Operant Conditioning Made Easy: A Beginner's Worksheet Guide
Understanding Operant Conditioning: A Beginner's Guide
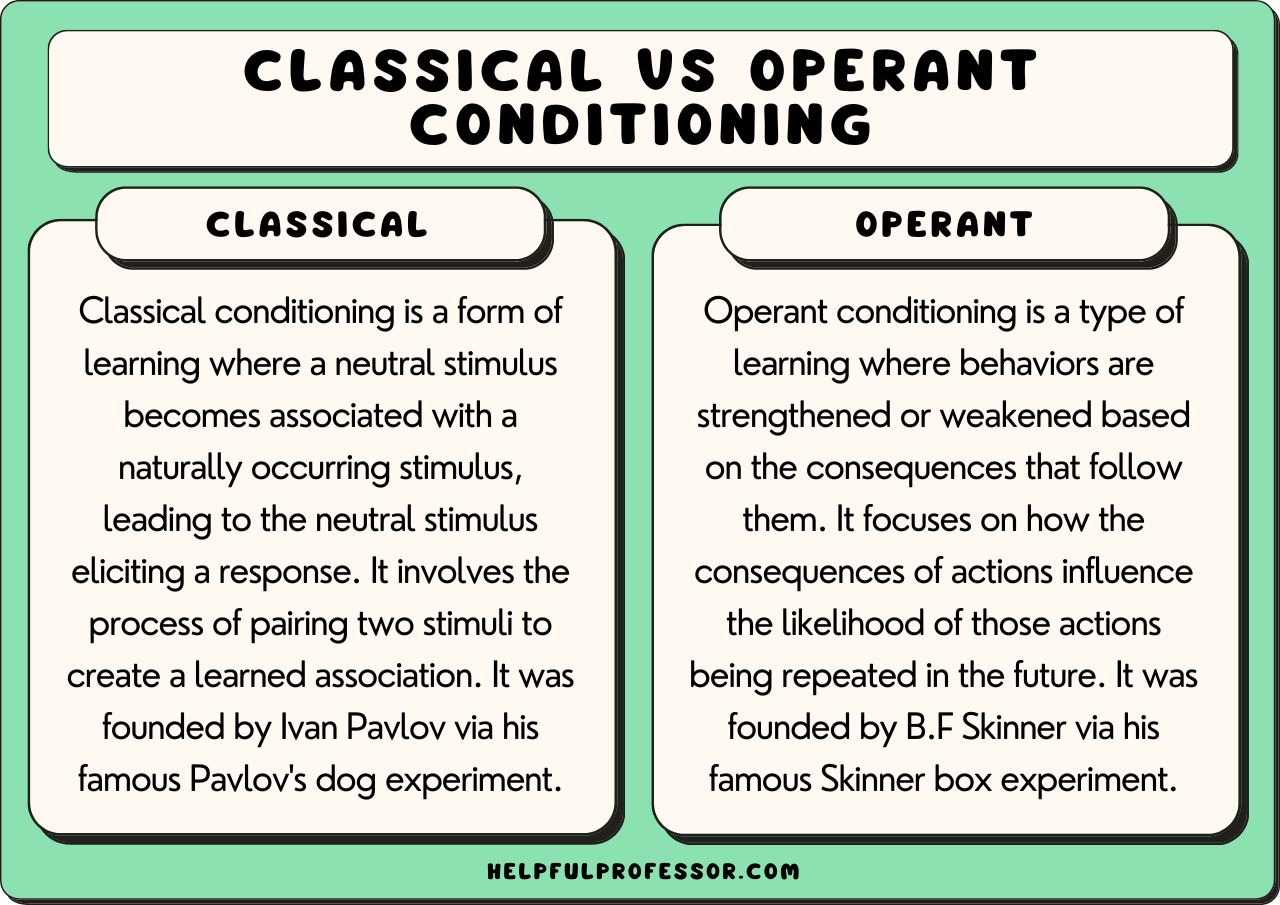
Operant conditioning is a fundamental concept in psychology that explains how behavior is modified by its consequences. Developed by B.F. Skinner, operant conditioning is a crucial aspect of understanding human behavior and learning. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the basics of operant conditioning, its key components, and provide a worksheet to help you practice and reinforce your understanding.
What is Operant Conditioning?
Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is modified by its consequences, such as rewards or punishments. The behavior is “operant” because it operates on the environment to produce a consequence. The goal of operant conditioning is to understand how behavior is controlled by its environment and how it can be modified to achieve desired outcomes.
Key Components of Operant Conditioning
There are several key components of operant conditioning that you need to understand:
- Behavior: The action or response that is being modified.
- Consequence: The event that follows the behavior, such as a reward or punishment.
- Stimulus: The event or situation that triggers the behavior.
- Reinforcer: A consequence that increases the frequency of the behavior.
- Punisher: A consequence that decreases the frequency of the behavior.
Types of Reinforcers
There are several types of reinforcers that can be used to increase the frequency of a behavior:
- Positive Reinforcer: A pleasing or desirable consequence, such as a reward or praise.
- Negative Reinforcer: The removal of an unpleasant or aversive consequence.
- Primary Reinforcer: A natural or innate reinforcer, such as food or water.
- Secondary Reinforcer: A learned reinforcer, such as money or tokens.
Types of Punishers
There are several types of punishers that can be used to decrease the frequency of a behavior:
- Positive Punisher: An unpleasant or aversive consequence, such as a fine or scolding.
- Negative Punisher: The removal of a pleasing or desirable consequence.
Schedules of Reinforcement
Schedules of reinforcement refer to the frequency and timing of reinforcement. There are several types of schedules:
- Fixed-Ratio Schedule: Reinforcement is provided after a fixed number of responses.
- Variable-Ratio Schedule: Reinforcement is provided after an unpredictable number of responses.
- Fixed-Interval Schedule: Reinforcement is provided at fixed intervals, regardless of the number of responses.
- Variable-Interval Schedule: Reinforcement is provided at unpredictable intervals.
Worksheet: Operant Conditioning in Action
Now that you have a basic understanding of operant conditioning, it’s time to practice with a worksheet. Please complete the following exercises:
| Scenario | Behavior | Consequence | Reinforcer/Punisher |
|---|---|---|---|
| A child cleans their room and receives praise from their parent. | Cleaning the room | Praise from parent | Positive Reinforcer |
| An employee arrives late to work and is docked a day's pay. | Arriving late to work | Docked pay | Positive Punisher |
| A student studies for an exam and receives a good grade. | Studying for the exam | Good grade | Secondary Reinforcer |
| A person smokes a cigarette and experiences a nicotine rush. | Smoking a cigarette | Nicotine rush | Primary Reinforcer |
📝 Note: Please complete the worksheet by filling in the blanks with the correct answers.
Conclusion
Operant conditioning is a powerful tool for understanding and modifying behavior. By understanding the key components and schedules of reinforcement, you can apply operant conditioning principles in various settings, from education to personal development. Remember to practice and reinforce your understanding with real-life scenarios and worksheets.
What is the difference between a positive and negative reinforcer?
+A positive reinforcer is a pleasing or desirable consequence, such as a reward or praise. A negative reinforcer is the removal of an unpleasant or aversive consequence.
What is the purpose of a schedule of reinforcement?
+The purpose of a schedule of reinforcement is to determine the frequency and timing of reinforcement, which can affect the strength and duration of the behavior.
Can operant conditioning be used to modify complex behaviors?
+Yes, operant conditioning can be used to modify complex behaviors by breaking them down into smaller components and reinforcing each step of the process.