6 Key Differences: Photosynthesis vs Cellular Respiration
Understanding the Two Essential Processes in Living Organisms
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes that occur in living organisms. While they are related and interdependent, they have distinct differences in terms of their functions, reactants, products, and energy transformations. In this article, we will delve into the six key differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, helping you understand the intricacies of these vital processes.
Difference 1: Purpose and Function
Photosynthesis: The primary function of photosynthesis is to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds, such as glucose. This process occurs in plants, algae, and some bacteria, and is essential for producing the energy and organic compounds needed to support life on Earth.
Cellular Respiration: In contrast, the primary function of cellular respiration is to convert chemical energy from glucose and other organic molecules into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This process occurs in the cells of all living organisms, including animals, plants, and microorganisms, and is necessary for the proper functioning of cells.
Difference 2: Reactants and Products
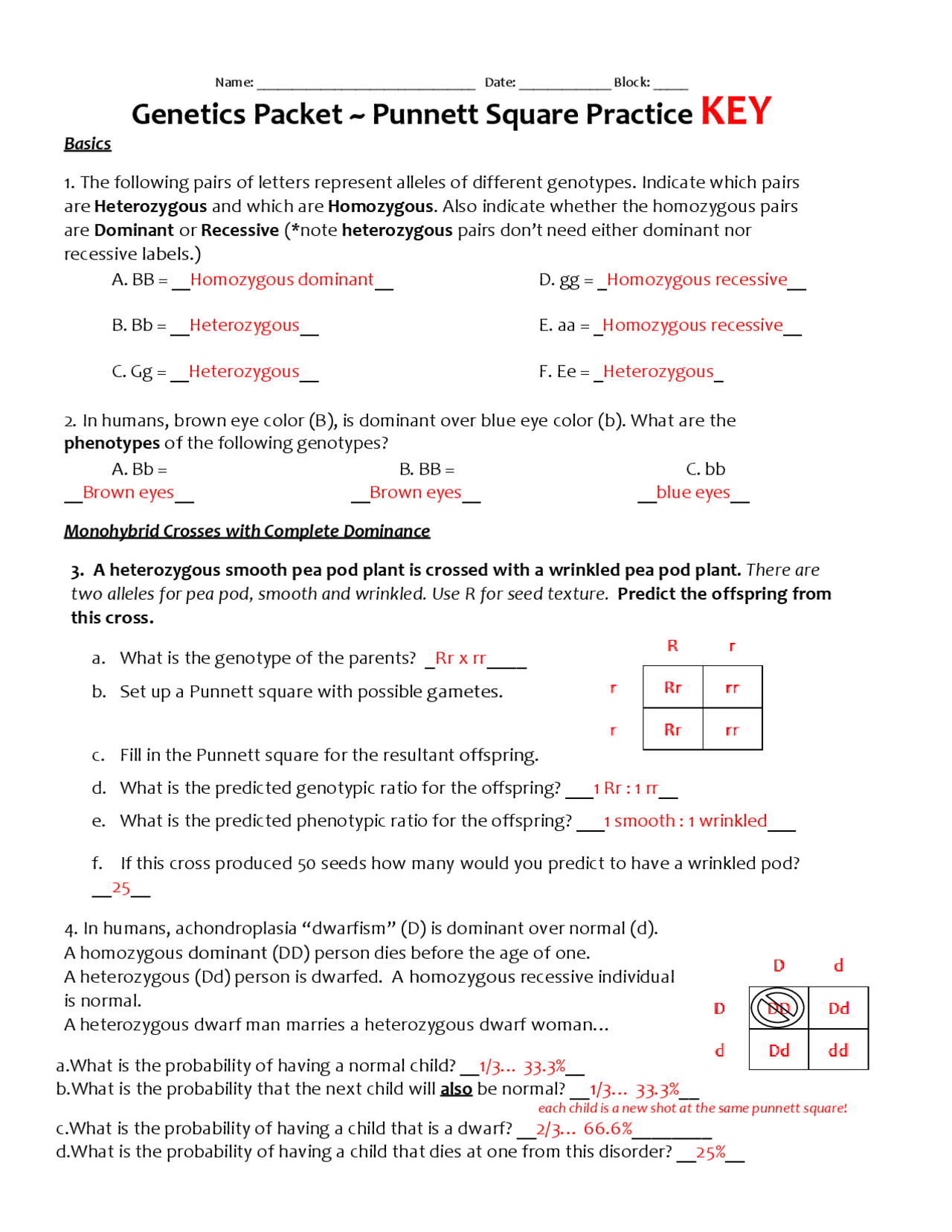
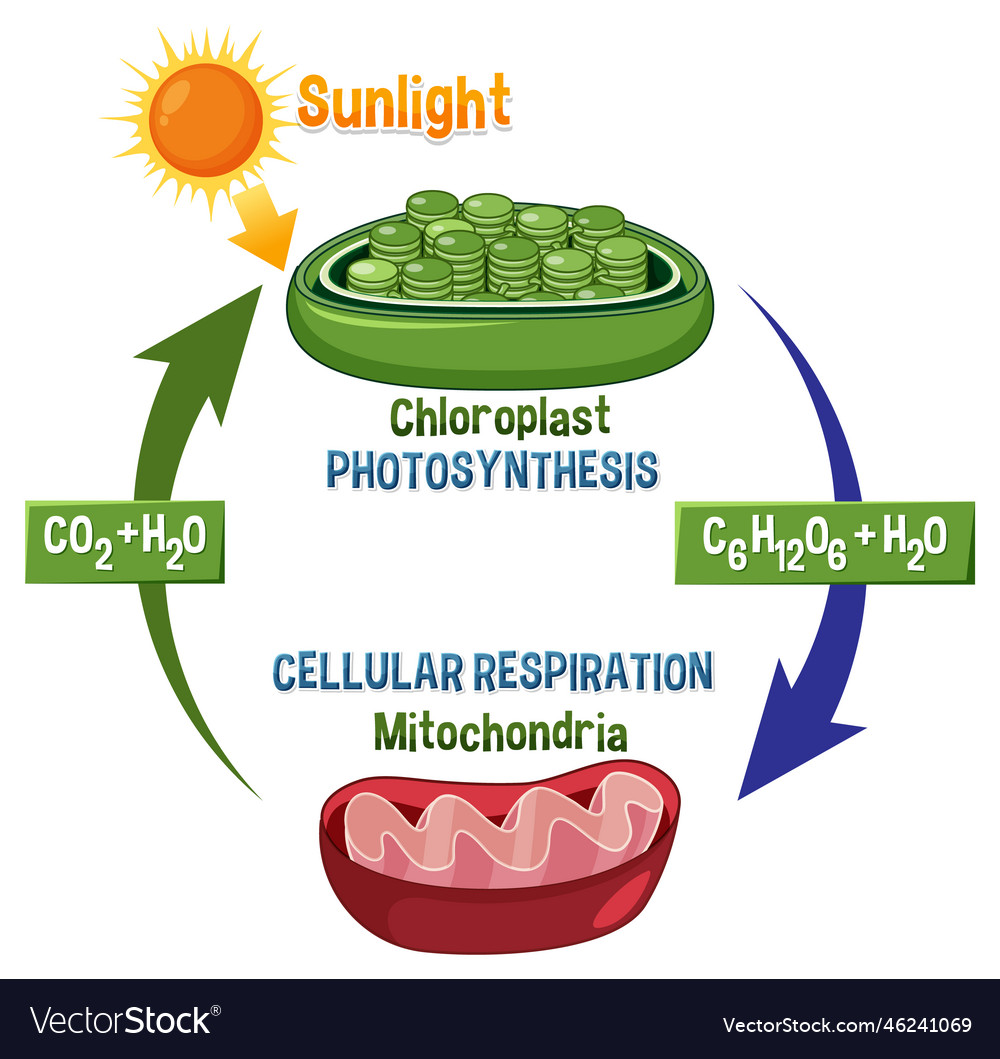
Photosynthesis: The reactants of photosynthesis are:
- Light energy from the sun
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Water (H2O)
The products of photosynthesis are:
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Oxygen (O2)
Cellular Respiration: The reactants of cellular respiration are:
- Glucose (C6H12O6)
- Oxygen (O2)
The products of cellular respiration are:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Water (H2O)
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Difference 3: Energy Transformation
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of glucose molecules. This process requires energy from the sun and occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration involves the conversion of chemical energy from glucose into ATP, which is then used to power the cell’s various activities. This process releases energy from the bonds of glucose molecules and occurs in the mitochondria.
Difference 4: Location and Organelles
