6 Ways to Master Radiation Convection Conduction
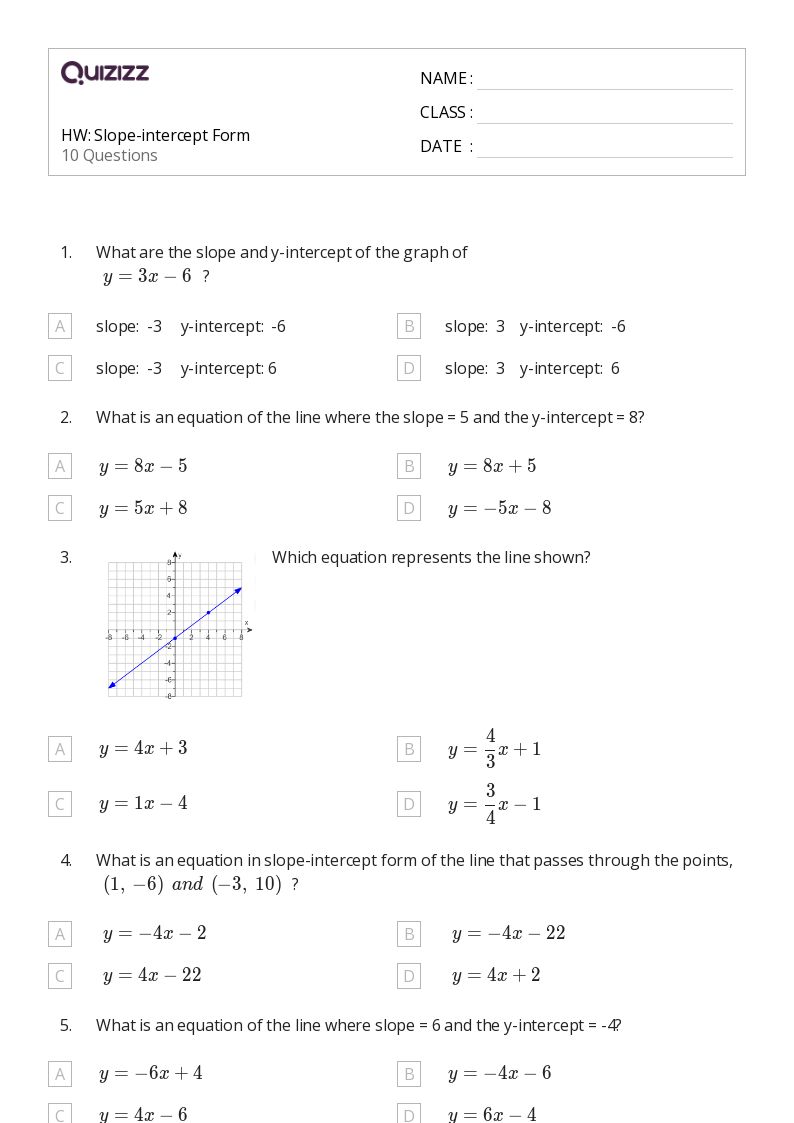
Understanding the Fundamentals of Heat Transfer
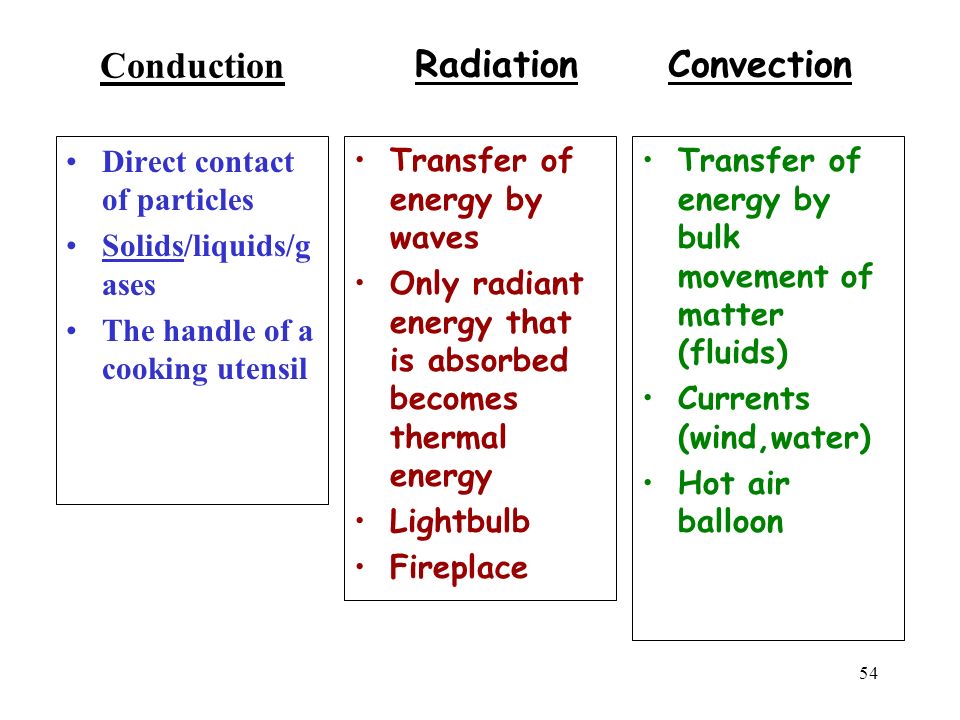
Heat transfer is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that involves the movement of thermal energy from one body or location to another. There are three primary methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Mastering these methods is crucial in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and even cooking. In this article, we will delve into the world of radiation, convection, and conduction, exploring their definitions, examples, and applications.
