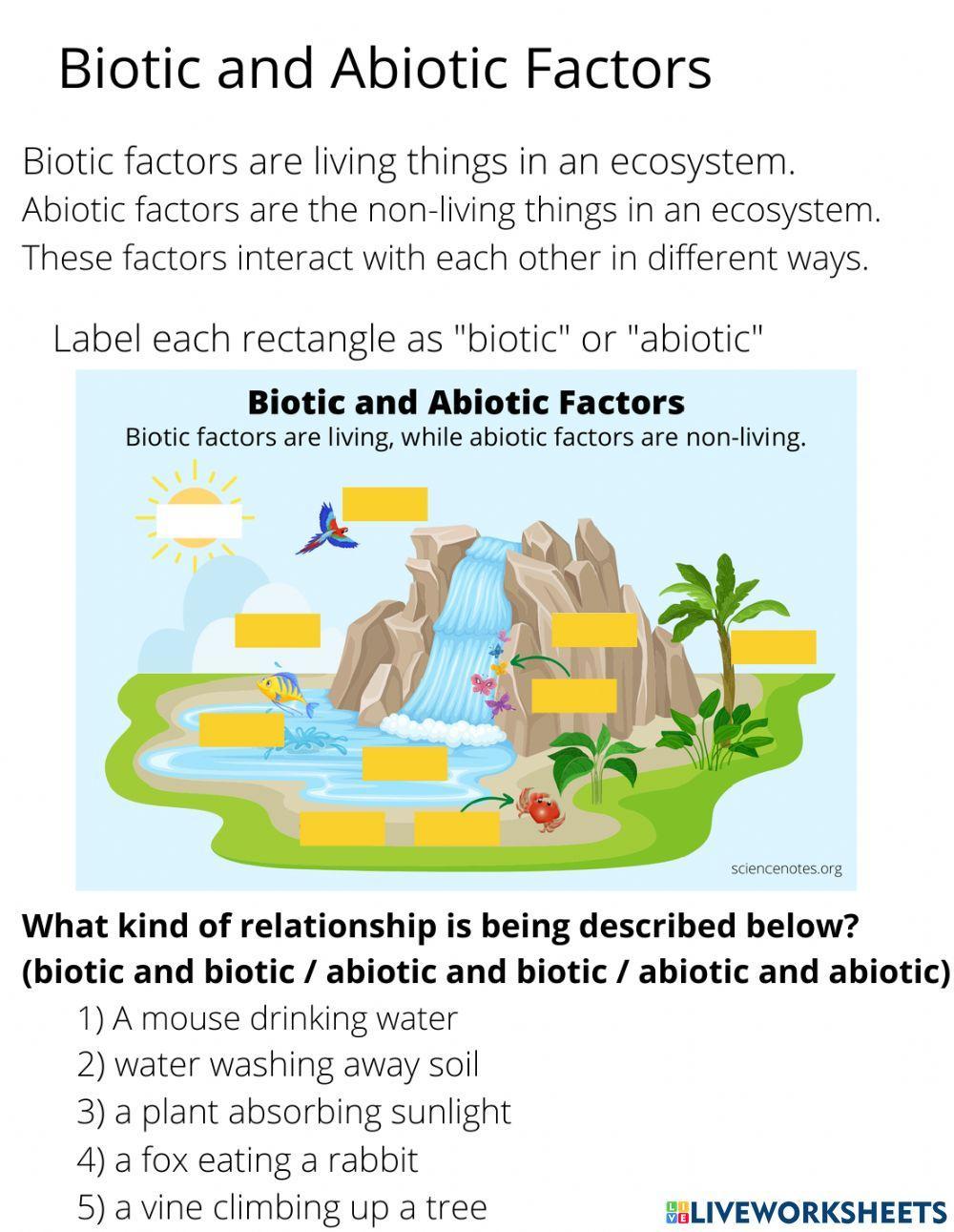
Biotic and Abiotic Factors Worksheet for Students
Understanding Biotic and Abiotic Factors: A Comprehensive Guide for Students
As students of biology and environmental science, it is essential to grasp the concept of biotic and abiotic factors. These terms are often used in the context of ecosystems, and understanding their differences and interactions is crucial for appreciating the complexity of our natural world.
What are Biotic Factors?
Biotic factors are living components of an ecosystem. They include:
- Producers: plants, algae, and other organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
- Consumers: animals, fungi, and other organisms that consume other organisms or organic matter for energy.
- Decomposers: bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that break down dead organisms and organic matter.
Biotic factors interact with each other in complex ways, influencing the structure and function of ecosystems. For example, predators prey on herbivores, which in turn affect the population of plants.
What are Abiotic Factors?
Abiotic factors, on the other hand, are non-living components of an ecosystem. They include:
- Light: intensity and duration of sunlight, which affects photosynthesis and temperature.
- Temperature: affects metabolic rates, growth, and distribution of organisms.
- Water: availability and quality, which affects the survival and distribution of organisms.
- Soil: composition, pH, and nutrient availability, which affects plant growth and decomposition.
- Topography: landscape features, such as hills, valleys, and mountains, which affect soil formation and erosion.
Abiotic factors can also interact with biotic factors, influencing the distribution and abundance of organisms. For example, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the availability of food and habitat for certain species.
Interactions between Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Biotic and abiotic factors interact in complex ways, shaping the structure and function of ecosystems. Some examples of these interactions include:
- Predation: predators affect prey populations, which in turn affect vegetation growth.
- Competition: competition for resources, such as light, water, and nutrients, affects the growth and survival of organisms.
- Symbiosis: relationships between organisms, such as mutualism and parasitism, affect the growth and survival of organisms.
- Decomposition: decomposers break down dead organisms, releasing nutrients that affect plant growth.
🌟 Note: Understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors is crucial for managing ecosystems and conserving biodiversity.
Real-World Applications
Understanding biotic and abiotic factors has many real-world applications, including:
- Conservation biology: understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors informs conservation strategies for endangered species.
- Ecological restoration: restoring ecosystems requires understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors.
- Agriculture: understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors can improve crop yields and reduce environmental impacts.
- Climate change: understanding the interactions between biotic and abiotic factors can inform strategies for mitigating and adapting to climate change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, biotic and abiotic factors are essential components of ecosystems, interacting in complex ways to shape the structure and function of our natural world. Understanding these interactions is crucial for managing ecosystems, conserving biodiversity, and addressing the challenges of climate change.
What is the difference between biotic and abiotic factors?
+Biotic factors are living components of an ecosystem, such as plants and animals, while abiotic factors are non-living components, such as light, temperature, and water.
How do biotic and abiotic factors interact?
+Biotic and abiotic factors interact in complex ways, shaping the structure and function of ecosystems. For example, changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can affect the availability of food and habitat for certain species.
Why is it important to understand biotic and abiotic factors?
+Understanding biotic and abiotic factors is crucial for managing ecosystems, conserving biodiversity, and addressing the challenges of climate change.