Exploring Molecules and Atoms: A Science Worksheet Guide
Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms and molecules are the fundamental building blocks of matter, and understanding their structure and properties is crucial for any science enthusiast. This worksheet guide is designed to help students and learners of all ages explore the fascinating world of atoms and molecules.
Atomic Structure
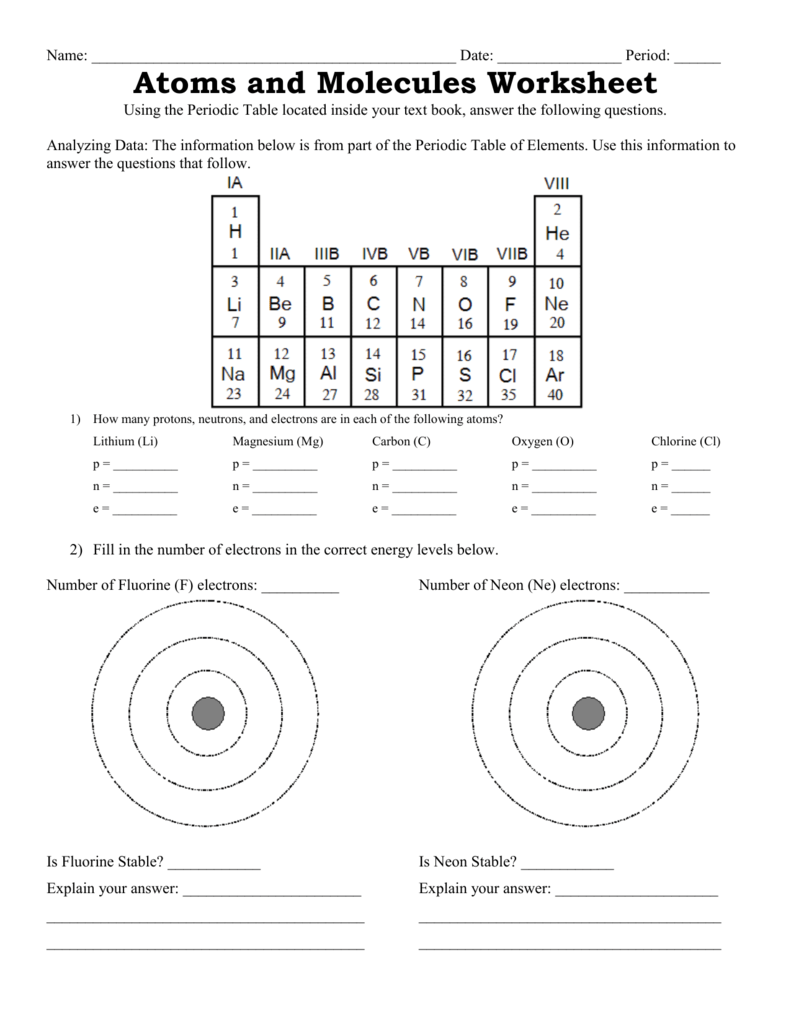
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element, and it consists of three main parts: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus (center) of the atom.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus.
The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms. For example, hydrogen has one proton, helium has two protons, and oxygen has eight protons.
💡 Note: The number of protons in an atom is also known as the atomic number.
Molecular Structure
A molecule is a group of atoms that are chemically bonded together. Molecules can be made up of atoms of the same element (such as oxygen gas, O2) or different elements (such as water, H2O).
- Chemical Bonds: Atoms share or exchange electrons to form chemical bonds, which hold the atoms together in a molecule.
- Molecular Formula: A way of expressing the number of atoms of each element in a molecule, using chemical symbols and numbers.
For example, the molecular formula for water is H2O, indicating that one molecule of water consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Types of Chemical Bonds
There are several types of chemical bonds that can form between atoms, including:
- Ionic Bonds: Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges.
- Covalent Bonds: Formed when two or more atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
- Hydrogen Bonds: A type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine).
Worksheet Activities
Now it’s time to put your knowledge of atoms and molecules to the test! Complete the following worksheet activities:
- Activity 1: Atomic Structure
- Draw a diagram of the atomic structure of hydrogen, helium, and oxygen.
- Label the protons, neutrons, and electrons in each atom.
- Activity 2: Molecular Formula
- Write the molecular formula for the following molecules: CO2, CH4, and NH3.
- Identify the number of atoms of each element in each molecule.
- Activity 3: Chemical Bonds
- Identify the type of chemical bond that forms between the following atoms: Na and Cl, H and O, and C and O.
- Explain why each type of bond forms.
Additional Resources
- Online Simulations: Explore online simulations of atomic and molecular structures, such as PhET Interactive Simulations or Molecular Workbench.
- Science Videos: Watch videos on atomic and molecular structure, such as Crash Course Chemistry or Khan Academy.
📚 Note: For more advanced learners, explore topics such as quantum mechanics, molecular orbitals, and spectroscopy.
In summary, understanding the structure and properties of atoms and molecules is essential for any science enthusiast. By completing the worksheet activities and exploring additional resources, learners can gain a deeper appreciation for the fascinating world of atoms and molecules.
What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
+An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element, while a molecule is a group of atoms that are chemically bonded together.
What is the atomic number of an element?
+The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in an atom of that element.
What type of chemical bond forms between atoms with a large difference in electronegativity?
+An ionic bond forms between atoms with a large difference in electronegativity.
Related Terms:
- Atoms and molecules Worksheet PDF