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts, which are found in plant cells, algae, and some bacteria. Chloroplasts contain pigments such as chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria, which are found in the cells of all living organisms. Mitochondria are often referred to as the “powerhouses” of the cell, as they generate most of the energy that the cell needs to function.
Difference 5: Energy Yield
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis produces a net gain of energy, as light energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This process requires energy from the sun, but produces a net yield of energy that is stored in the bonds of glucose molecules.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration produces a net release of energy, as chemical energy from glucose is converted into ATP. This process releases energy from the bonds of glucose molecules, which is then used to power the cell’s various activities.
Difference 6: Oxygen Requirements
Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis does not require oxygen, as it uses light energy from the sun to produce glucose and oxygen.
Cellular Respiration: Cellular respiration requires oxygen, as it uses oxygen to convert glucose into ATP and releases carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.
👍 Note: While photosynthesis and cellular respiration have distinct differences, they are interdependent processes that work together to sustain life on Earth. Photosynthesis produces the glucose and oxygen needed for cellular respiration, while cellular respiration produces the ATP needed to power the cell's various activities.
As we conclude our discussion of the six key differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration, it is clear that these two processes are fundamental to life on Earth. Understanding the intricacies of these processes can help us appreciate the complex interplay between light energy, chemical energy, and life itself.
What is the primary function of photosynthesis?
+The primary function of photosynthesis is to convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy in the form of organic compounds, such as glucose.
What is the primary function of cellular respiration?
+The primary function of cellular respiration is to convert chemical energy from glucose and other organic molecules into energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What is the energy transformation in photosynthesis?
+Photosynthesis involves the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, which is stored in the bonds of glucose molecules.