Bohr Models Worksheet: Understand Atomic Structure with Ease

Introduction to Atomic Structure
Atomic structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the composition of atoms, which are the building blocks of matter. The atomic structure consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Understanding the atomic structure is crucial for learning chemistry and physics, and it starts with the Bohr model.
What is the Bohr Model?
The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, is a simplified representation of the atomic structure. It describes the atom as a small, heavy nucleus surrounded by electrons that orbit around it in circular paths called energy levels or electron shells. The Bohr model is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, and it provides a basic understanding of atomic structure.
Key Components of the Bohr Model
The Bohr model consists of the following key components:
- Nucleus: The nucleus is the central part of the atom that contains protons and neutrons. It is positively charged and is responsible for the overall charge of the atom.
- Protons: Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Neutrons: Neutrons are particles that have no charge and reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes of an element.
- Electrons: Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus in energy levels or electron shells. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, and it determines the chemical properties of an element.
- Energy Levels: Energy levels or electron shells are the circular paths that electrons follow around the nucleus. Each energy level has a specific capacity, and electrons occupy the lowest available energy level.
How to Draw Bohr Models
Drawing Bohr models is a simple and effective way to visualize atomic structure. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to draw Bohr models:
- Determine the number of protons and neutrons: The number of protons determines the element, and the number of neutrons determines the isotope.
- Draw the nucleus: Represent the nucleus as a small circle in the center of the atom.
- Add protons and neutrons: Represent protons as positive (+) charges and neutrons as neutral (0) charges inside the nucleus.
- Draw energy levels: Represent energy levels as circular paths around the nucleus.
- Add electrons: Represent electrons as negative (-) charges in the energy levels.
Example: Drawing a Bohr Model of Oxygen
Let’s draw a Bohr model of oxygen, which has 8 protons and 8 neutrons in its atomic nucleus.
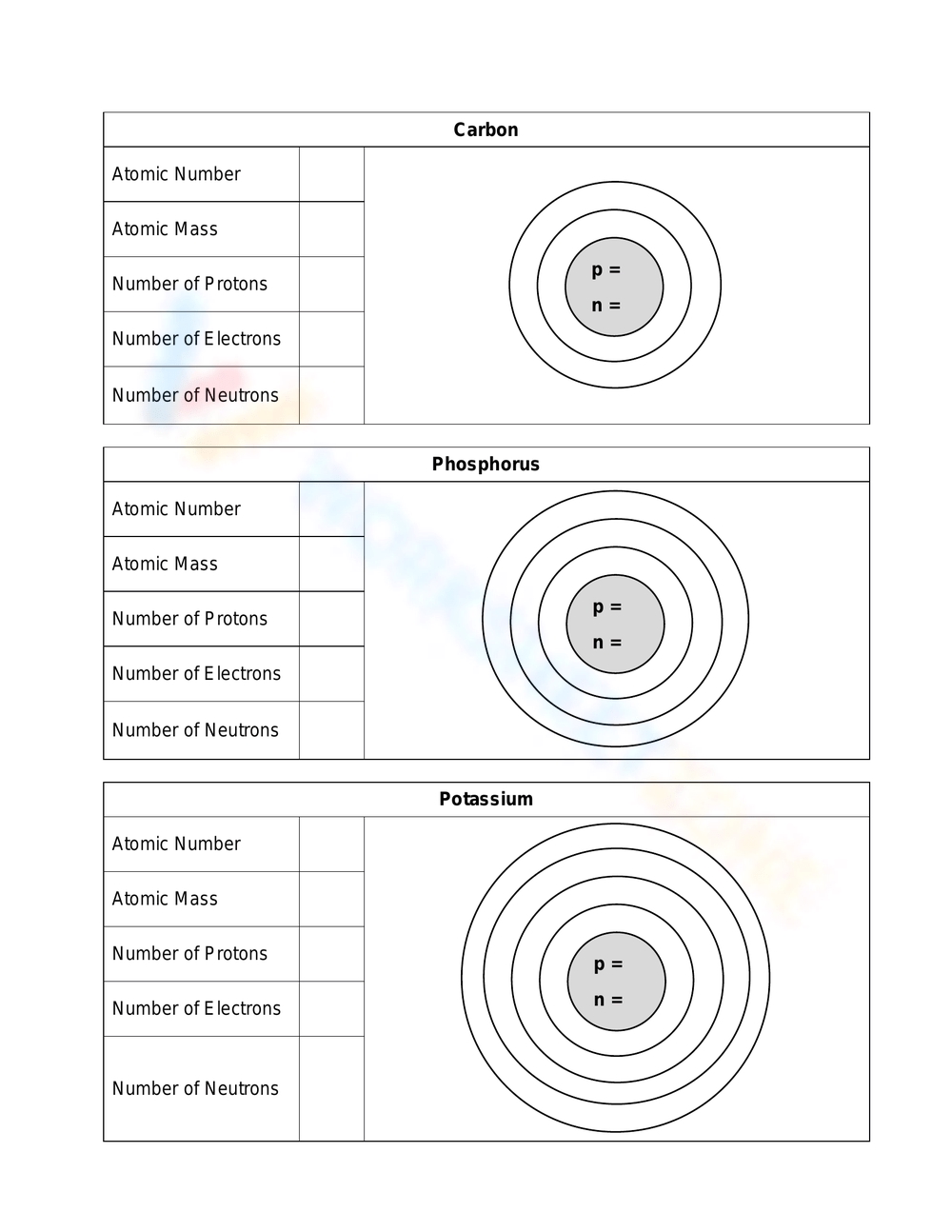
| Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 8 | 8 |
Draw the nucleus with 8 protons and 8 neutrons:
+++++++++
00000000
Draw the energy levels with 8 electrons:
2 electrons in the first energy level
6 electrons in the second energy level
The completed Bohr model of oxygen looks like this:
+++++++++
00000000
---------
2 electrons
---------
6 electrons
📝 Note: Bohr models are simplified representations of atomic structure, and they do not show the actual shapes and sizes of energy levels.
Common Errors in Drawing Bohr Models
Here are some common errors to avoid when drawing Bohr models:
- Incorrect number of protons and neutrons: Make sure to use the correct number of protons and neutrons for the element.
- Incorrect energy level configuration: Make sure to follow the Aufbau principle and the Pauli Exclusion Principle when adding electrons to energy levels.
- Incorrect electron configuration: Make sure to show the correct number of electrons in each energy level.
Conclusion
Bohr models are a simple and effective way to visualize atomic structure. By understanding the key components of the Bohr model and following the steps to draw Bohr models, you can easily create accurate diagrams of atomic structure. Remember to avoid common errors and use the correct number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for each element.
What is the main purpose of the Bohr model?
+The main purpose of the Bohr model is to provide a simplified representation of atomic structure, showing the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom.
How many energy levels are there in an atom?
+There are multiple energy levels in an atom, and each energy level has a specific capacity. The number of energy levels increases as you move from the first energy level to the outermost energy level.
What is the difference between protons and neutrons?
+Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus, while neutrons are neutral particles that reside in the nucleus along with protons.