Properties of Waves Worksheet for Physics Students
Understanding the Properties of Waves
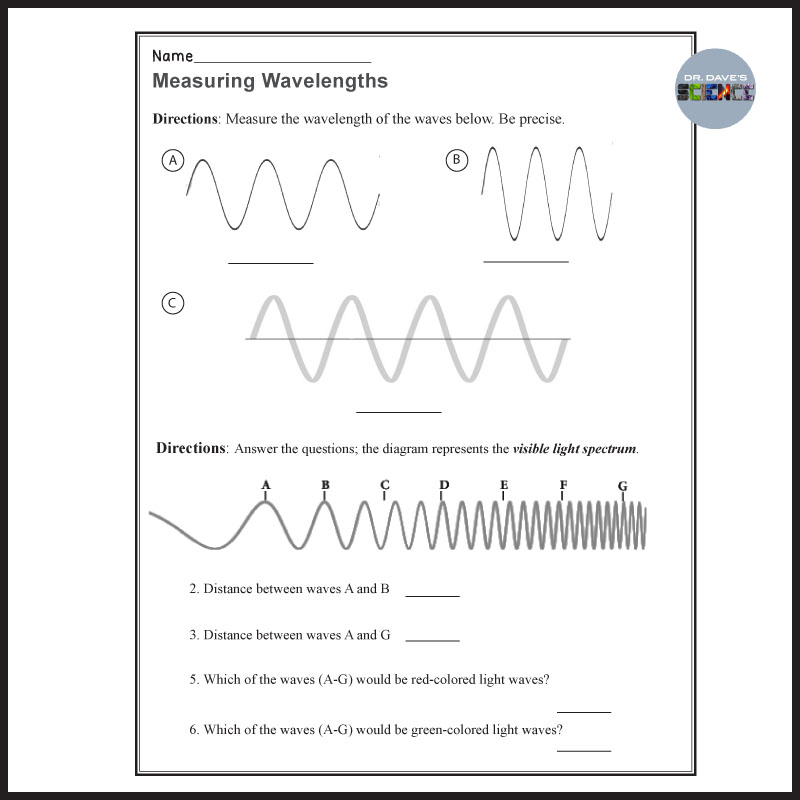
Waves are a fundamental concept in physics, and understanding their properties is crucial for students to grasp the subject. In this worksheet, we will delve into the key properties of waves, including amplitude, wavelength, frequency, speed, and phase.
Amplitude
The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of the wave from its equilibrium position. It is a measure of the wave’s intensity or magnitude. The amplitude of a wave can be affected by various factors, such as the energy of the source and the medium through which the wave is traveling.
- Key points to remember:
- Amplitude is measured in units of length (e.g., meters, centimeters).
- A higher amplitude wave has a greater displacement from its equilibrium position.
- Amplitude is not directly related to the frequency or wavelength of a wave.
Wavelength
The wavelength of a wave is the distance between two consecutive points on the wave that are in phase with each other. It is a measure of the wave’s length or size. Wavelength is typically represented by the Greek letter lambda (λ).
- Key points to remember:
- Wavelength is measured in units of length (e.g., meters, centimeters).
- A longer wavelength corresponds to a lower frequency wave.
- Wavelength is directly related to the speed of the wave and the frequency of the wave.
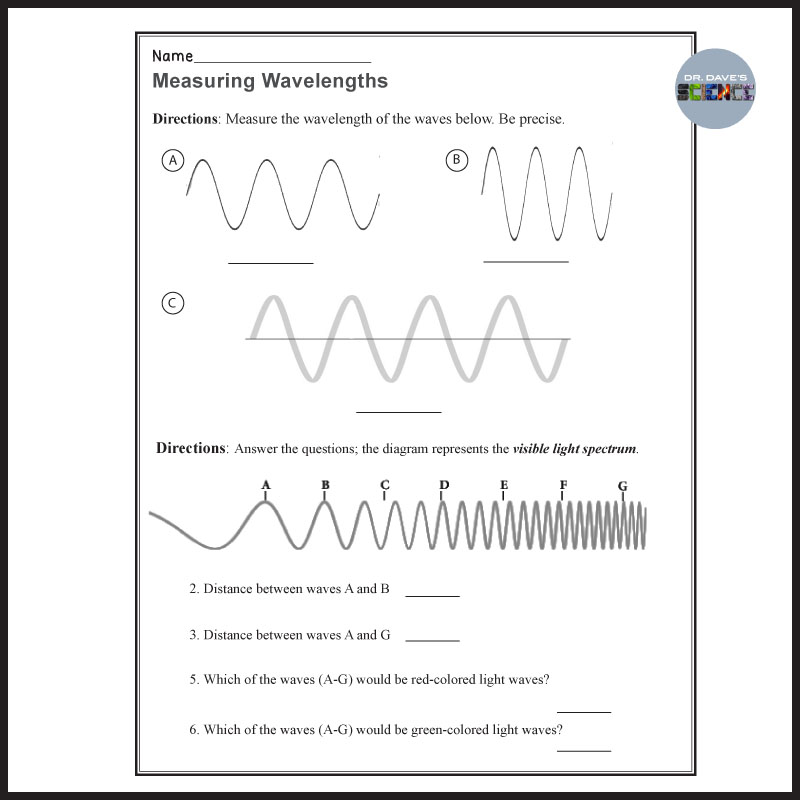
| Wavelength (λ) | Frequency (f) | Speed (v) |
|---|---|---|
| Short wavelength | High frequency | Fast speed |
| Long wavelength | Low frequency | Slow speed |
Frequency
The frequency of a wave is the number of oscillations or cycles per second. It is a measure of the wave’s rate of vibration or oscillation. Frequency is typically represented by the letter f.
- Key points to remember:
- Frequency is measured in units of time (e.g., hertz, Hz).
- A higher frequency wave has more oscillations per second.
- Frequency is directly related to the wavelength and speed of the wave.
Speed
The speed of a wave is the rate at which the wave propagates through a medium. It is a measure of how fast the wave is moving. Speed is typically represented by the letter v.
- Key points to remember:
- Speed is measured in units of length per time (e.g., meters per second, m/s).
- The speed of a wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it is traveling.
- Speed is directly related to the frequency and wavelength of the wave.
Phase
The phase of a wave is the angular position of the wave at a given time. It is a measure of the wave’s timing or synchronization. Phase is typically represented by the Greek letter phi (φ).
- Key points to remember:**
- Phase is measured in units of radians (rad).
- A wave can be in phase or out of phase with another wave.
- Phase is important for understanding wave interference and superposition.
📝 Note: Make sure to review the relationships between amplitude, wavelength, frequency, speed, and phase to better understand the properties of waves.
In conclusion, understanding the properties of waves is crucial for physics students to grasp the fundamental concepts of wave behavior. By reviewing the key points and relationships between amplitude, wavelength, frequency, speed, and phase, students can better comprehend the properties of waves and apply this knowledge to solve problems and analyze wave behavior.
What is the relationship between wavelength and frequency?
+A longer wavelength corresponds to a lower frequency wave, while a shorter wavelength corresponds to a higher frequency wave.
What is the difference between amplitude and intensity?
+Amplitude is a measure of the wave’s displacement from its equilibrium position, while intensity is a measure of the wave’s energy or power.
What is the significance of phase in wave behavior?
+Phase is important for understanding wave interference and superposition, as it determines the timing and synchronization of wave behavior.