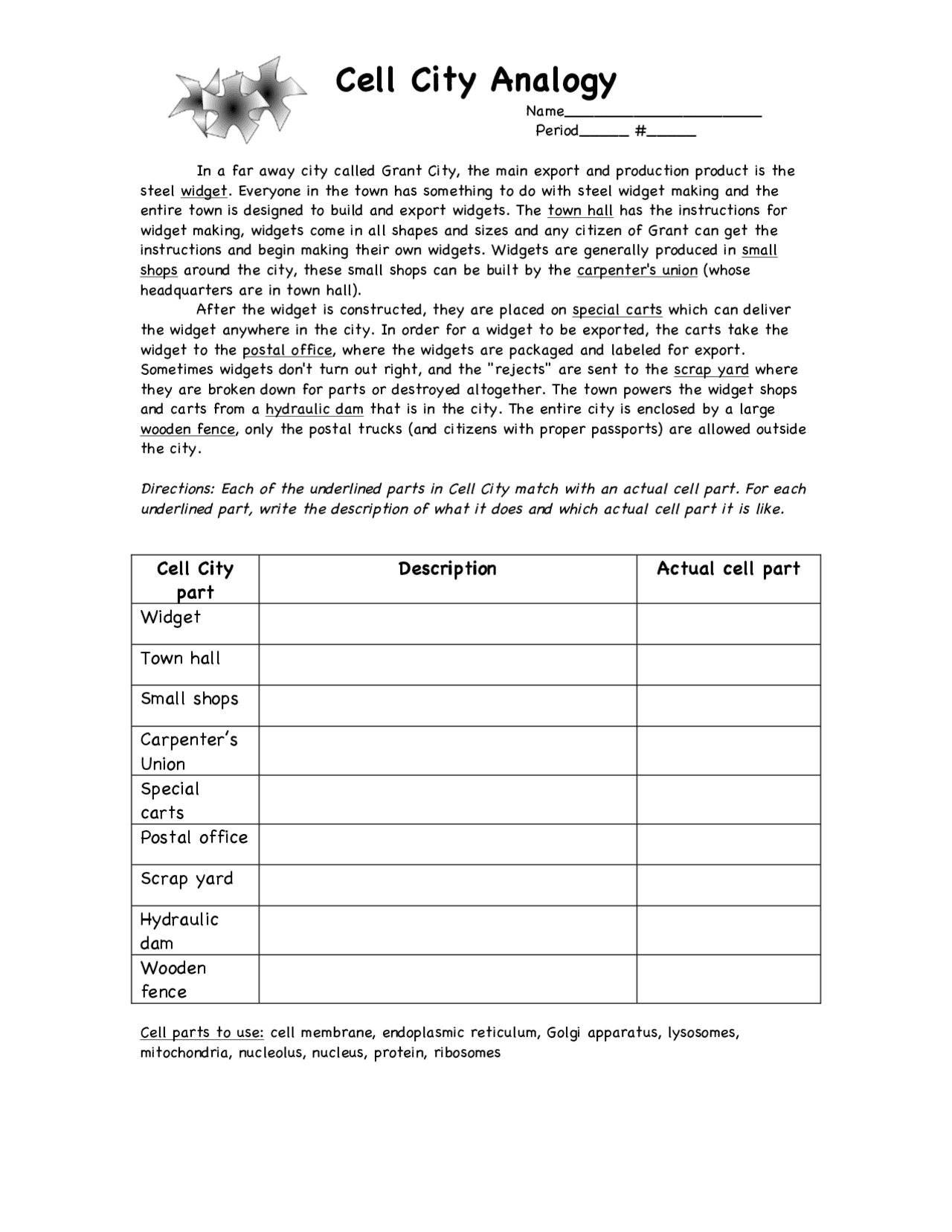
5 Key Cell City Worksheet Answers
Unlocking the Secrets of Cell City: A Comprehensive Guide to the Worksheet Answers
In the vast world of biology, understanding the intricacies of cells is crucial for any aspiring scientist. Cell City, a concept that likens the cell to a bustling metropolis, is a popular teaching tool used to help students grasp the various components and functions of cells. This guide will delve into the 5 Key Cell City Worksheet Answers, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the cell’s inner workings.
What is Cell City?
