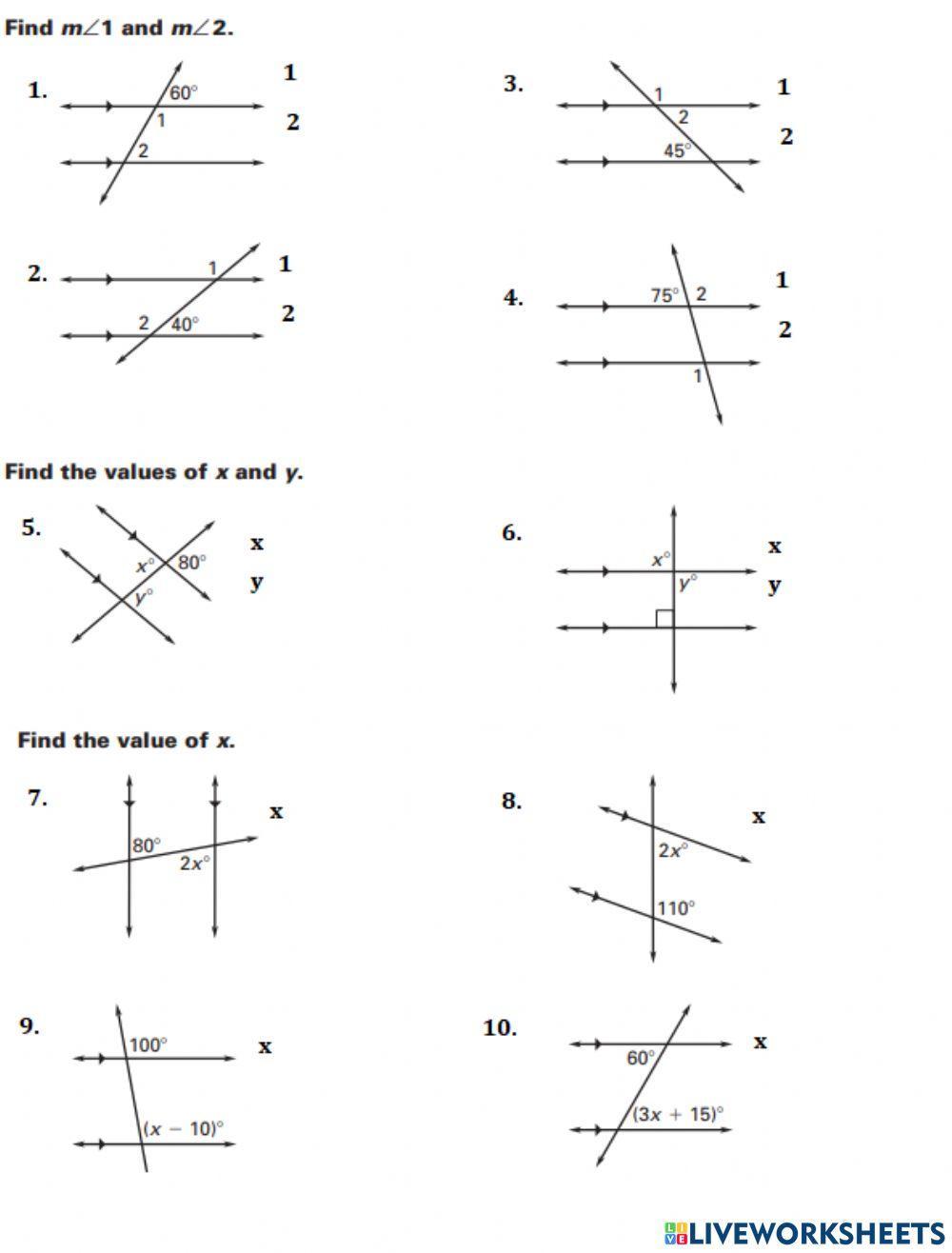
10 Ways to Master Ratios and Rates Worksheets

Mastering Ratios and Rates Worksheets: A Comprehensive Guide
Ratios and rates are fundamental concepts in mathematics, and mastering them is crucial for problem-solving and critical thinking. Whether you’re a student, teacher, or parent, understanding how to work with ratios and rates can help you navigate a wide range of mathematical challenges. In this article, we’ll explore 10 ways to master ratios and rates worksheets, along with tips, examples, and best practices to help you achieve success.
Understanding the Basics: What are Ratios and Rates?
Before diving into the world of ratios and rates worksheets, it’s essential to understand the basics. A ratio is a comparison of two quantities, often expressed as a fraction or using a colon (:). For example, a ratio of 2:3 can be written as 2⁄3. A rate, on the other hand, is a special type of ratio that compares a quantity to a unit of measurement. For instance, a rate of 50 miles per hour can be written as 50 miles/hour.
