5 Operant Conditioning Examples You Need to Know
Understanding Operant Conditioning: A Powerful Tool for Behavior Modification
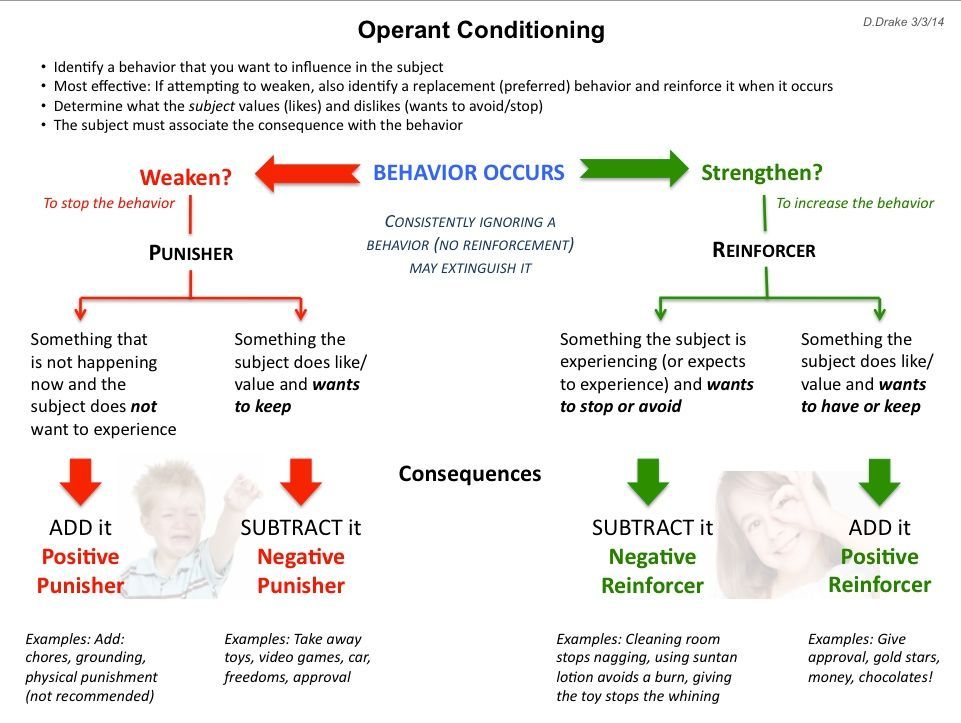
Operant conditioning is a type of learning process in which the strength of a behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment. It is also known as instrumental conditioning, as the behavior is modified by its consequences. This concept was first introduced by psychologist B.F. Skinner and is widely used in various fields, including psychology, education, and animal training.
In this article, we will explore five operant conditioning examples that demonstrate how this concept works in real-life situations.
Example 1: Rewards and Praise in the Classroom
In a classroom setting, a teacher uses positive reinforcement to encourage good behavior in students. When a student answers a question correctly, the teacher gives them a sticker or verbal praise. This positive reinforcement increases the likelihood of the student answering questions correctly in the future.
- Behavior: Answering questions correctly
- Consequence: Sticker or verbal praise
- Result: Increased likelihood of answering questions correctly
📚 Note: Positive reinforcement is a powerful tool in operant conditioning, as it encourages desired behavior without using punishment or negative reinforcement.
Example 2: Token Economy in a Workplace
In a workplace, a manager implements a token economy system to encourage employees to meet their sales targets. For every sale made, an employee receives a token that can be redeemed for rewards, such as gift cards or extra time off. This system motivates employees to work harder to meet their targets and earn more tokens.
- Behavior: Meeting sales targets
- Consequence: Tokens that can be redeemed for rewards
- Result: Increased sales and productivity
Example 3: Punishment and Fines for Traffic Violations
When a driver exceeds the speed limit, they receive a fine or penalty. This punishment decreases the likelihood of the driver speeding in the future.
- Behavior: Speeding
- Consequence: Fine or penalty
- Result: Decreased likelihood of speeding
🚗 Note: Punishment is a type of operant conditioning that decreases the likelihood of a behavior by associating it with an unpleasant consequence.
Example 4: Variable Ratio Scheduling in Animal Training
In animal training, a variable ratio schedule is used to encourage desired behavior. For example, a trainer rewards a dog with treats at unpredictable intervals for performing a trick. This schedule creates a high level of motivation, as the dog is never sure when the reward will come.
- Behavior: Performing a trick
- Consequence: Treats at unpredictable intervals
- Result: High level of motivation and consistent behavior
Example 5: Negative Reinforcement in a Therapeutic Setting
In a therapeutic setting, a patient undergoes a painful medical procedure. To alleviate the pain, the patient can press a button that administers a pain-relieving medication. This negative reinforcement encourages the patient to press the button to escape the pain.
- Behavior: Pressing the button
- Consequence: Relief from pain
- Result: Increased likelihood of pressing the button to escape pain
💊 Note: Negative reinforcement is a type of operant conditioning that increases the likelihood of a behavior by removing an unpleasant stimulus.
In conclusion, operant conditioning is a powerful tool for modifying behavior. By understanding the different types of reinforcement and punishment, we can apply this concept in various fields to encourage desired behavior and achieve our goals.
What is the difference between positive and negative reinforcement?
+Positive reinforcement adds a pleasing stimulus to the environment, increasing the likelihood of a behavior. Negative reinforcement removes an unpleasant stimulus, also increasing the likelihood of a behavior.
Can operant conditioning be used to modify complex behaviors?
+Yes, operant conditioning can be used to modify complex behaviors by breaking them down into smaller components and reinforcing each step in the process.
What is the role of punishment in operant conditioning?
+Punishment is used to decrease the likelihood of a behavior by associating it with an unpleasant consequence. However, punishment should be used judiciously, as it can have unintended consequences, such as fear and anxiety.