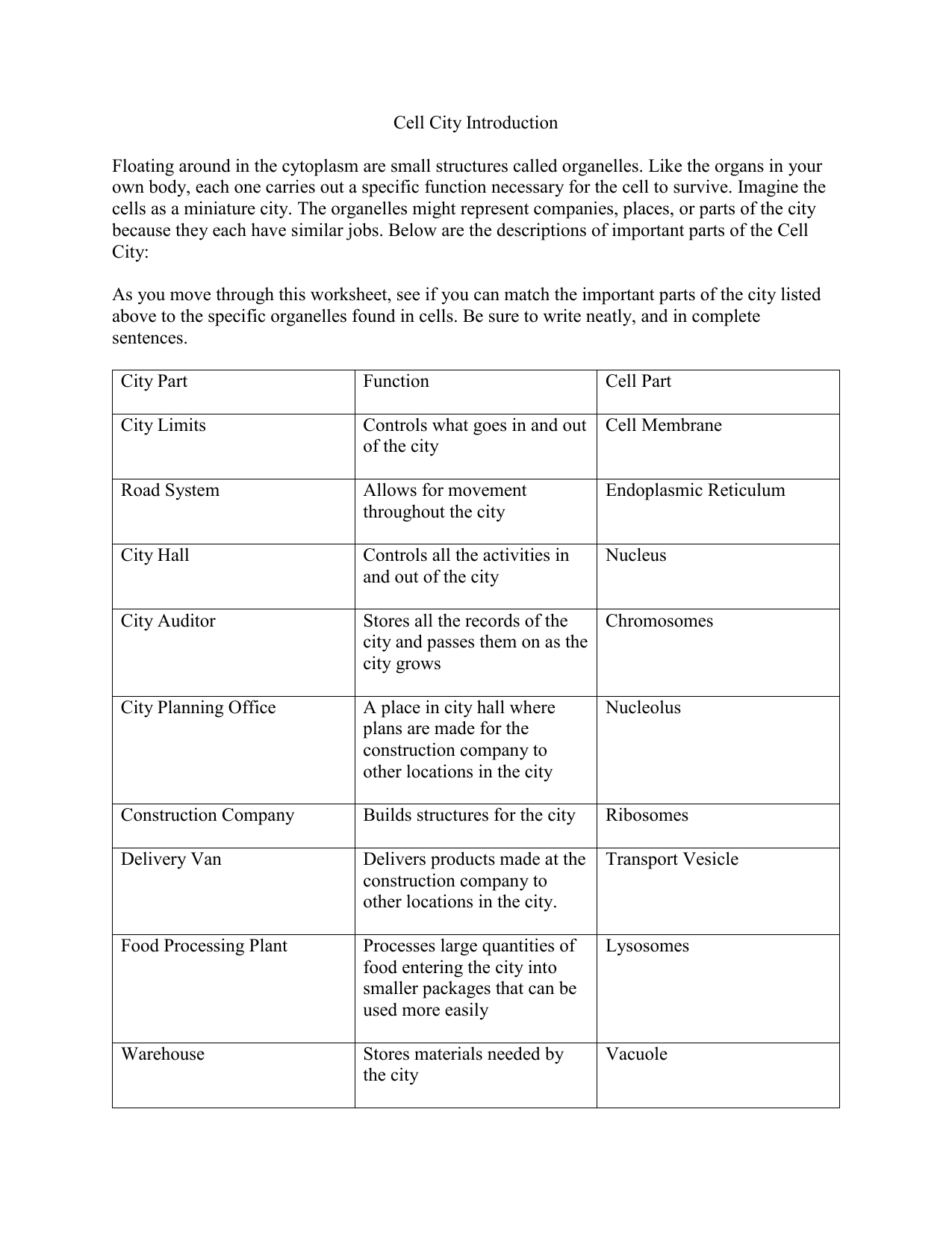
Cell City is an analogy that compares the cell to a city, with different organelles representing various city structures. This comparison helps students visualize and understand the complex relationships between the cell’s components. Just as a city has its government, infrastructure, and services, a cell has its own “government” (nucleus), “power plants” (mitochondria), and “transportation systems” (cytoskeleton).
5 Key Cell City Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to the 5 key questions in the Cell City worksheet:
1. What is the role of the Nucleus in Cell City?
The nucleus serves as the “city hall” or “government” of Cell City. It contains the cell’s DNA and is responsible for controlling the cell’s growth, reproduction, and function.
2. What is the function of the Mitochondria in Cell City?
The mitochondria act as the “power plants” of Cell City, generating energy for the cell through the process of cellular respiration.
3. What is the role of the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) in Cell City?
The ER serves as the “highway system” of Cell City, providing a network of tubules and cisternae for the transportation of materials throughout the cell.
4. What is the function of the Lysosomes in Cell City?
The lysosomes act as the “recycling centers” of Cell City, breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances.
5. What is the role of the Cell Membrane in Cell City?
The cell membrane serves as the “border patrol” of Cell City, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell while maintaining the cell’s internal environment.
Additional Key Concepts in Cell City
In addition to the 5 key answers, here are some additional key concepts to consider:
- Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm is the “city streets” where many of the cell’s metabolic reactions take place.
- Ribosomes: Ribosomes are the “construction sites” where proteins are synthesized.
- Golgi Apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is the “shipping and receiving” department, responsible for processing and packaging proteins and lipids for transport out of the cell.
| Cell City Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Nucleus | Controls cell growth, reproduction, and function |
| Mitochondria | Generates energy for the cell |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Provides a network for transportation of materials |
| Lysosomes | Breaks down and recycles cellular waste and foreign substances |
| Cell Membrane | Regulates movement of materials in and out of the cell |
💡 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the 5 Key Cell City Worksheet Answers. However, it is essential to remember that Cell City is an analogy, and some functions may overlap or be simplified for the sake of comparison.
In conclusion, understanding the 5 Key Cell City Worksheet Answers is crucial for any student of biology. By recognizing the roles of the nucleus, mitochondria, ER, lysosomes, and cell membrane, you can better comprehend the intricate relationships within the cell. Remember to apply this knowledge in context, considering the cell as a dynamic and interconnected system.
What is the main function of the nucleus in Cell City?
+The nucleus serves as the “city hall” or “government” of Cell City, controlling the cell’s growth, reproduction, and function.
What is the role of the mitochondria in Cell City?
+The mitochondria act as the “power plants” of Cell City, generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration.
What is the function of the cell membrane in Cell City?
+The cell membrane serves as the “border patrol” of Cell City, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell while maintaining the cell’s internal environment.