5 Ways to Master Mitosis and Meiosis

Understanding Cell Division: A Comprehensive Guide
Cell division is a crucial process in living organisms, allowing for growth, repair, and reproduction. Two types of cell division, mitosis and meiosis, are fundamental to understanding how cells reproduce and pass on genetic information. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of cell division, exploring the intricacies of mitosis and meiosis, and provide you with practical tips to master these complex processes.
What is Mitosis?
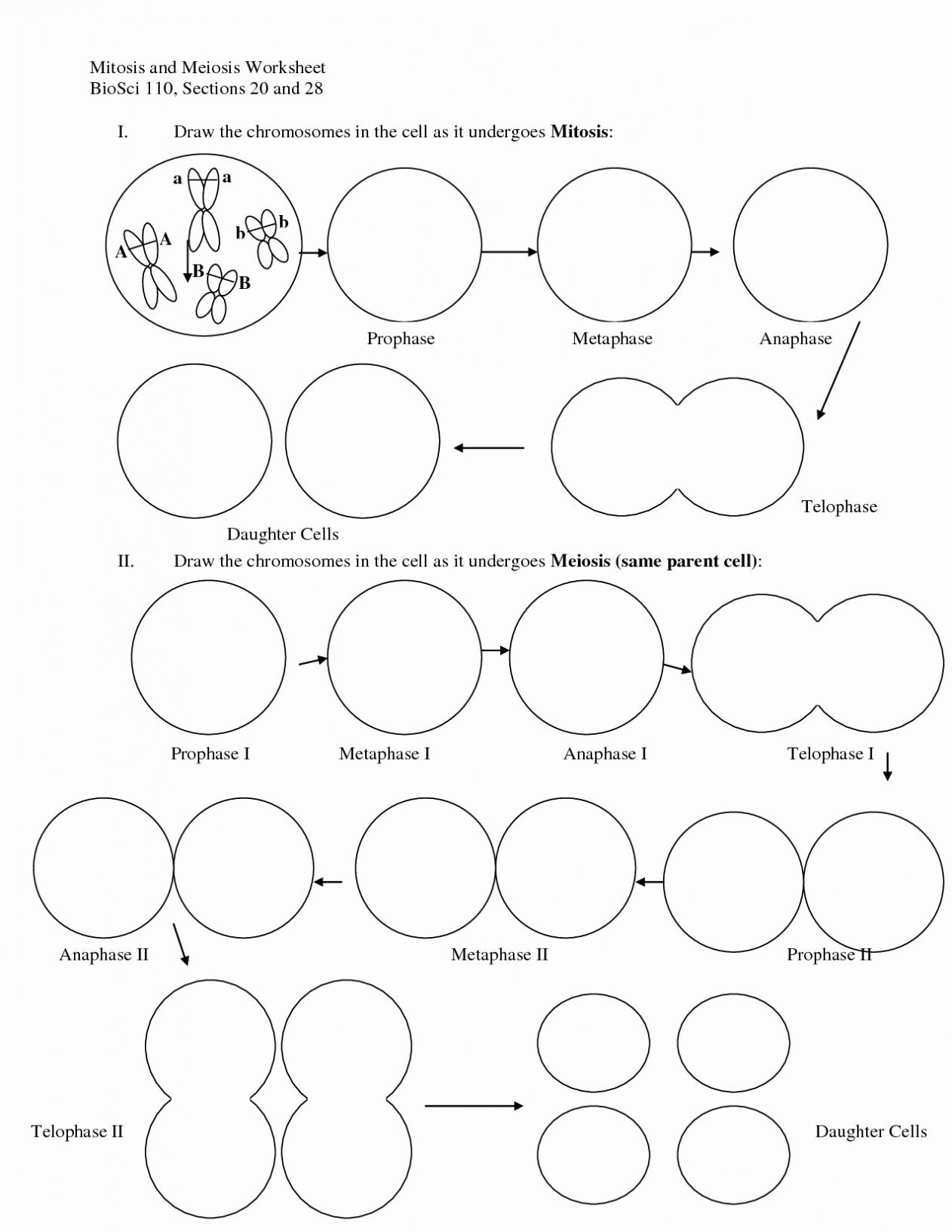
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell. This process is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in multicellular organisms. Mitosis consists of several stages, including:
- Interphase: The cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division.
- Prophase: The chromatin condenses, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase: The chromosomes line up at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
What is Meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four non-identical daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for reproduction, allowing for genetic diversity and the creation of gametes (sperm and egg cells). Meiosis consists of two consecutive cell divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, each with its own stages:
- Meiosis I:
- Prophase I: The chromatin condenses, and homologous chromosomes pair up.
- Metaphase I: The paired chromosomes line up at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase I: The homologous chromosomes separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase I: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
- Meiosis II:
- Prophase II: The chromatin condenses again, and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
- Metaphase II: The sister chromatids line up at the center of the cell.
- Anaphase II: The sister chromatids separate, moving to opposite poles of the cell.
- Telophase II: The nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil.
5 Ways to Master Mitosis and Meiosis
Mastering mitosis and meiosis requires a deep understanding of the processes, as well as practice and repetition. Here are five ways to help you master these complex processes:
- Create Concept Maps: Visualize the stages of mitosis and meiosis using concept maps or diagrams. This will help you understand the relationships between each stage and how they fit together.
- Watch Video Animations: Watch video animations of mitosis and meiosis to see the processes in action. This will help you understand the dynamic nature of cell division.
- Practice with Flashcards: Create flashcards to help you memorize the stages of mitosis and meiosis. Quiz yourself by covering the answers and recalling the stages from memory.
- Use Online Resources: Utilize online resources, such as interactive tutorials and quizzes, to test your knowledge and understanding of mitosis and meiosis.
- Teach Someone Else: Teach the concepts of mitosis and meiosis to someone else. This will help you reinforce your own understanding and identify areas where you need more practice.
📝 Note: Practice is key to mastering mitosis and meiosis. Set aside dedicated time to review and practice these concepts, and you'll see improvement over time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When studying mitosis and meiosis, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can confuse and frustrate you. Here are a few mistakes to watch out for:
- Confusing mitosis and meiosis: Make sure you understand the differences between these two types of cell division.
- Forgetting the stages: Review the stages of mitosis and meiosis regularly to avoid forgetting them.
- Not understanding the purpose: Understand the purpose of mitosis and meiosis in living organisms.
Conclusion
Mastering mitosis and meiosis requires dedication, practice, and patience. By following these five tips and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll be well on your way to understanding these complex processes. Remember to practice regularly and reinforce your knowledge with visual aids and online resources.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced. Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
+The purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) with unique combinations of chromosomes, allowing for genetic diversity and the creation of offspring with unique traits.
What is the role of cytokinesis in cell division?
+Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division, where the cytoplasm divides and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
Related Terms:
- Meiosis Worksheet with answers
- Pdf mitosis and meiosis
- Mitosis Worksheet