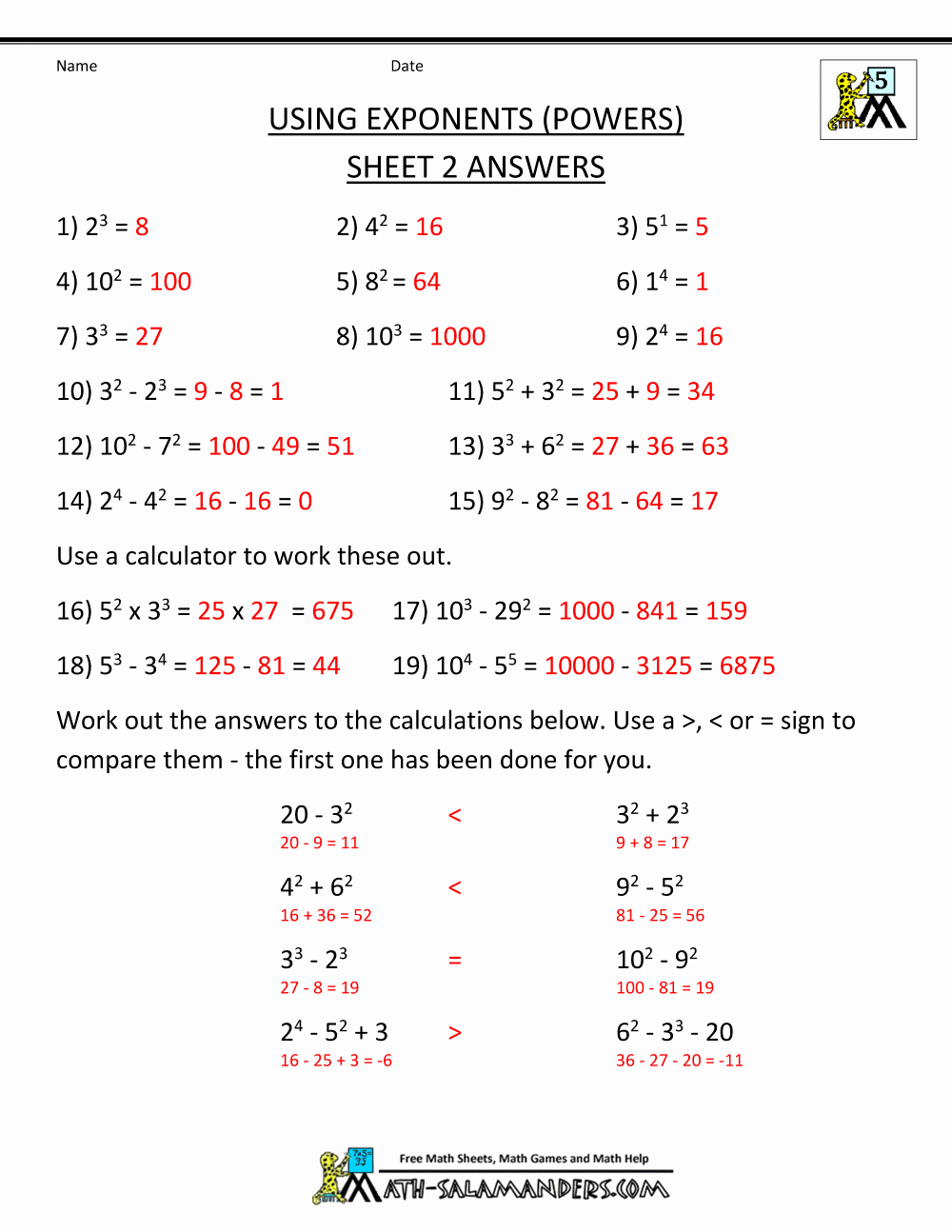
Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers for Easy Learning
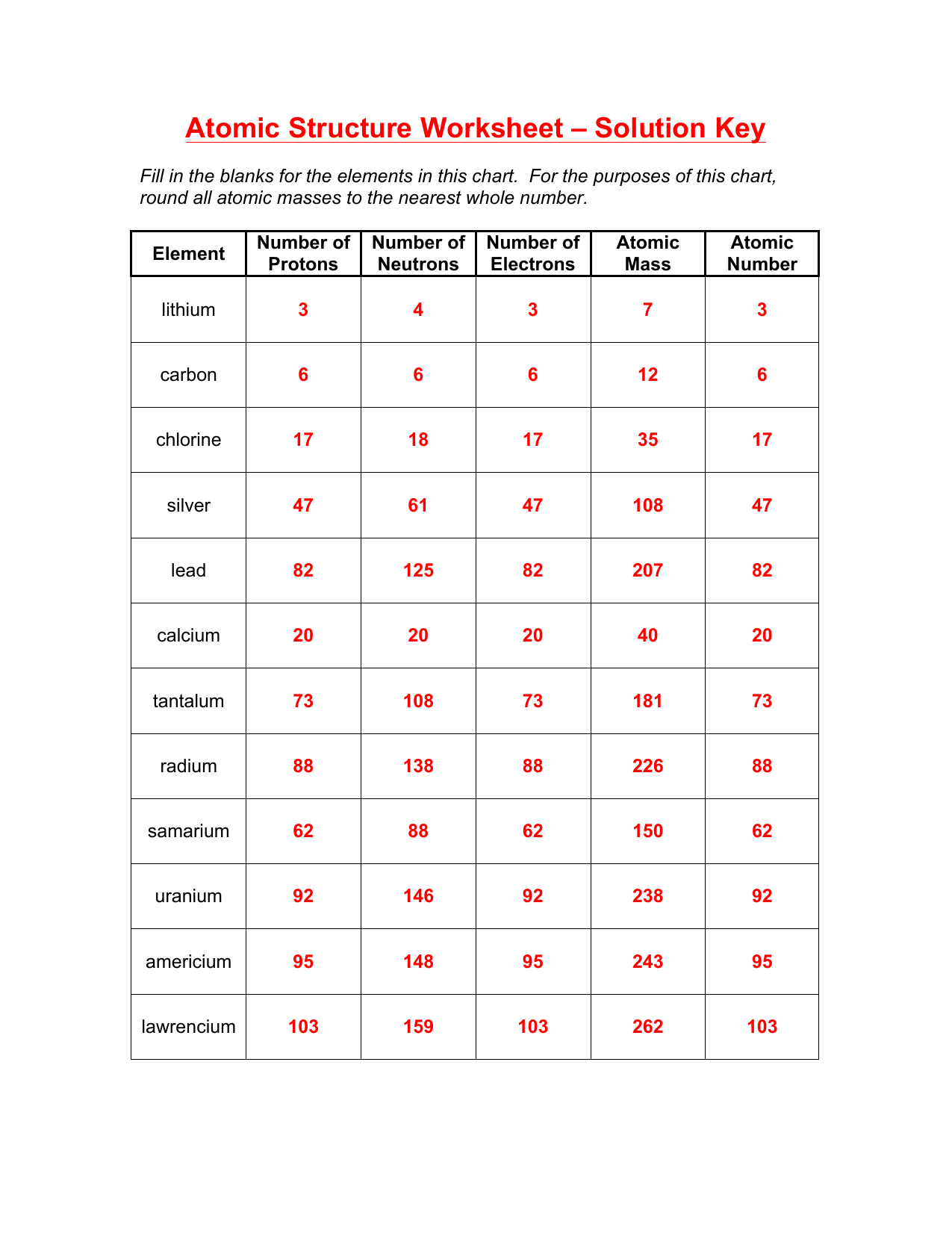
Atomic Structure: Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter
Atomic structure is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics that describes the composition of atoms, the basic building blocks of matter. Atoms are the smallest units of a chemical element, and understanding their structure is crucial for understanding the properties and behavior of matter.
What is an Atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element. Atoms are composed of three main parts:
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus.
Subatomic Particles: A Closer Look
- Protons:
- Charge: +1
- Mass: 1 atomic mass unit (amu)
- Location: Nucleus
- Neutrons:
- Charge: 0
- Mass: 1 amu
- Location: Nucleus
- Electrons:
- Charge: -1
- Mass: 1⁄1836 amu (negligible compared to protons and neutrons)
- Location: Orbitals around the nucleus
Atomic Number and Mass Number
- Atomic Number (Z): The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus, which defines the element.
- Mass Number (A): The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus, which determines the atom’s mass.
