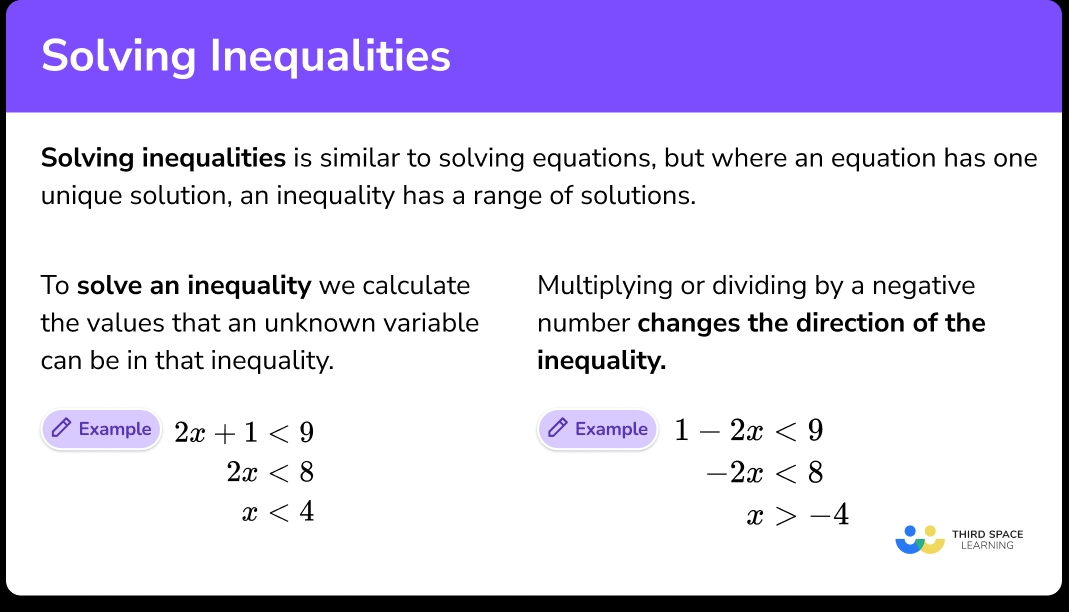
6 Easy Steps to Balance Chemical Equations
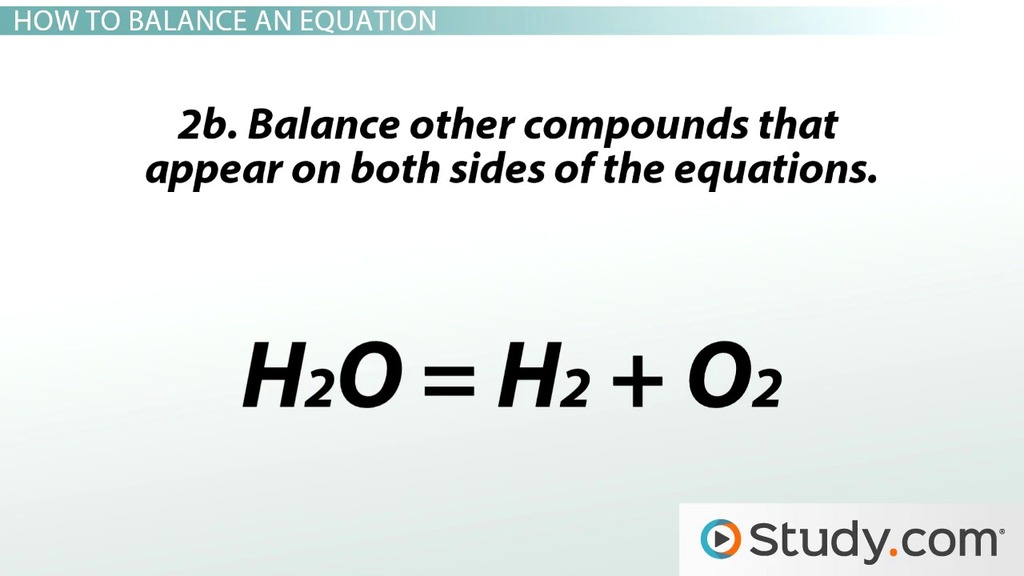
Understanding the Importance of Balancing Chemical Equations
Chemical equations play a crucial role in chemistry as they provide a concise representation of chemical reactions. A chemical equation is a symbolic representation of the reactants, products, and sometimes the reaction conditions and catalysts involved in a chemical reaction. However, a chemical equation is only meaningful if it is balanced, meaning that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. Balancing chemical equations is a critical skill for chemistry students to master, as it allows them to accurately predict the amounts of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction.
Step 1: Write Down the Unbalanced Equation
To balance a chemical equation, start by writing down the unbalanced equation. This involves listing the reactants on the left side of the equation and the products on the right side, using the correct chemical formulas for each substance. For example, let’s consider the combustion reaction of methane (CH4) with oxygen (O2) to form carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The unbalanced equation would be:
CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Step 2: Count the Number of Atoms of Each Element
Next, count the number of atoms of each element on both the reactant and product sides of the equation. This will help you identify which elements are not balanced.
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| C | 1 | 1 |
| H | 4 | 2 |
| O | 2 | 4 |
From the table, we can see that the number of hydrogen and oxygen atoms is not the same on both sides of the equation.
Step 3: Balance the Equation by Adding Coefficients
To balance the equation, we need to add coefficients (numbers in front of the formulas of reactants or products) to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. Start by balancing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. In this case, we’ll start with carbon, which is already balanced.
Next, balance the hydrogen atoms. Since there are 4 hydrogen atoms on the reactant side and 2 on the product side, we can add a coefficient of 2 in front of the H2O formula to balance the hydrogen atoms:
CH4 + O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Now, let’s update the table:
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| C | 1 | 1 |
| H | 4 | 4 |
| O | 2 | 4 |
Step 4: Balance the Oxygen Atoms
With the hydrogen atoms balanced, we can now focus on the oxygen atoms. Since there are 2 oxygen atoms on the reactant side and 4 on the product side, we can add a coefficient of 2 in front of the O2 formula to balance the oxygen atoms:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
Now, let’s update the table:
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| C | 1 | 1 |
| H | 4 | 4 |
| O | 4 | 4 |
The equation is now balanced!
🔥 Note: When adding coefficients, always multiply the entire formula by the coefficient, not just the element.
Step 5: Check the Balanced Equation
Finally, double-check the balanced equation to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. You can do this by recounting the atoms or by using the table.
Step 6: Write the Balanced Equation with the Correct Format
Once you’re confident that the equation is balanced, write the final balanced equation with the correct format. In this case, the balanced equation is:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
And that’s it! With these 6 easy steps, you can balance any chemical equation.
In conclusion, balancing chemical equations is a critical skill for chemistry students to master. By following these 6 easy steps, you can ensure that your chemical equations are accurate and reliable. Remember to always double-check your work to avoid errors.
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
+
The purpose of balancing chemical equations is to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides, allowing for accurate predictions of the amounts of reactants and products involved in a chemical reaction.
How do I know if a chemical equation is balanced?
+
A chemical equation is balanced if the number of atoms of each element is the same on both the reactant and product sides. You can check this by counting the atoms or by using a table.
What is the difference between a coefficient and a subscript in a chemical equation?
+
A coefficient is a number in front of a formula that indicates how many molecules of that substance are involved in the reaction. A subscript is a small number that indicates the number of atoms of an element within a molecule.