Mastering Molecular Geometry with This Essential Worksheet Guide
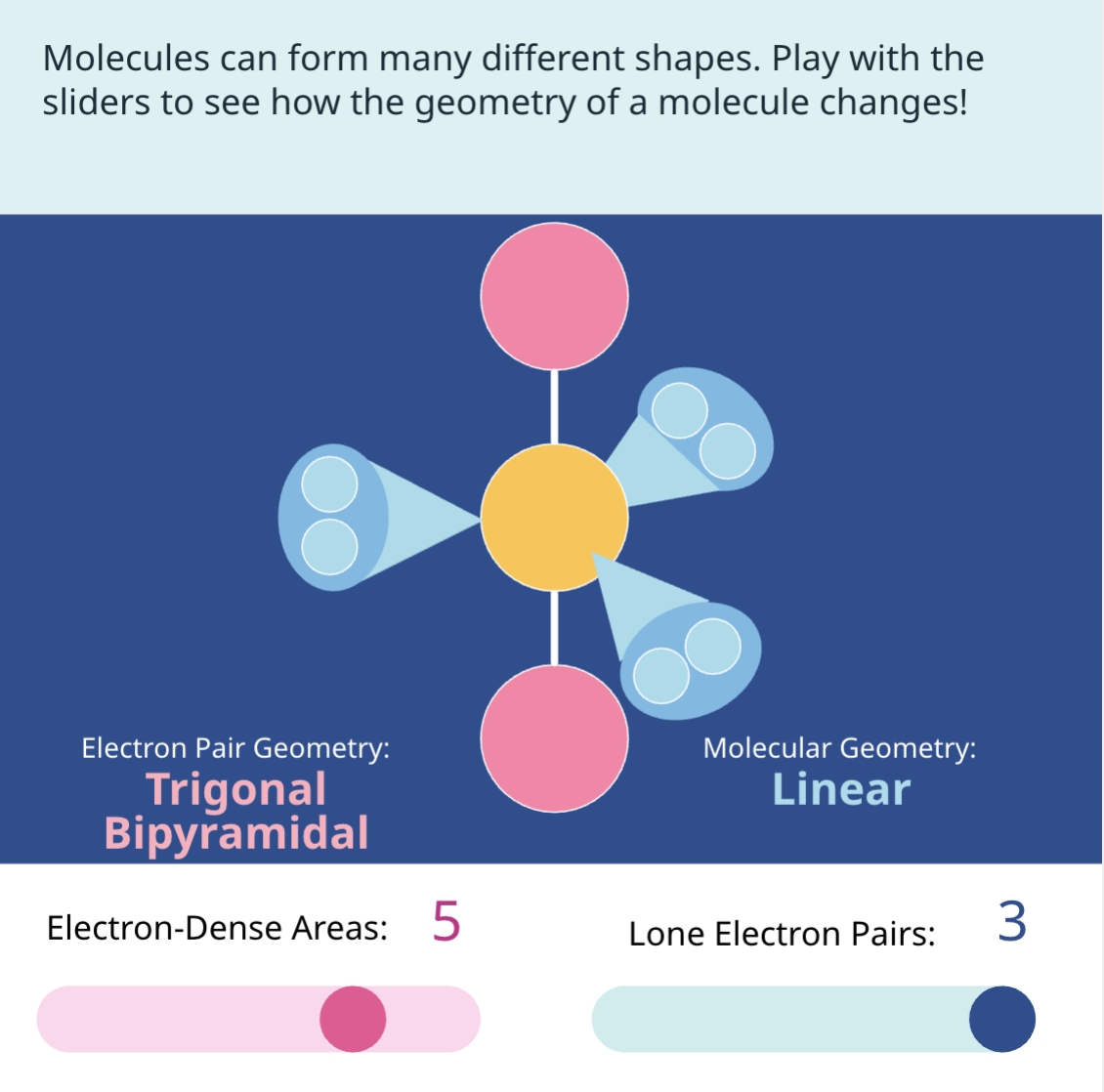
Understanding Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry is a crucial concept in chemistry that helps us understand the shape and structure of molecules. It is determined by the arrangement of atoms and electron pairs around a central atom. In this guide, we will provide you with a comprehensive worksheet to master molecular geometry.
What is Molecular Geometry?
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule. It is determined by the number of electron pairs around a central atom, which in turn affects the shape of the molecule. There are several factors that influence molecular geometry, including:
- The number of bonding pairs around the central atom
- The number of lone pairs around the central atom
- The type of bonding pairs (sigma or pi)
- The electronegativity of the atoms involved
The VSEPR Theory
The Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory is a useful tool for predicting molecular geometry. This theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion between them. The VSEPR theory can be used to predict the shape of molecules with two, three, or four electron pairs around the central atom.
Worksheet: Molecular Geometry
Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions
- What is the primary factor that determines molecular geometry? a) Number of bonding pairs b) Number of lone pairs c) Type of bonding pairs d) Electronegativity of atoms
Answer: a) Number of bonding pairs
- Which theory is used to predict molecular geometry? a) VSEPR theory b) MO theory c) VB theory d) AO theory
Answer: a) VSEPR theory
Part 2: Short Answer Questions
- Describe the shape of a molecule with two bonding pairs and no lone pairs around the central atom.
Answer: The shape of the molecule is linear.
- What is the shape of a molecule with three bonding pairs and one lone pair around the central atom?
Answer: The shape of the molecule is trigonal pyramidal.
Part 3: Problems
- Determine the molecular geometry of the following molecules:
| Molecule | Central Atom | Number of Bonding Pairs | Number of Lone Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O | O | 2 | 2 |
| CO2 | C | 2 | 0 |
| NH3 | N | 3 | 1 |
Answers:
- H2O: bent or V-shape
- CO2: linear
- NH3: trigonal pyramidal
- Predict the shape of the following molecules using the VSEPR theory:
| Molecule | Central Atom | Number of Bonding Pairs | Number of Lone Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | C | 4 | 0 |
| CCl4 | C | 4 | 0 |
| XeF4 | Xe | 4 | 2 |
Answers:
- CH4: tetrahedral
- CCl4: tetrahedral
- XeF4: square planar
Important Notes
💡 Note: The VSEPR theory assumes that electron pairs are equally spaced around the central atom. However, in reality, electron pairs may not be equally spaced due to factors such as electronegativity and hybridization.
📝 Note: Molecular geometry is not the same as electron geometry. Electron geometry refers to the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom, while molecular geometry refers to the arrangement of atoms in a molecule.
Molecular Geometry Table
| Electron Pairs | Lone Pairs | Shape | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | Linear | CO2 |
| 2 | 2 | Bent or V-shape | H2O |
| 3 | 0 | Trigonal planar | BF3 |
| 3 | 1 | Trigonal pyramidal | NH3 |
| 4 | 0 | Tetrahedral | CH4 |
| 4 | 2 | Square planar | XeF4 |
Conclusion
Mastering molecular geometry is essential for understanding the structure and properties of molecules. By using the VSEPR theory and understanding the factors that influence molecular geometry, you can predict the shape of molecules with ease. Remember to practice, practice, practice, and you will become proficient in molecular geometry in no time.
What is the difference between molecular geometry and electron geometry?
+
Molecular geometry refers to the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, while electron geometry refers to the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom.
What is the VSEPR theory?
+
The VSEPR theory is a tool used to predict molecular geometry. It states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion between them.
What are the factors that influence molecular geometry?
+
The factors that influence molecular geometry include the number of bonding pairs, the number of lone pairs, the type of bonding pairs, and the electronegativity of the atoms involved.



