Cell Differences: Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answers
Understanding Cell Structure: Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
Cells are the basic units of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. While both types of cells perform similar functions, such as metabolizing energy and reproducing, they have distinct differences in terms of their structure, organization, and complexity.
Prokaryotic Cells
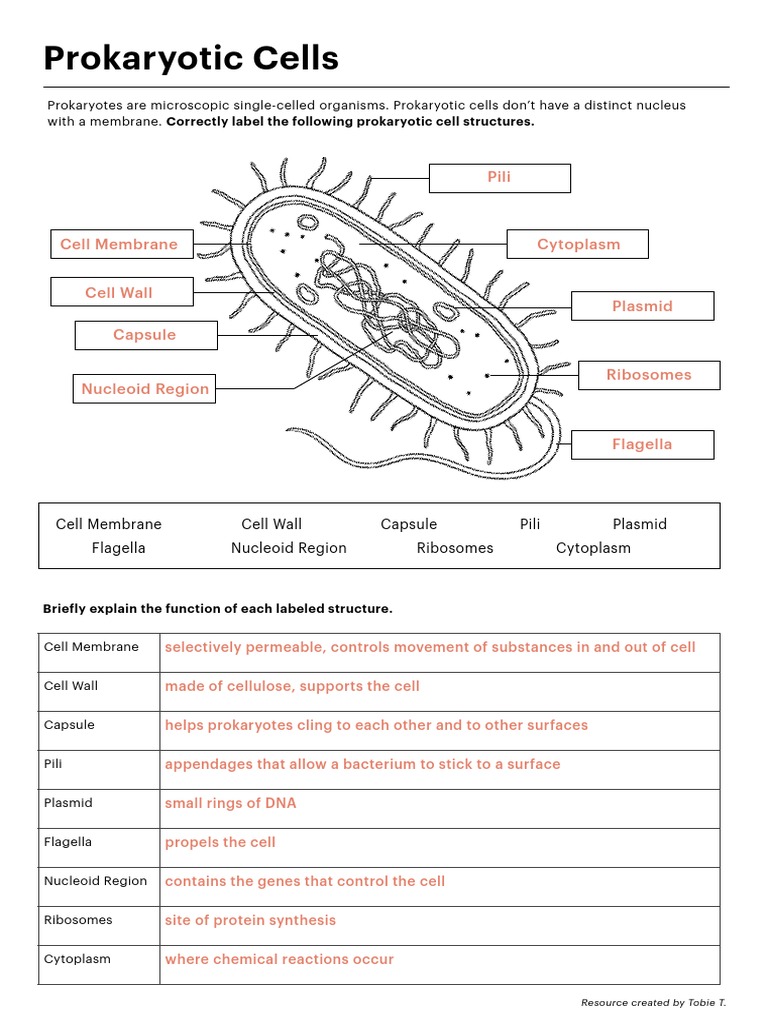
Prokaryotic cells are the simplest and most ancient type of cells. They lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The characteristics of prokaryotic cells include:
- Lack of a true nucleus: Prokaryotic cells do not have a membrane-bound nucleus. Instead, their genetic material is found in a single circular chromosome that is located in the cytoplasm.
- Small size: Prokaryotic cells are typically small, ranging from 1-5 micrometers in size.
- Simple structure: Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles and have a simple structure.
- Rapid reproduction: Prokaryotic cells can reproduce rapidly, with some species able to divide in as little as 15-20 minutes.
Examples of prokaryotic cells include bacteria, such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and evolved than prokaryotic cells. They have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The characteristics of eukaryotic cells include:
- True nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus that contains their genetic material.
- Large size: Eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells, ranging from 10-100 micrometers in size.
- Complex structure: Eukaryotic cells have a complex structure with membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- Slower reproduction: Eukaryotic cells reproduce more slowly than prokaryotic cells, with some species taking hours or even days to divide.
Examples of eukaryotic cells include plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Comparison of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Characteristics | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | No true nucleus | True nucleus |
| Size | Small (1-5 micrometers) | Large (10-100 micrometers) |
| Structure | Simple | Complex |
| Reproduction | Rapid (15-20 minutes) | Slower (hours or days) |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Membrane-bound organelles (e.g. mitochondria, chloroplasts) |
📝 Note: This table highlights the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Key Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- Presence of a true nucleus: Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not.
- Size and complexity: Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells.
- Organelles: Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells do not.
- Reproduction: Prokaryotic cells reproduce more rapidly than eukaryotic cells.
In conclusion, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are two distinct types of cells that have evolved to perform different functions. Understanding the differences between these two types of cells is essential for understanding the complexity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
+The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence of a true nucleus. Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not.
Which type of cell is larger?
+Eukaryotic cells are larger than prokaryotic cells, ranging from 10-100 micrometers in size.
Which type of cell reproduces more rapidly?
+Prokaryotic cells reproduce more rapidly than eukaryotic cells, with some species able to divide in as little as 15-20 minutes.
Related Terms:
- Eukaryotic cell worksheet answers
- Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells PDF
- Prokaryotic cells Worksheet Answer Key