Mastering Electricity: Circuits Worksheet for Students

Introduction to Electricity and Circuits
Electricity is a fundamental part of our daily lives, powering everything from our homes and schools to our favorite gadgets and devices. Understanding electricity and how it works is crucial for students of all ages. In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of electricity and provide a comprehensive worksheet on circuits for students to practice and reinforce their knowledge.
What is Electricity?
Electricity is a form of energy that is generated by the movement of charged particles, such as electrons. It is a secondary energy source, meaning it is derived from other energy sources like coal, natural gas, or renewable sources like solar or wind power. Electricity is measured in units of watts (W), which represent the rate of energy transfer.
Electric Circuits
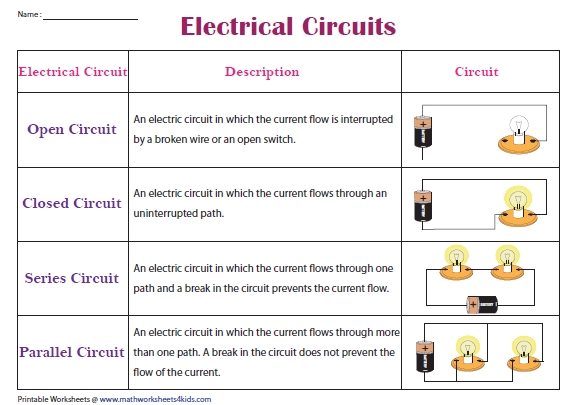
An electric circuit is a path through which electric current flows. It consists of a conductor, such as a wire, and a power source, like a battery. The circuit also includes a load, such as a light bulb or a device, that uses the electricity. When the circuit is closed, the electric current flows from the power source, through the conductor, and back to the power source.
Types of Electric Circuits
There are two main types of electric circuits: series and parallel circuits.
- Series Circuits: In a series circuit, the components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for the electric current to flow.
- Parallel Circuits: In a parallel circuit, the components are connected between the same two points, and there are multiple paths for the electric current to flow.
Circuit Components
A circuit consists of several components, including:
- Conductors: Materials that allow electric current to flow, such as copper wire.
- Insulators: Materials that prevent electric current from flowing, such as rubber or plastic.
- Resistors: Components that reduce the voltage of the electric current, such as light bulbs or heaters.
- Switches: Devices that control the flow of electric current, such as on/off switches.
Circuit Symbols
Circuit symbols are used to represent the different components of a circuit. Here are some common circuit symbols:
| Symbol | Component |
|---|---|
| – | Wire |
| ∧ | Battery |
| Ω | Resistor |
| S | Switch |
| ⊥ | Ground |
Circuits Worksheet for Students
Here is a comprehensive worksheet on circuits for students to practice and reinforce their knowledge:
Section 1: Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the unit of measurement for electricity?
- A) Watt (W)
- B) Volt (V)
- C) Ampere (A)
- D) Ohm (Ω)
- What type of circuit has only one path for the electric current to flow?
- A) Series Circuit
- B) Parallel Circuit
- C) Closed Circuit
- D) Open Circuit
- What is the function of a resistor in a circuit?
- A) To increase the voltage
- B) To decrease the voltage
- C) To increase the current
- D) To decrease the current
Section 2: Short Answer Questions
- What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
- What is the function of a switch in a circuit?
- What is the purpose of a ground in a circuit?
Section 3: Circuit Diagrams
- Draw a simple series circuit with a battery, a resistor, and a switch.
- Draw a simple parallel circuit with a battery, two resistors, and a switch.
Section 4: True or False Questions
- Electric current flows from the negative terminal of a battery to the positive terminal. (True or False)
- A closed circuit has a break in the conductor. (True or False)
- A resistor increases the voltage of the electric current. (True or False)
Conclusion
Mastering electricity and circuits is essential for students to understand the fundamental principles of energy and power. By practicing with this comprehensive worksheet, students can reinforce their knowledge and develop a deeper understanding of electric circuits.
Master the Basics of Electricity and Circuits
By understanding the basics of electricity and circuits, students can develop a strong foundation in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Practice makes perfect, so encourage students to practice with this worksheet and explore more resources to master the basics of electricity and circuits.
What is the difference between a series circuit and a parallel circuit?
+
A series circuit has only one path for the electric current to flow, while a parallel circuit has multiple paths for the electric current to flow.
What is the function of a resistor in a circuit?
+
A resistor decreases the voltage of the electric current in a circuit.
What is the purpose of a ground in a circuit?
+
A ground provides a safe path for electric current to flow to the earth, preventing shock or injury.