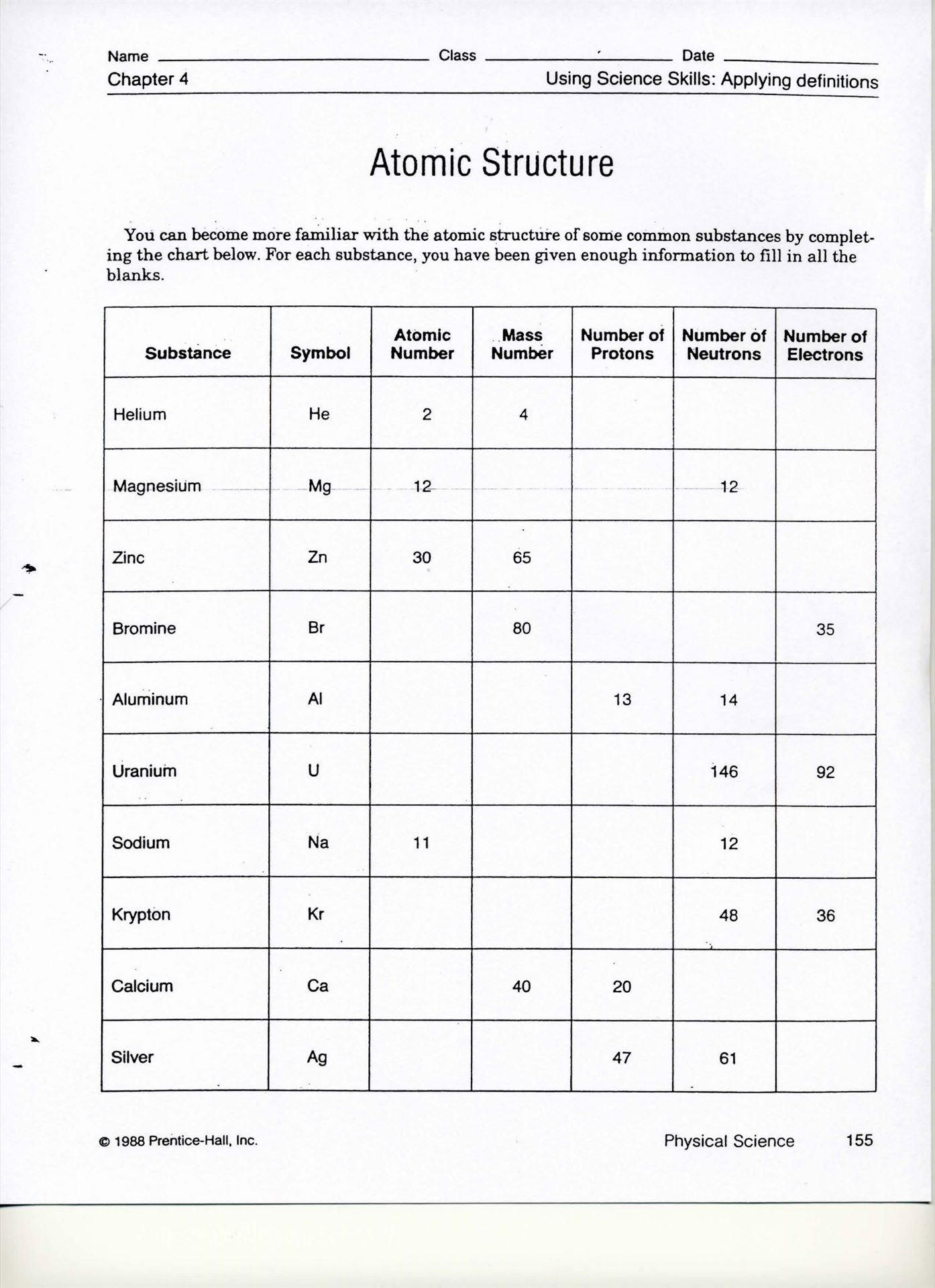
| Element | Atomic Number (Z) | Mass Number (A) |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 1 |
| Helium | 2 | 4 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 16 |
Energy Levels and Electron Configuration
Energy Levels: Electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
Electron Configuration: The arrangement of electrons in an atom’s energy levels, which determines the atom’s chemical properties.
Aufbau Principle: Electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.
Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each energy level can hold a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposite spins.
Hund’s Rule: Electrons occupy empty energy levels before pairing up with other electrons.
Key Concepts to Remember
- Atoms are the smallest units of a chemical element.
- Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the subatomic particles that make up an atom.
- Atomic number and mass number are used to identify and describe atoms.
- Energy levels and electron configuration determine an atom’s chemical properties.
📝 Note: Understanding atomic structure is crucial for understanding the properties and behavior of matter.
Worksheets and Practice Problems
For a deeper understanding of atomic structure, try solving these practice problems:
- What is the atomic number and mass number of an atom with 10 protons and 12 neutrons?
- Draw the electron configuration for an atom with 6 electrons.
- What is the Aufbau principle, and how does it relate to electron configuration?
Answers:
- Atomic number: 10, Mass number: 22
- Electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p²
- The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels.
What is the smallest unit of a chemical element?
+An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element.
What are the three main parts of an atom?
+Protons, neutrons, and electrons are the three main parts of an atom.
What is the atomic number, and how is it used?
+The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, which defines the element.
The key to mastering atomic structure is practice and repetition. By understanding the basics of atomic structure, you’ll be well on your way to a deeper understanding of chemistry and physics. Remember to practice, practice, practice, and you’ll become a pro at atomic structure in no time!
Related Terms:
- Atomic Structure Worksheet pdf