7 Ways to Understand Membrane Structure and Function
Understanding Membrane Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Guide
Cell membranes are the outermost layer of cells, serving as a barrier between the cell and its environment. They play a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating the movement of materials in and out of the cell, and facilitating communication between cells. In this article, we will delve into the structure and function of cell membranes, exploring seven key aspects that will help you gain a deeper understanding of this complex biological system.
1. Lipid Bilayer: The Basic Structure of Cell Membranes
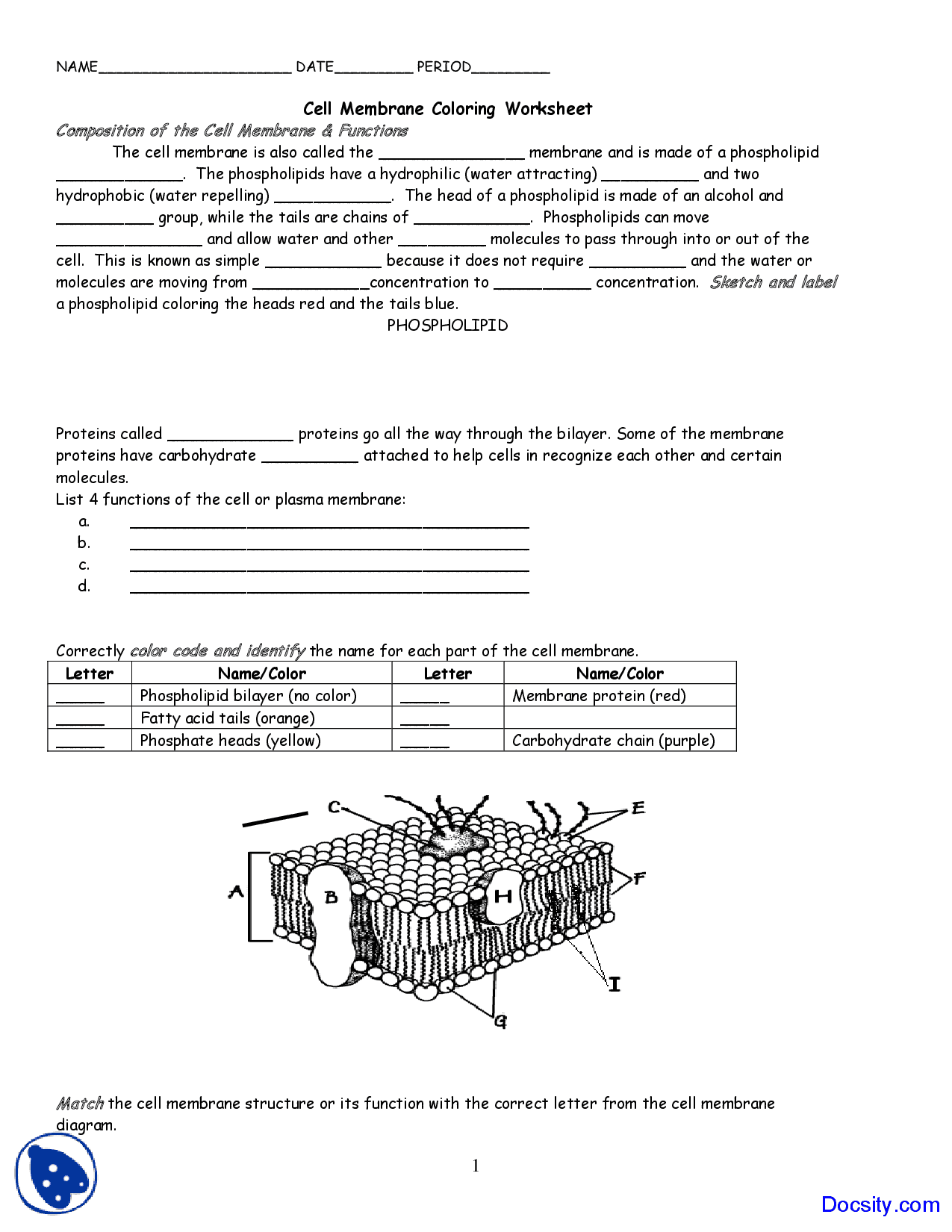
The cell membrane is primarily composed of a phospholipid bilayer, with the hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and the hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards. This arrangement creates a stable and flexible structure that allows the membrane to maintain its integrity while still permitting the movement of molecules across it.
💡 Note: The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while restricting others.
2. Protein Components: Embedded and Peripheral Proteins
Embedded proteins are integral to the membrane structure, spanning the entire lipid bilayer. These proteins can function as channels, pumps, or receptors, facilitating the movement of molecules across the membrane. Peripheral proteins, on the other hand, are attached to the surface of the membrane and often play a role in signaling and communication between cells.

| Protein Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Embedded Proteins | Channels, pumps, receptors |
| Peripheral Proteins | Signaling, communication |
3. Fluid Mosaic Model: The Dynamic Nature of Cell Membranes
The fluid mosaic model proposes that the cell membrane is a dynamic, fluid-like structure composed of a mixture of lipids and proteins. This model explains the membrane’s ability to change shape and move molecules across it. The fluidity of the membrane is influenced by factors such as temperature, cholesterol content, and the presence of certain proteins.
4. Membrane Transport: Passive and Active Processes
Membrane transport refers to the movement of molecules across the cell membrane. There are two primary types of transport: passive and active. Passive transport involves the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, requiring no energy input. Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
- Passive Transport:
- Diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active Transport:
- Primary active transport (using ATP)
- Secondary active transport (using an electrochemical gradient)
5. Cell Signaling: Communication through the Cell Membrane
Cell signaling involves the transmission of information from one cell to another through the cell membrane. This process can occur through various mechanisms, including receptor-ligand interactions, ion channels, and signaling cascades.
📣 Note: Cell signaling plays a crucial role in coordinating cellular responses to environmental changes.
6. Membrane Specializations: Microvilli and Cilia
Microvilli and cilia are specialized structures found on the surface of certain cells. Microvilli increase the surface area of the cell, allowing for enhanced absorption of nutrients. Cilia, on the other hand, are involved in movement and sensing the environment.
7. Membrane Structure and Function in Disease
Alterations in membrane structure and function have been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders. Understanding the changes that occur in membrane structure and function in these diseases can provide valuable insights into the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
In conclusion, the cell membrane is a complex and dynamic structure that plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. By understanding the structure and function of cell membranes, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate mechanisms that govern cellular behavior. This knowledge can be applied to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for various diseases.
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
+The primary function of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the cell, while maintaining cellular homeostasis.
What is the difference between embedded and peripheral proteins?
+Embedded proteins are integral to the membrane structure, spanning the entire lipid bilayer, while peripheral proteins are attached to the surface of the membrane.
What is the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure?
+The fluid mosaic model proposes that the cell membrane is a dynamic, fluid-like structure composed of a mixture of lipids and proteins.
Related Terms:
- Membrane function pogil answer key
- Membrane structure POGIL