5 Ways to Master Solubility Graphs
Understanding Solubility Graphs: A Key to Unlocking Chemistry Secrets
Solubility graphs are a fundamental concept in chemistry that can seem daunting at first, but with practice and the right approach, anyone can master them. These graphs represent the relationship between the solubility of a substance and various factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration of the solvent. In this article, we will explore five ways to master solubility graphs, making it easier to understand and analyze the behavior of different substances.
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Basics
Before diving into the world of solubility graphs, it’s essential to understand the fundamental concepts of solubility. Solubility refers to the maximum amount of a substance that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature and pressure. The solubility of a substance can be affected by various factors, including temperature, pressure, and the presence of other substances.
📝 Note: Solubility is usually expressed in units of concentration, such as grams per liter (g/L) or moles per liter (mol/L).
2. Learn to Read and Interpret Solubility Graphs
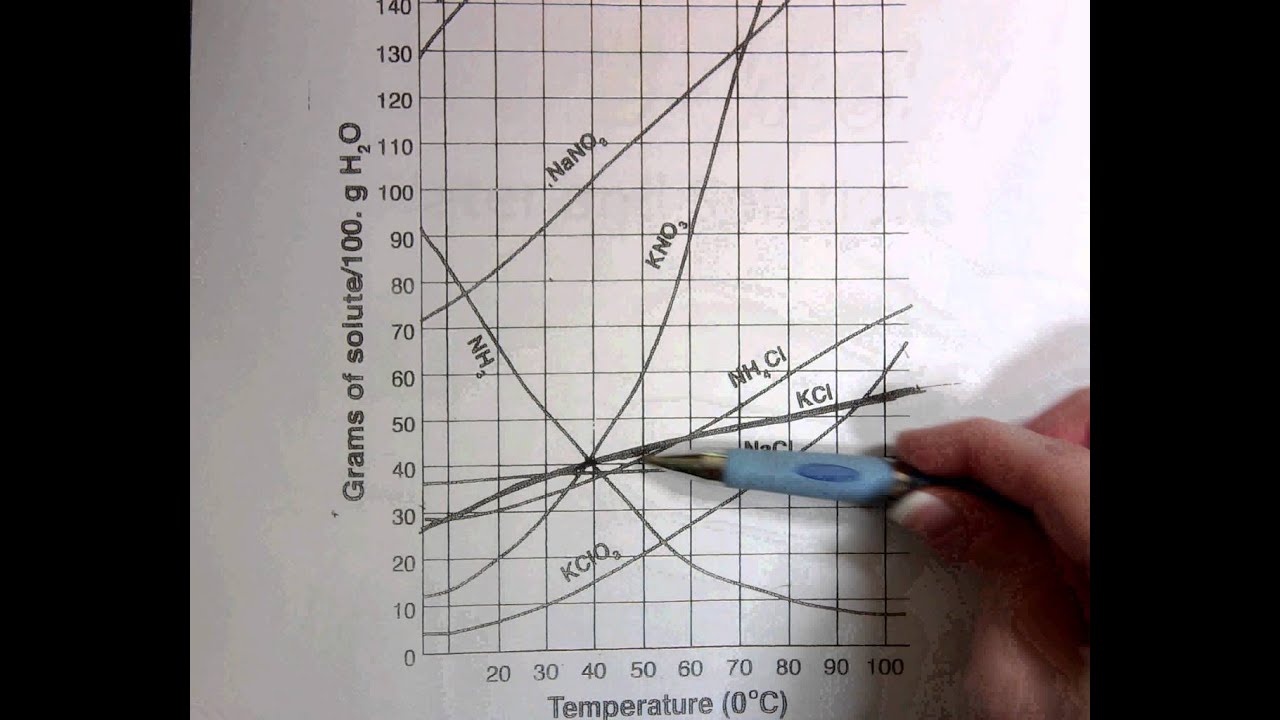
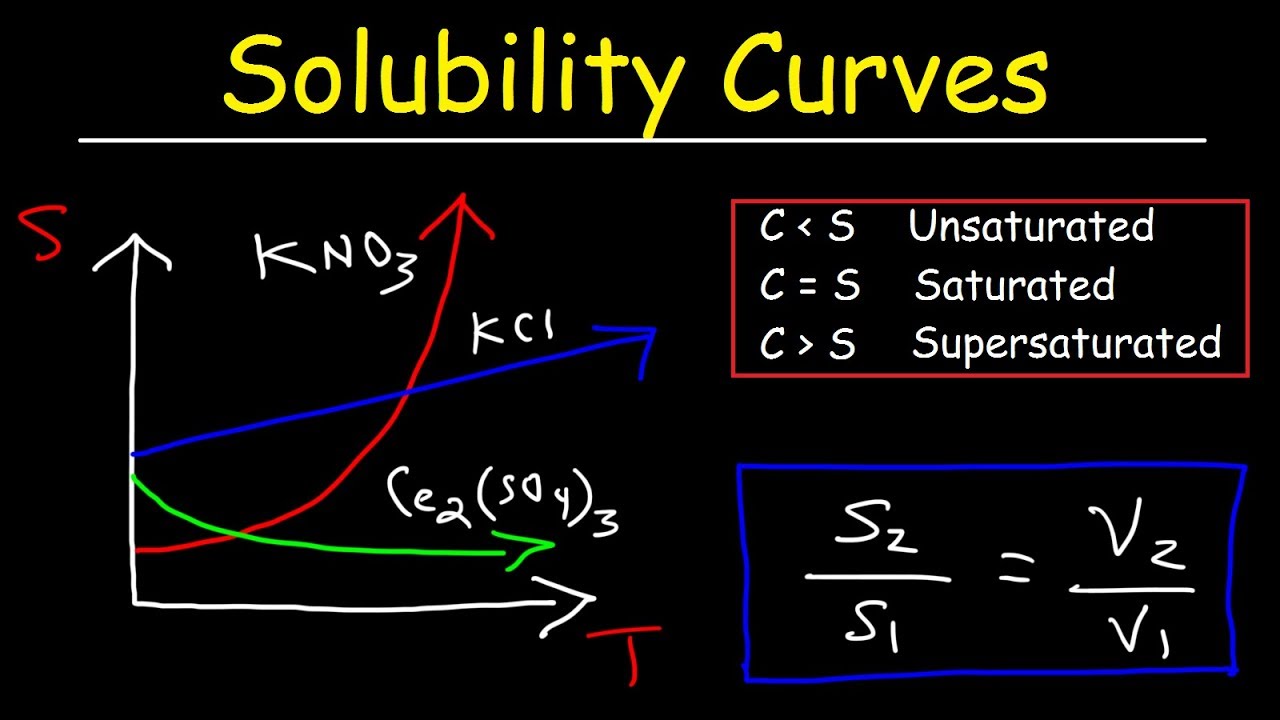
Solubility graphs are typically plotted with the solubility of a substance on the y-axis and the temperature or other variable on the x-axis. The graph shows how the solubility of the substance changes in response to changes in the variable.
- Increasing solubility: If the graph shows an increase in solubility as the temperature increases, it means that the substance is more soluble at higher temperatures.
- Decreasing solubility: If the graph shows a decrease in solubility as the temperature increases, it means that the substance is less soluble at higher temperatures.
- Constant solubility: If the graph shows a constant solubility over a range of temperatures, it means that the substance has a constant solubility over that range.
| Temperature (°C) | Solubility (g/L) |
|---|---|
| 20 | 10 |
| 30 | 15 |
| 40 | 20 |
| 50 | 25 |
