Worksheets On Plot
Understanding Plot: A Comprehensive Guide with Worksheets
When it comes to storytelling, plot is one of the most crucial elements that can make or break a narrative. A well-crafted plot can captivate readers, evoke emotions, and leave a lasting impression. In this article, we will delve into the world of plot, exploring its definition, types, and key elements. To help reinforce your understanding, we’ve also included worksheets that you can use to practice and analyze plots.
What is Plot?
Plot is the sequence of events that make up the narrative of a story. It is the structure that underlies the story, including the exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution. A good plot should have a clear beginning, middle, and end, and should be driven by character motivations and conflicts.
Types of Plot
There are several types of plots, including:
- Linear Plot: A linear plot is a straightforward narrative that proceeds in a chronological order.
- Non-Linear Plot: A non-linear plot is a narrative that jumps back and forth in time, often using flashbacks or flash-forwards.
- Episodic Plot: An episodic plot is a narrative that consists of a series of loosely connected events.
- Character-Driven Plot: A character-driven plot is a narrative that focuses on the characters’ thoughts, feelings, and motivations.
Key Elements of Plot
A good plot should have the following key elements:
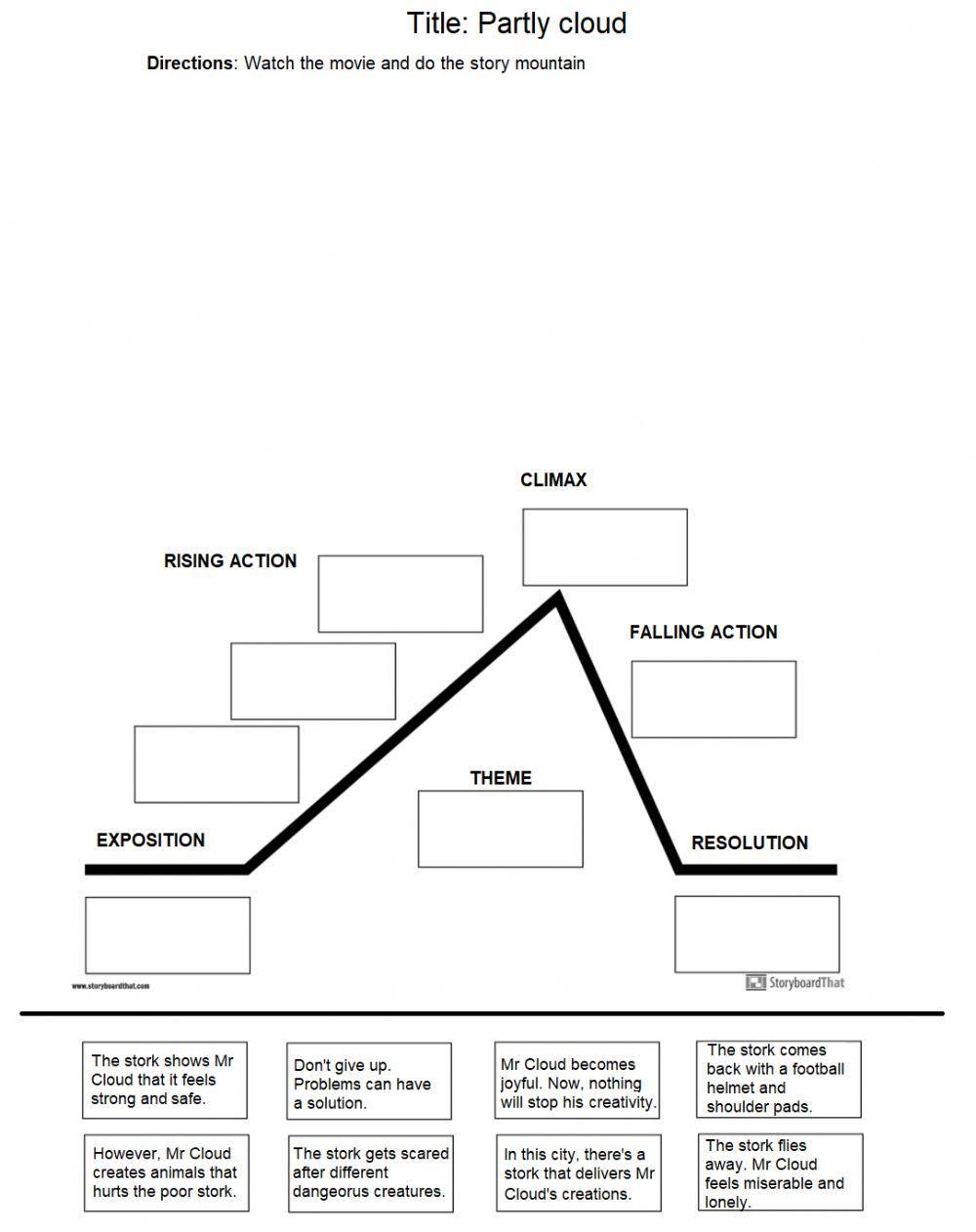
- Exposition: The exposition is the introduction to the story, where the setting, characters, and situation are established.