1. Start with Simple Ratios and Rates Worksheets
To build a strong foundation in ratios and rates, start with simple worksheets that focus on basic concepts. Practice writing ratios in different forms, such as fractions or decimals, and work on identifying equivalent ratios. For example:
- Write the ratio 3:4 as a fraction: 3⁄4
- Write the ratio 2:5 as a decimal: 0.4
- Identify equivalent ratios: 2:3 = 4:6 = 6:9
2. Use Real-World Examples to Illustrate Ratios and Rates
Using real-world examples can help make ratios and rates more relatable and interesting. Try incorporating everyday scenarios into your worksheets, such as:
- A recipe that serves 4 people requires 2 cups of flour. If you want to serve 6 people, how much flour will you need?
- A car travels 250 miles in 5 hours. What is the rate of speed in miles per hour?
3. Practice Converting Between Ratios and Rates
Converting between ratios and rates is an essential skill. Practice converting ratios to rates and vice versa using worksheets that provide examples like:
- Convert the ratio 3:4 to a rate: 3⁄4 = 0.75
- Convert the rate 50 miles/hour to a ratio: 50 miles/hour = 50:1
4. Focus on Word Problems Involving Ratios and Rates
Word problems are an excellent way to apply ratios and rates to real-world scenarios. Use worksheets that provide a mix of straightforward and more complex word problems, such as:
- A bakery sells a total of 250 loaves of bread per day. They sell a combination of whole wheat and white bread. If the ratio of whole wheat to white bread is 3:5, how many loaves of each type are sold?
- A car rental company charges 40 per day plus an additional 0.25 per mile driven. If a customer rents a car for 3 days and drives 200 miles, what is the total cost?
5. Use Visual Aids to Illustrate Ratios and Rates
Visual aids like diagrams, charts, and graphs can help students understand complex ratios and rates concepts. Incorporate visual aids into your worksheets, such as:
- A diagram showing the ratio of boys to girls in a class
- A chart illustrating the rate of growth of a plant over time
6. Incorporate Multi-Step Word Problems
Multi-step word problems involving ratios and rates can be challenging, but they’re an excellent way to build critical thinking skills. Use worksheets that provide examples like:
- A store has a sale on shirts and pants. The ratio of shirts to pants is 2:3. If the store sells 120 shirts, how many pants are sold? If each shirt costs 15 and each pair of pants costs 25, what is the total revenue from the sale?
7. Use Technology to Enhance Ratios and Rates Practice
Technology can be a powerful tool for practicing ratios and rates. Utilize online worksheets, apps, and software that provide interactive and engaging activities, such as:
- Online quizzes that provide immediate feedback
- Interactive charts and graphs that allow students to explore ratios and rates in real-time
8. Focus on Equivalent Ratios and Rates
Equivalent ratios and rates are a crucial concept in mathematics. Practice identifying equivalent ratios and rates using worksheets that provide examples like:
- Identify equivalent ratios: 2:3 = 4:6 = 6:9
- Identify equivalent rates: 50 miles/hour = 50:1 = 0.5 miles/minute
9. Use Games and Activities to Make Practice Fun
Making practice fun can help increase engagement and motivation. Incorporate games and activities into your worksheets, such as:
- A “Ratios and Rates Scavenger Hunt” where students find examples of ratios and rates in real-world scenarios
- A “Ratios and Rates Bingo” game where students match equivalent ratios and rates
10. Provide Feedback and Encouragement
Finally, it’s essential to provide feedback and encouragement to students as they practice ratios and rates. Use worksheets that allow for self-assessment and provide feedback on areas where students need improvement.
📝 Note: Remember to adjust the level of difficulty and complexity of the worksheets according to the student's skill level and grade.
What is the difference between a ratio and a rate?
+A ratio is a comparison of two quantities, while a rate is a special type of ratio that compares a quantity to a unit of measurement.
How can I help my students understand ratios and rates?
+Use real-world examples, visual aids, and interactive activities to make practice engaging and fun. Provide feedback and encouragement to help students build confidence and skills.
What are some common applications of ratios and rates in real life?
+Ratios and rates are used in a wide range of applications, including finance, science, engineering, and cooking. Examples include calculating interest rates, determining the ratio of ingredients in a recipe, and measuring the rate of speed of a car.
By following these 10 ways to master ratios and rates worksheets, you’ll be well on your way to building a strong foundation in mathematics and helping students achieve success. Remember to make practice engaging and fun, provide feedback and encouragement, and use real-world examples to illustrate complex concepts.