3. Practice Drawing Solubility Graphs
Drawing solubility graphs is an excellent way to reinforce your understanding of the concept. Start by drawing a graph with the solubility on the y-axis and the temperature on the x-axis. Then, use data from a table or experiment to plot the points on the graph.
- Use a consistent scale: Make sure to use a consistent scale for both axes to ensure that the graph is accurate and easy to read.
- Label the axes: Label the x-axis and y-axis clearly, including the units of measurement.
- Plot the points: Plot the points on the graph using the data from the table or experiment.
4. Analyze Real-World Applications of Solubility Graphs
Solubility graphs have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Solubility graphs are used to determine the solubility of drugs in different solvents, which is crucial for developing effective medications.
- Food industry: Solubility graphs are used to determine the solubility of food additives and preservatives, which is essential for ensuring food safety and quality.
- Environmental science: Solubility graphs are used to study the behavior of pollutants in water and soil, which is critical for understanding and mitigating environmental pollution.
5. Use Online Resources and Tools to Enhance Your Understanding
There are numerous online resources and tools available to help you master solubility graphs. Some popular options include:
- Interactive simulations: Interactive simulations allow you to explore solubility graphs in a virtual environment, making it easier to understand complex concepts.
- Graphing software: Graphing software allows you to create and analyze solubility graphs quickly and easily.
- Online tutorials: Online tutorials provide step-by-step instructions and examples to help you learn how to draw and interpret solubility graphs.
By following these five steps, you’ll be well on your way to mastering solubility graphs and unlocking the secrets of chemistry.
When it comes to mastering solubility graphs, practice is key. With persistence and dedication, you can develop a deep understanding of this fundamental concept in chemistry.