- Rising Action: The rising action is the series of events that build up to the climax.
- Climax: The climax is the most intense or critical moment in the story.
- Falling Action: The falling action is the series of events that follow the climax.
- Resolution: The resolution is the conclusion of the story.
Worksheet 1: Identifying Plot Elements
Read the following passage and identify the plot elements:
“The sun was setting over the horizon as Sarah walked along the beach. She had always loved the beach, and today was no exception. As she walked, she stumbled upon a mysterious object buried in the sand. As she reached down to pick it up, she heard a voice behind her. ‘Don’t touch that!’ it said. Sarah turned around to see a stranger standing behind her.”
- What is the exposition of the passage?
- What is the rising action of the passage?
- What is the climax of the passage?
- What is the falling action of the passage?
- What is the resolution of the passage?
Worksheet 2: Creating a Plot Diagram
Create a plot diagram for the following story:
“A young boy named Jack wants to buy a new bike. He saves up his allowance for weeks, but when he finally has enough money, he realizes that the bike he wants is no longer available. He is devastated, but then he meets a friend who offers to take him to a different bike shop. Jack finds an even better bike at the new shop, and he is thrilled.”
- Exposition:
- Rising Action:
- Climax:
- Falling Action:
- Resolution:
Worksheet 3: Analyzing Plot Structure
Read the following passage and analyze the plot structure:
“The story begins with a description of a beautiful day in the park. The protagonist, a young woman named Emily, is walking through the park when she sees a group of children playing tag. As she watches, she is suddenly transported back to her childhood, when she used to play tag with her friends. The story then flashes forward to the present, where Emily is now a successful businesswoman, but she is still haunted by memories of her past.”
- What type of plot structure is used in this passage?
- What is the effect of the non-linear plot structure on the reader?
- How does the plot structure contribute to the overall meaning of the story?
📝 Note: The worksheets above are designed to help you practice and analyze plots. You can use them as a starting point for your own creative writing projects or to analyze your favorite stories.
As we’ve seen, plot is a crucial element of storytelling that can make or break a narrative. By understanding the different types of plots and key elements of plot, you can create compelling stories that captivate readers. Remember to practice and analyze plots regularly to improve your writing skills.
What is the difference between a linear and non-linear plot?
+A linear plot is a straightforward narrative that proceeds in a chronological order, while a non-linear plot jumps back and forth in time, often using flashbacks or flash-forwards.
What is the purpose of the exposition in a story?
+The exposition is the introduction to the story, where the setting, characters, and situation are established. It sets the stage for the rest of the narrative.
How can I create a compelling plot for my story?
+To create a compelling plot, focus on developing well-rounded characters, creating conflicts and tensions, and using plot twists and surprises to keep the reader engaged.
Related Terms:
- Story plot worksheets PDF
- Story plot worksheets 4th grade
- character, setting, plot worksheet pdf
- Plot worksheets 5th grade
- Free plot worksheets