Radiation: The Invisible Heat Transfer
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. This method of heat transfer does not require a medium, meaning it can occur in a vacuum. Radiation is the primary method of heat transfer in space, where there is no air or water to facilitate conduction or convection.
Examples of Radiation:
- The sun’s rays warming the Earth’s surface
- A fire emitting heat and light
- A microwave oven cooking food using electromagnetic waves
Convection: The Heat Transfer with a Helping Hand
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids. When a fluid is heated, it expands and becomes less dense than the surrounding fluid, causing it to rise. As the fluid rises, it carries heat away from the source, creating a circulation of fluid known as a convective cell.
Examples of Convection:
- A pot of boiling water, where the heated water rises to the surface and is replaced by cooler water
- A chimney, where the heated air rises and carries heat away from the fire
- The Earth’s atmosphere, where convection currents drive weather patterns
Conduction: The Direct Heat Transfer
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between particles or objects. This method of heat transfer requires a physical medium, such as a solid, liquid, or gas, to facilitate the transfer of heat.
Examples of Conduction:
- A metal spoon in a hot cup of coffee, where the heat is transferred from the coffee to the spoon
- A building’s foundation, where the heat from the ground is transferred to the building
- A person holding a hot cup of coffee, where the heat is transferred from the cup to their hand
Mastering Radiation, Convection, and Conduction
To master radiation, convection, and conduction, it is essential to understand the fundamental principles and applications of each method. Here are six ways to improve your understanding and skills:
- Study the Fundamentals: Understand the definitions, formulas, and equations that govern each method of heat transfer. Familiarize yourself with the concepts of temperature, heat capacity, and thermal conductivity.
- Practice with Real-World Examples: Use everyday examples to illustrate the concepts of radiation, convection, and conduction. For instance, observe how a building’s design takes into account the natural convection of air to improve ventilation.
- Experiment with Heat Transfer: Conduct experiments to demonstrate the principles of heat transfer. For example, create a homemade solar oven using a pizza box and plastic wrap to demonstrate radiation.
- Analyze Heat Transfer in Different Materials: Investigate how different materials respond to heat transfer. For instance, compare the thermal conductivity of metals, woods, and plastics.
- Apply Heat Transfer to Real-World Problems: Use your knowledge of heat transfer to solve real-world problems. For example, design a more efficient heating system for a building or develop a cooling system for an electronic device.
- Stay Up-to-Date with Advances in Heat Transfer: Follow the latest research and developments in heat transfer, such as new materials and technologies that improve heat transfer efficiency.
🔍 Note: Mastering radiation, convection, and conduction requires a deep understanding of the fundamental principles and applications of each method. Practice, experimentation, and real-world analysis are essential to developing expertise in heat transfer.
What is the primary method of heat transfer in space?
+Radiation is the primary method of heat transfer in space, where there is no air or water to facilitate conduction or convection.
What is an example of convection in everyday life?
+A pot of boiling water is an example of convection, where the heated water rises to the surface and is replaced by cooler water.
How can I improve my understanding of heat transfer?
+You can improve your understanding of heat transfer by studying the fundamentals, practicing with real-world examples, experimenting with heat transfer, analyzing heat transfer in different materials, applying heat transfer to real-world problems, and staying up-to-date with advances in heat transfer.
In conclusion, mastering radiation, convection, and conduction is crucial for understanding various phenomena in physics, engineering, and everyday life. By following the six ways outlined in this article, you can improve your knowledge and skills in heat transfer, leading to a deeper appreciation of the world around us.