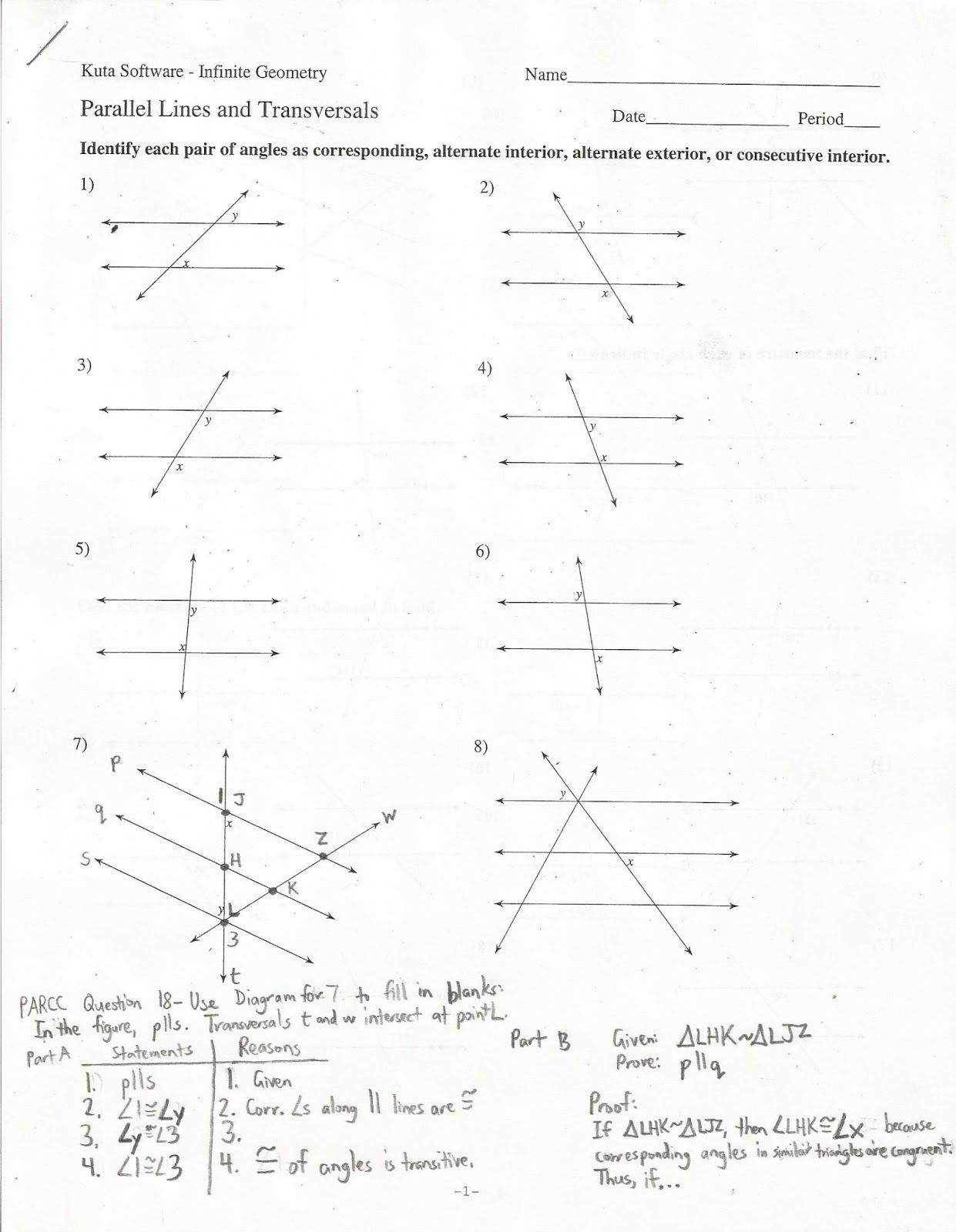
5 Properties of Matter to Know

Understanding the Properties of Matter
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space by having volume. All physical objects in the universe are composed of matter, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest structures. To comprehend the nature of matter, it is essential to be familiar with its fundamental properties. These properties help in identifying and distinguishing one substance from another. Here are five key properties of matter that you should know:
1. Mass
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a fundamental property that does not change regardless of the object’s location in the universe. Unlike weight, which can vary depending on the gravitational force acting on an object, mass remains constant. For example, if you were to travel to the moon, your weight would decrease due to the moon’s lower gravity, but your mass would remain the same.
2. Volume
Volume is the amount of three-dimensional space that is occupied by a substance. It is typically measured in cubic units such as cubic meters (m³) or cubic centimeters (cm³). The volume of an object can change depending on external conditions such as temperature and pressure. For instance, when water freezes, its volume expands, and when it melts, its volume decreases.
3. Density
Density is defined as the mass per unit volume of a substance. It is calculated by dividing the mass of an object by its volume (density = mass/volume). Density is a unique property of each substance, allowing us to distinguish between different materials. For example, the density of water is approximately 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), while the density of iron is about 7.9 g/cm³.
4. Melting and Boiling Points
The melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes state from solid to liquid. The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes state from liquid to gas. These points are specific to each substance and can be used to identify and characterize materials. For instance, the melting point of ice is 0 degrees Celsius (°C) at standard pressure, and the boiling point of water is 100°C at standard pressure.
5. Solubility
Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, typically a liquid. It is a measure of the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature and pressure. Solubility varies greatly among different substances and is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the chemical properties of the solute and solvent. For example, sugar is highly soluble in water, while oil is not.
🔍 Note: Understanding the properties of matter is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
To further illustrate the concept of these properties, let’s consider a simple example:
Example:
Suppose you have a glass of water at room temperature.
- The mass of the water is constant, regardless of the location of the glass.
- The volume of the water is approximately equal to the volume of the glass.
- The density of the water is around 1 g/cm³, which is a characteristic property of water.
- The melting point of the water is 0°C, and the boiling point is 100°C.
- The solubility of sugar in water is high, allowing you to easily dissolve sugar in the water.
In conclusion, the properties of matter are essential in understanding the behavior and characteristics of various substances. By familiarizing yourself with these properties, you can better comprehend the world around you and make informed decisions in various fields of study.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
+Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Mass remains constant, while weight can vary depending on the gravitational force acting on an object.
How does temperature affect the volume of a substance?
+Temperature can cause a substance to expand or contract, resulting in a change in volume. For example, water expands when it freezes and contracts when it melts.
What is the significance of solubility in everyday life?
+Solubility plays a crucial role in various applications, such as cooking, cleaning, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding solubility helps us to select the appropriate solvents and solutes for specific tasks.