5 Ways to Master Sentences and Fragments
Understanding the Basics of Sentences and Fragments
In the world of writing, sentences and fragments are the building blocks of effective communication. A sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought, while a fragment is a group of words that doesn’t express a complete thought. Mastering the art of crafting sentences and fragments is crucial for any writer, as it can make or break the clarity and coherence of their writing.
1. Identifying and Correcting Sentence Fragments
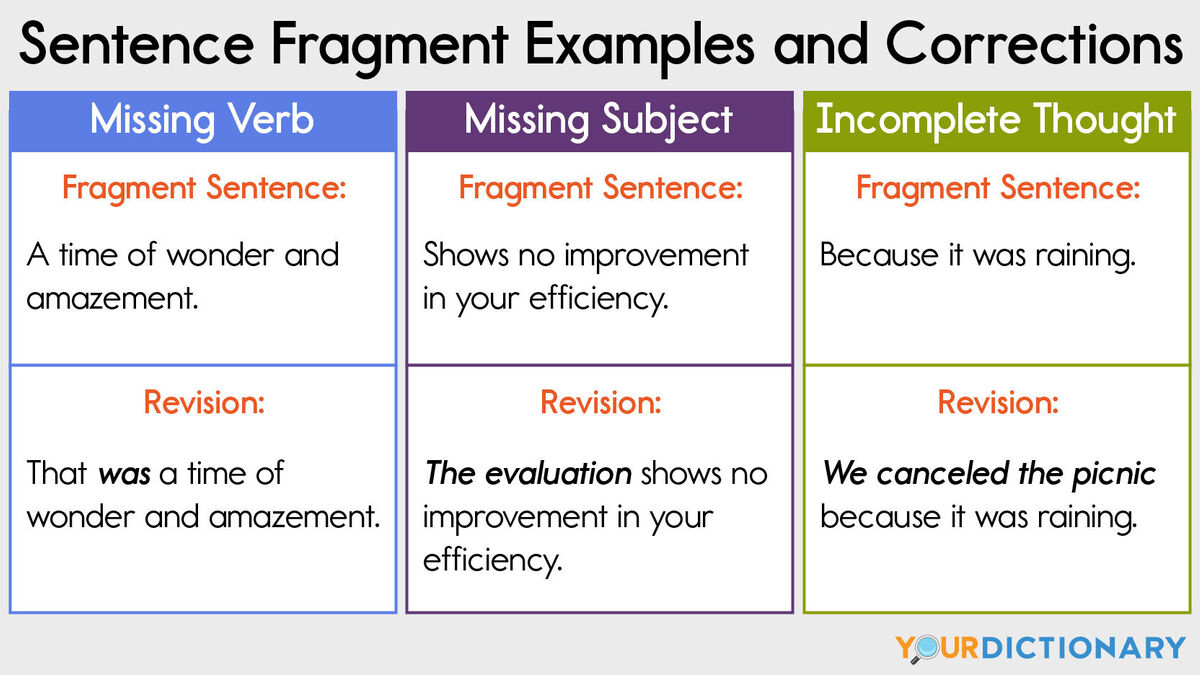
A sentence fragment is a group of words that doesn’t express a complete thought. It often lacks a subject or a verb, or both. For example:
- “Running down the street.” (This fragment lacks a subject.)
- “The big red car.” (This fragment lacks a verb.)
To correct a sentence fragment, you need to add a subject or a verb, or both. For example:
- “The kids were running down the street.” (This sentence has a subject and a verb.)
- “The big red car sped down the highway.” (This sentence has a subject and a verb.)
📝 Note: When correcting sentence fragments, make sure to add a subject or a verb, or both, to create a complete sentence.
2. Using Independent and Dependent Clauses
An independent clause is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. It has a subject and a verb, and can stand alone as a sentence. A dependent clause, on the other hand, is a group of words that doesn’t express a complete thought. It often starts with a subordinating conjunction, such as “because,” “although,” or “if.”
For example:
- “I went to the store.” (This is an independent clause.)
- “Because I needed milk.” (This is a dependent clause.)
To create a complete sentence, you can combine an independent clause and a dependent clause using a subordinating conjunction. For example:
- “I went to the store because I needed milk.” (This sentence combines an independent clause and a dependent clause.)
3. Using Relative Clauses to Add Information
A relative clause is a group of words that provides additional information about a noun or pronoun. It often starts with a relative pronoun, such as “who,” “which,” or “that.”
For example:
- “The book, which is on the table, is mine.” (This sentence uses a relative clause to add information about the book.)
- “The woman, who is standing over there, is my friend.” (This sentence uses a relative clause to add information about the woman.)
To use relative clauses effectively, make sure to place them immediately after the noun or pronoun they modify. For example:
- “The book that is on the table is mine.” (This sentence uses a relative clause to add information about the book.)
📝 Note: When using relative clauses, make sure to place them immediately after the noun or pronoun they modify.
4. Using Active and Passive Voice
Active voice is when the subject of the sentence performs the action described by the verb. Passive voice is when the subject of the sentence receives the action described by the verb.
For example:
- “The dog bit the man.” (This sentence is in active voice.)
- “The man was bitten by the dog.” (This sentence is in passive voice.)
To use active and passive voice effectively, make sure to choose the voice that best conveys the intended meaning. For example:
- “The scientists discovered the cure for the disease.” (This sentence uses active voice to emphasize the action of the scientists.)
- “The cure for the disease was discovered by the scientists.” (This sentence uses passive voice to emphasize the discovery.)
5. Using Modifiers to Add Emphasis
Modifiers are words or phrases that add emphasis or detail to a sentence. Adverbs, adjectives, and phrases can all be used as modifiers.
For example:
- “She spoke loudly.” (This sentence uses an adverb to add emphasis to the verb “spoke”.)
- “The big red car.” (This sentence uses adjectives to add detail to the noun “car”.)
- “With great enthusiasm, he accepted the award.” (This sentence uses a phrase to add emphasis to the verb “accepted”.)
To use modifiers effectively, make sure to place them as close as possible to the word they modify. For example:
- “She spoke loudly and clearly.” (This sentence uses adverbs to add emphasis to the verb “spoke”.)
📝 Note: When using modifiers, make sure to place them as close as possible to the word they modify.
Mastering the art of crafting sentences and fragments takes time and practice. By following these five tips, you can improve your writing skills and communicate more effectively.
In summary, mastering sentences and fragments requires a deep understanding of the basics of writing. By identifying and correcting sentence fragments, using independent and dependent clauses, relative clauses, active and passive voice, and modifiers, you can create clear and coherent writing that effectively communicates your intended meaning.
What is a sentence fragment?
+A sentence fragment is a group of words that doesn’t express a complete thought. It often lacks a subject or a verb, or both.
How do I correct a sentence fragment?
+To correct a sentence fragment, you need to add a subject or a verb, or both, to create a complete sentence.
What is the difference between active and passive voice?
+Active voice is when the subject of the sentence performs the action described by the verb, while passive voice is when the subject of the sentence receives the action described by the verb.
Related Terms:
- Sentence fragment worksheets pdf
- Sentence or fragment worksheet