Mitosis Phases Worksheet Explained

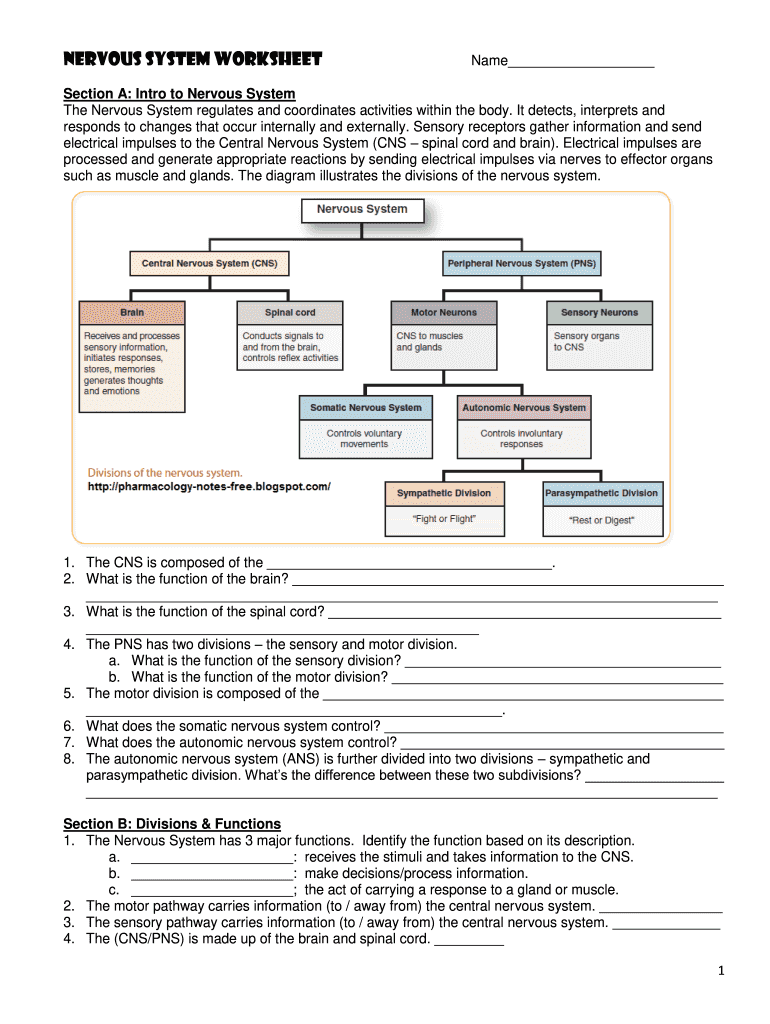
Understanding the Phases of Mitosis: A Comprehensive Guide
Mitosis is a fundamental process in biology where a cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. It’s crucial for growth, repair, and reproduction in eukaryotic organisms. The process of mitosis is divided into several phases, each with distinct characteristics and functions. In this guide, we’ll break down the phases of mitosis and provide a detailed explanation of each step.
Interphase: The Preparation Phase
Before mitosis begins, the cell goes through a period called interphase. During this phase, the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division. Interphase consists of three stages: Gap 1 (G1), Synthesis (S), and Gap 2 (G2).
- Gap 1 (G1): The cell grows and prepares for DNA replication.
- Synthesis (S): The cell replicates its DNA, resulting in two identical sets of chromosomes.
- Gap 2 (G2): The cell prepares for cell division by producing organelles and proteins needed for mitosis.
Prophase: Chromosome Condensation and Nuclear Envelope Breakdown
Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, where the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Chromosome condensation: The replicated chromosomes condense into visible, thread-like structures.
- Nuclear envelope breakdown: The nuclear envelope breaks down, releasing the chromosomes into the cytoplasm.
- Spindle fibers formation: The centrioles (microtubule organizing centers) begin to form spindle fibers that will separate the chromosomes during mitosis.
Metaphase: Chromosome Alignment
During metaphase, the chromosomes align at the center of the cell, attached to the spindle fibers.
- Chromosome alignment: The chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate, ensuring each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
- Spindle fibers attachment: The spindle fibers attach to the centromeres (specialized regions on the chromosomes) to prepare for chromosome separation.
Anaphase: Chromosome Separation
Anaphase is the phase where the sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Sister chromatid separation: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Spindle fibers contraction: The spindle fibers contract, pulling the sister chromatids apart.
Telophase: Nuclear Envelope Reformation
Telophase is the phase where the nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Nuclear envelope reformation: The nuclear envelope reforms around each set of chromosomes.
- Chromosome uncoiling: The chromosomes uncoil, returning to their interphase structure.
Cytokinesis: Cell Division
Cytokinesis is the final phase of mitosis, where the cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
- Cytokinesis in animal cells: A cleavage furrow forms, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
- Cytokinesis in plant cells: A cell plate forms, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
📝 Note: Cytokinesis is not technically a phase of mitosis but rather a separate process that occurs after mitosis is complete.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the phases of mitosis are a complex and highly regulated process that ensures the proper distribution of genetic material during cell division. Understanding each phase is crucial for appreciating the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular reproduction and growth. By mastering the phases of mitosis, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles of biology.
What is the primary purpose of mitosis?
+The primary purpose of mitosis is to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, ensuring the continuation of the species and the repair of damaged tissues.
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+Mitosis produces two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, while meiosis produces four daughter cells with unique combinations of chromosomes, resulting in genetic variation.
What is the significance of the spindle fibers in mitosis?
+The spindle fibers play a crucial role in separating the sister chromatids during anaphase, ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
Related Terms:
- Mitosis Worksheet PDF
- Mitosis Worksheet answer key PDF
- Mitosis Worksheet free
- Mitosis diagram Worksheet pdf