DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet Answers
Understanding DNA Replication: A Detailed Guide
DNA replication is a fundamental process in molecular biology that occurs in all living organisms. It is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. In this article, we will delve into the details of DNA replication, its stages, and the enzymes involved.
The Stages of DNA Replication
DNA replication is a complex process that involves several stages: initiation, unwinding, synthesis, and termination. Let’s explore each stage in detail.
Initiation Stage
The initiation stage is the first step in DNA replication. During this stage, the replication process is initiated, and the replication fork is formed. The replication fork is a region where the double helix is separated into two single strands.
Key Players:
- Helicase: An enzyme that unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases.
- Topoisomerase: An enzyme that relaxes the supercoiled DNA molecule by cutting and rejoining it.
Unwinding Stage
During the unwinding stage, the double helix is separated into two single strands. This stage is crucial for the synthesis of new DNA strands.
Key Players:
- Helicase: Continues to unwind the double helix, creating a replication fork.
- Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs): Proteins that bind to the single strands, preventing them from annealing (re-forming a double helix).
Synthesis Stage
The synthesis stage is where the new DNA strands are synthesized. This stage involves the addition of nucleotides to the template strands.
Key Players:
- DNA polymerase: An enzyme that adds nucleotides to the template strands, synthesizing new DNA strands.
- Primase: An enzyme that adds RNA primers to the template strands, providing a starting point for DNA synthesis.
Termination Stage
The termination stage is the final stage of DNA replication. During this stage, the replication process is completed, and the newly synthesized DNA strands are sealed.
Key Players:
- DNA ligase: An enzyme that seals the gaps between the nucleotides, forming a continuous DNA strand.
- Topoisomerase: Helps to relax the supercoiled DNA molecule, allowing the newly synthesized strands to be properly aligned.
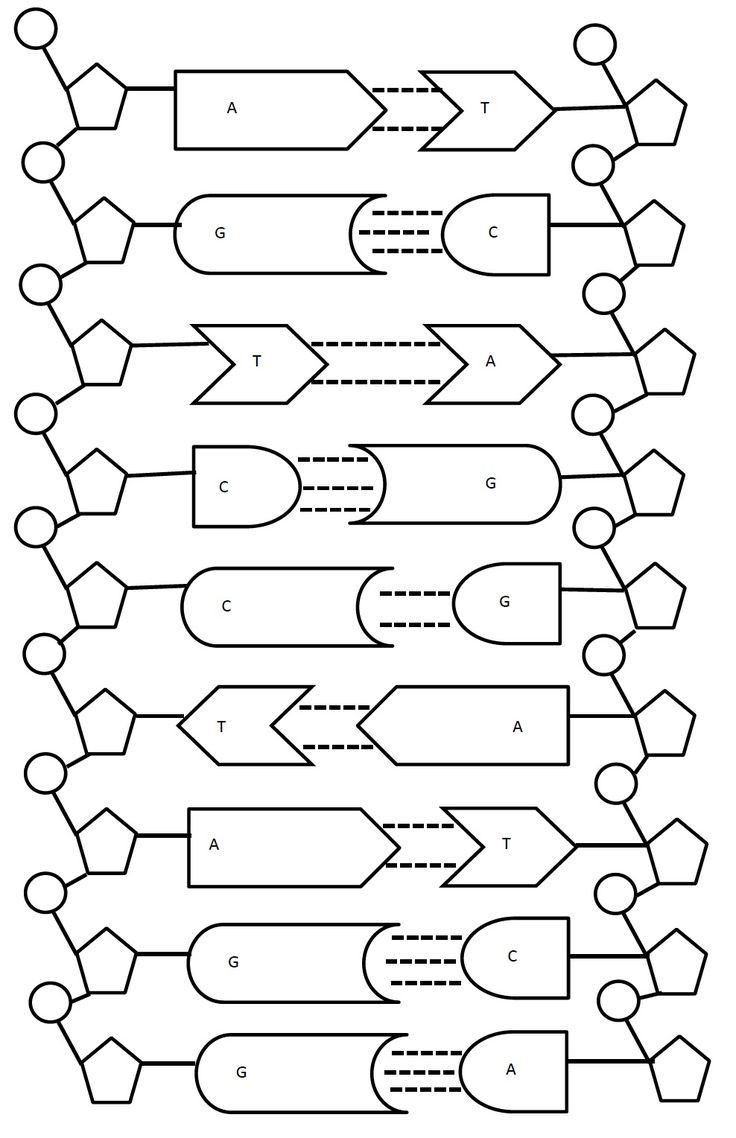
Coloring Worksheet Answers
Now that we have explored the stages of DNA replication, let’s review the coloring worksheet answers.

| Stage | Key Players | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Helicase, Topoisomerase | Blue |
| Unwinding | Helicase, Single-strand binding proteins (SSBs) | Red |
| Synthesis | DNA polymerase, Primase | Green |
| Termination | DNA ligase, Topoisomerase | Yellow |
🔍 Note: The colors used in the coloring worksheet are arbitrary and for illustrative purposes only.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNA replication is a complex process that involves several stages and key players. Understanding the stages of DNA replication and the enzymes involved is crucial for appreciating the intricacies of molecular biology. By reviewing the coloring worksheet answers, we hope to have provided a comprehensive overview of the DNA replication process.
What is DNA replication?
+DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division.
What are the stages of DNA replication?
+The stages of DNA replication are initiation, unwinding, synthesis, and termination.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
+Helicase is an enzyme that unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nucleotide bases.
Related Terms:
- Biologycorner com DNA coloring
- DNA coloring worksheet
- DNA Worksheet with Answers
- DNA replication worksheet answer key