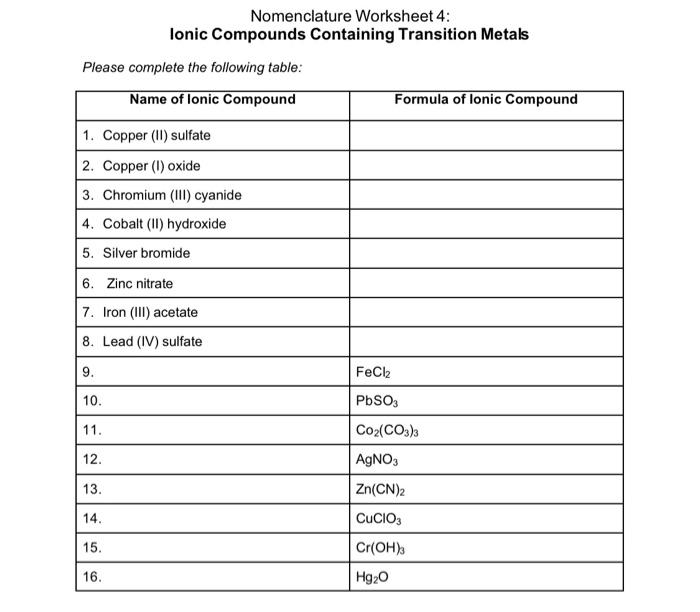
Nurse Dosage Calculation Practice Worksheets
Mastering Dosage Calculations: A Guide for Nurses
Dosage calculations are a critical aspect of nursing practice, requiring precision and attention to detail to ensure patient safety. As a nurse, it’s essential to master dosage calculations to administer medications accurately and effectively. In this article, we’ll provide you with practice worksheets and tips to help you improve your dosage calculation skills.
Understanding Dosage Calculations
Dosage calculations involve determining the correct dose of a medication based on a patient’s specific needs. This requires considering factors such as the patient’s weight, age, medical condition, and the medication’s recommended dosage range.
Key Concepts:
- Dose: The amount of medication administered to a patient at one time.
- Dosage: The total amount of medication administered to a patient over a specific period.
- Concentration: The amount of medication per unit volume or weight.
Practice Worksheets
Here are five practice worksheets to help you improve your dosage calculation skills. Each worksheet includes a scenario, medication order, and calculation question.
Worksheet 1:
Scenario: A patient weighs 70 kg and is prescribed 2 mg/kg of acetaminophen (Tylenol) every 6 hours.
Medication Order: Acetaminophen 140 mg PO every 6 hours.
Calculation Question: How many milligrams of acetaminophen should the patient receive per dose?
Answer: _______
Worksheet 2:
Scenario: A patient is prescribed 500 mg of amoxicillin (Amoxil) every 8 hours. The medication is available in 250 mg capsules.
Medication Order: Amoxicillin 250 mg PO every 8 hours.
Calculation Question: How many capsules should the patient receive per dose?
Answer: _______
Worksheet 3:
Scenario: A patient weighs 40 kg and is prescribed 1 mg/kg of furosemide (Lasix) IV every 12 hours.
Medication Order: Furosemide 40 mg IV every 12 hours.
Calculation Question: How many milligrams of furosemide should the patient receive per dose?
Answer: _______
Worksheet 4:
Scenario: A patient is prescribed 10 mg of lisinopril (Zestril) PO every 24 hours. The medication is available in 5 mg tablets.
Medication Order: Lisinopril 5 mg PO every 24 hours.
Calculation Question: How many tablets should the patient receive per dose?
Answer: _______
Worksheet 5:
Scenario: A patient weighs 60 kg and is prescribed 2 mg/kg of morphine sulfate IV every 4 hours.
Medication Order: Morphine sulfate 120 mg IV every 4 hours.
Calculation Question: How many milligrams of morphine sulfate should the patient receive per dose?
Answer: _______
Tips for Mastering Dosage Calculations
- Read medication orders carefully: Ensure you understand the medication, dose, and frequency before performing calculations.
- Use a consistent formula: Use the formula D = (A x B) / C, where D = dose, A = amount, B = body weight, and C = concentration.
- Double-check calculations: Verify calculations with a colleague or use a calculator to ensure accuracy.
- Consider patient-specific factors: Take into account patient age, weight, and medical condition when performing calculations.
- Practice regularly: Regular practice helps reinforce dosage calculation skills and builds confidence.
💡 Note: Always verify medication orders with a healthcare provider or pharmacist before administering medications to patients.
Conclusion
Mastering dosage calculations is essential for nurses to ensure patient safety and effective medication administration. By practicing with these worksheets and following the tips outlined in this article, you’ll become more confident and proficient in your dosage calculation skills.
What is the purpose of dosage calculations in nursing?
+The purpose of dosage calculations is to determine the correct dose of a medication based on a patient’s specific needs, ensuring accurate and safe medication administration.
What factors should be considered when performing dosage calculations?
+Factors to consider include patient age, weight, medical condition, and the medication’s recommended dosage range.
How can I improve my dosage calculation skills?
+Practice regularly, use a consistent formula, double-check calculations, and consider patient-specific factors to improve your dosage calculation skills.